Sockets - Server & Client - 2020
The basic mechanisms of client-server setup are:
- A client app send a request to a server app.
- The server app returns a reply.
- Some of the basic data communications between client and server are:
- File transfer - sends name and gets a file.
- Web page - sends url and gets a page.
- Echo - sends a message and gets it back.
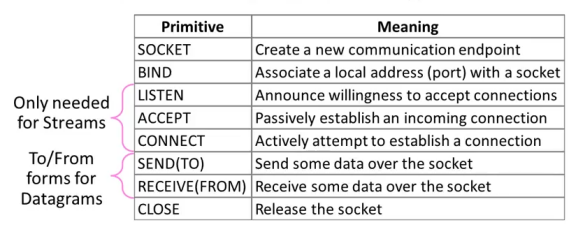
- create a socket - Get the file descriptor!
- bind to an address -What port am I on?
- listen on a port, and wait for a connection to be established.
- accept the connection from a client.
- send/recv - the same way we read and write for a file.
- shutdown to end read/write.
- close to releases data.
- create a socket.
- bind* - this is probably be unnecessary because you're the client, not the server.
- connect to a server.
- send/recv - repeat until we have or receive data
- shutdown to end read/write.
- close to releases data.
For socket programming with Boost.Asio, please visit:
- Boost.Asio - 1. Blocking and non-blocking wait with timers
- Boost.Asio - 2. Binding arguments to a callback handler member function
- Boost.Asio - 3. Multithreading, synchronizing, and handler
- Boost.Asio - 4. TCP Socket Programming
For socket programming with Qt, please visit
http://www.bogotobogo.com/cplusplus/sockets_server_client_QT.php.
Qt 5 Tutorials:
- Qt QHttp - Downloading Files
- Qt 5 QNetworkAccessManager and QNetworkRequest - Downloading Files
- Qt 5 QTcpSocket
- Qt 5 QTcpSocket with Signals and Slots
- Qt 5 QTcpServer - Client and Server
- Qt 5 QTcpServer - Client and Server using MultiThreading
- Qt 5 QTcpServer - Client and Server using QThreadPool
Here is the summary of key concepts:
- Socket is a way of speaking to other programs using standard file descriptors.
- Where do we get the file descriptor for network communication?
Well, we make a call to the socket() system routine.
After the socket() returns the socket descriptor, we start communicate through it using the specialized send()/recv() socket API calls. - A TCP socket is an endpoint instance
- A TCP socket is not a connection, it is the endpoint of a specific connection.
- A TCP connection is defined by two endpoints aka sockets.
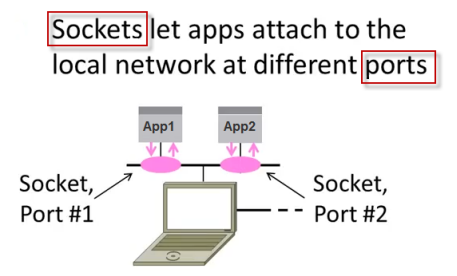
- The purpose of ports is to differentiate multiple endpoints on a given network address.
- The port numbers are encoded in the transport protocol packet header, and they can be readily interpreted not only by the sending and receiving computers, but also by other components of the networking infrastructure. In particular, firewalls are commonly configured to differentiate between packets based on their source or destination port numbers as in port forwarding.
- It is the socket pair (the 4-tuple consisting of the client IP address, client port number, server IP address, and server port number) that specifies the two endpoints that uniquely identifies each TCP connection in an internet.
- Only one process may bind to a specific IP address and port combination using the same transport protocol. Otherwise, we'll have port conflicts, where multiple programs attempt to bind to the same port numbers on the same IP address using the same protocol.
To connect to another machine, we need a socket connection.
What's a connection?
A relationship between two machines, where two pieces of software know about each other. Those two pieces of software know how to communicate with each other. In other words, they know how to send bits to each other.A socket connection means the two machines have information about each other, including network