MongoDB with pyMongo II (Connecting and accessing)
List of MongoDB with PyMongo
- MongoDB with PyMongo I - Installing MongoDB
- MongoDB with PyMongo II - Connecting and accessing MongoDB
- MongoDB with pyMongo III - Range Querying MongoDB
- MongoDB RESTful API with Flask
The first step when working with PyMongo is to create a MongoClient against the running mongod instance:
>>> from pymongo import MongoClient >>> client = MongoClient()
We're now connected on the default host and port. We can also specify the host and port explicitly, as follows:
>>> client = MongoClient('localhost', 27017)
or MongoDB URI format:
>>> client = MongoClient('mongodb://localhost:27017/')
This MongoClient represents the connection to the MongoDB instance that runs on port 27017 on the localhost.
With a single instance of MongoDB, we can use multiple independent databases. Using PyMongo, we can access databases via attribute style access on MongoClient instances. MongoDB creates new databases implicitly upon their first use.
>>> mydb = client.test_database_1
Note that we can also use dictionary style access instead:
>>> mydb = client['test_database_1']
note: initially I used dash('-') for the database name but now it doesn't allow dash. So, I used underscore('_') instead.
We call a group of documents stored in MongoDB a collection. It is the equivalent of a table in a RDBMS. We can access a collection in PyMongo the same as we access a database:
>>> my_collection = mydb.test-database-1
Or via dictionary style access:
my_collection = mydb['test-database-1']
Note on the lazy creation of MongoDB:
Collections and databases are created when the first document is inserted into them. So, none of the above commands have actually performed any operations on the MongoDB server.
Though the data in MongoDB is stored by JSON-style, PyMongo use dictionaries to store documents. The following is a sample document:
>>> import datetime
>>> myrecord = {"author": "Duke",
... "title" : "PyMongo 101",
... "tags" : ["MongoDB", "PyMongo", "Tutorial"],
... "date" : datetime.datetime.utcnow()
... }
Note that we used the native Python types such as datetime.datetime instances. But it will be automatically converted to and from the appropriate BSON types. BSON is a binary-encoded serialization of JSON-like documents. BSON is designed to be lightweight, traversable, and efficient. BSON, like JSON, supports the embedding of objects and arrays within other objects and arrays.
For more information about BSON, visit here.
we can use the insert() method to insert a document into our collection:
>>> record_id = mydb.mytable.insert(myrecord)
>>> record_id
ObjectId('5659393d312f910b5b05c18a')
At the insert(), a special key, _id is automatically added if the document doesn't already contain an _id key which must be unique across the collection.
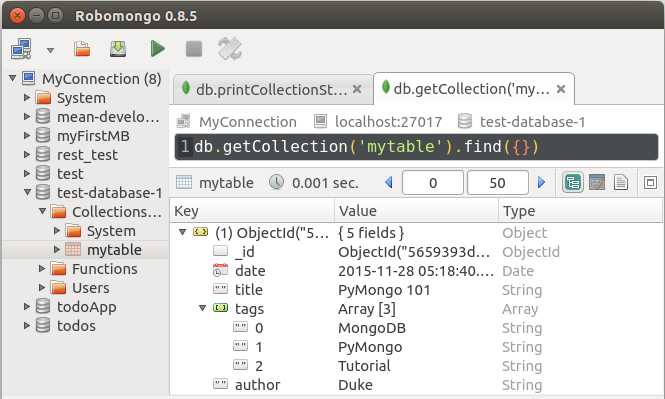
After inserting the first document, the mytable collection has actually been created on the server as we can see below:
>>> mydb.collection_names() [u'system.indexes', u'mytable']
Here is the file:
# mongo1.py
from pymongo import MongoClient
client = MongoClient('mongodb://localhost:27017/')
# data base name : 'test-database-1'
mydb = client['test-database-1']
import datetime
myrecord = {
"author": "Duke",
"title" : "PyMongo 101",
"tags" : ["MongoDB", "PyMongo", "Tutorial"],
"date" : datetime.datetime.utcnow()
}
record_id = mydb.mytable.insert(myrecord)
print record_id
print mydb.collection_names()
Let's could have run the file rather than typing each command line:
$ python mongo1.py
We can check our database and collection using MongoDB Management tool : robomongo:
We can insert several records at one shot by running the following script:
# mongo2.py
from pymongo import MongoClient
client = MongoClient('mongodb://localhost:27017/')
mydb = client['test-database-1']
import datetime
myrecord2 = [
{ "author": "Duke II",
"title" : "PyMongo II 101",
"tags" : ["MongoDB II", "PyMongo II", "Tutorial II"],
"date" : datetime.datetime.utcnow() },
{ "author": "Duke III",
"title" : "PyMongo III 101",
"tags" : ["MongoDB III", "PyMongo III", "Tutorial III"],
"date" : datetime.datetime.utcnow() }
]
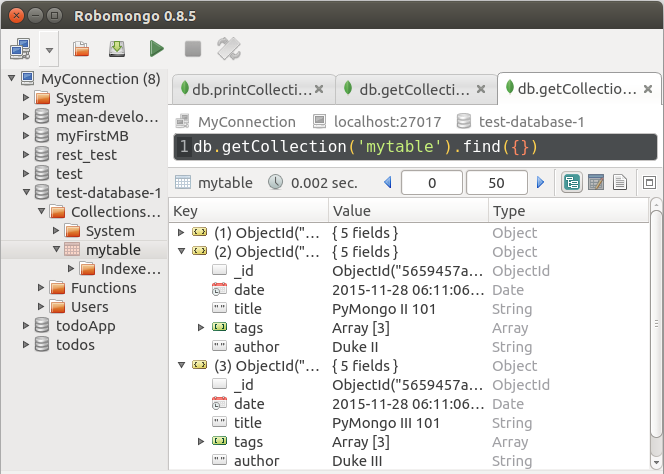
mydb.mytable.insert(myrecord2)
print mydb.collection_names()
List of MongoDB with PyMongo
- MongoDB with PyMongo I - Installing MongoDB
- MongoDB with PyMongo II - Connecting and accessing MongoDB
- MongoDB with pyMongo III - Range Querying MongoDB
- MongoDB RESTful API with Flask
Python tutorial
Python Home
Introduction
Running Python Programs (os, sys, import)
Modules and IDLE (Import, Reload, exec)
Object Types - Numbers, Strings, and None
Strings - Escape Sequence, Raw String, and Slicing
Strings - Methods
Formatting Strings - expressions and method calls
Files and os.path
Traversing directories recursively
Subprocess Module
Regular Expressions with Python
Regular Expressions Cheat Sheet
Object Types - Lists
Object Types - Dictionaries and Tuples
Functions def, *args, **kargs
Functions lambda
Built-in Functions
map, filter, and reduce
Decorators
List Comprehension
Sets (union/intersection) and itertools - Jaccard coefficient and shingling to check plagiarism
Hashing (Hash tables and hashlib)
Dictionary Comprehension with zip
The yield keyword
Generator Functions and Expressions
generator.send() method
Iterators
Classes and Instances (__init__, __call__, etc.)
if__name__ == '__main__'
argparse
Exceptions
@static method vs class method
Private attributes and private methods
bits, bytes, bitstring, and constBitStream
json.dump(s) and json.load(s)
Python Object Serialization - pickle and json
Python Object Serialization - yaml and json
Priority queue and heap queue data structure
Graph data structure
Dijkstra's shortest path algorithm
Prim's spanning tree algorithm
Closure
Functional programming in Python
Remote running a local file using ssh
SQLite 3 - A. Connecting to DB, create/drop table, and insert data into a table
SQLite 3 - B. Selecting, updating and deleting data
MongoDB with PyMongo I - Installing MongoDB ...
Python HTTP Web Services - urllib, httplib2
Web scraping with Selenium for checking domain availability
REST API : Http Requests for Humans with Flask
Blog app with Tornado
Multithreading ...
Python Network Programming I - Basic Server / Client : A Basics
Python Network Programming I - Basic Server / Client : B File Transfer
Python Network Programming II - Chat Server / Client
Python Network Programming III - Echo Server using socketserver network framework
Python Network Programming IV - Asynchronous Request Handling : ThreadingMixIn and ForkingMixIn
Python Coding Questions I
Python Coding Questions II
Python Coding Questions III
Python Coding Questions IV
Python Coding Questions V
Python Coding Questions VI
Python Coding Questions VII
Python Coding Questions VIII
Python Coding Questions IX
Python Coding Questions X
Image processing with Python image library Pillow
Python and C++ with SIP
PyDev with Eclipse
Matplotlib
Redis with Python
NumPy array basics A
NumPy Matrix and Linear Algebra
Pandas with NumPy and Matplotlib
Celluar Automata
Batch gradient descent algorithm
Longest Common Substring Algorithm
Python Unit Test - TDD using unittest.TestCase class
Simple tool - Google page ranking by keywords
Google App Hello World
Google App webapp2 and WSGI
Uploading Google App Hello World
Python 2 vs Python 3
virtualenv and virtualenvwrapper
Uploading a big file to AWS S3 using boto module
Scheduled stopping and starting an AWS instance
Cloudera CDH5 - Scheduled stopping and starting services
Removing Cloud Files - Rackspace API with curl and subprocess
Checking if a process is running/hanging and stop/run a scheduled task on Windows
Apache Spark 1.3 with PySpark (Spark Python API) Shell
Apache Spark 1.2 Streaming
bottle 0.12.7 - Fast and simple WSGI-micro framework for small web-applications ...
Flask app with Apache WSGI on Ubuntu14/CentOS7 ...
Fabric - streamlining the use of SSH for application deployment
Ansible Quick Preview - Setting up web servers with Nginx, configure enviroments, and deploy an App
Neural Networks with backpropagation for XOR using one hidden layer
NLP - NLTK (Natural Language Toolkit) ...
RabbitMQ(Message broker server) and Celery(Task queue) ...
OpenCV3 and Matplotlib ...
Simple tool - Concatenating slides using FFmpeg ...
iPython - Signal Processing with NumPy
iPython and Jupyter - Install Jupyter, iPython Notebook, drawing with Matplotlib, and publishing it to Github
iPython and Jupyter Notebook with Embedded D3.js
Downloading YouTube videos using youtube-dl embedded with Python
Machine Learning : scikit-learn ...
Django 1.6/1.8 Web Framework ...
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization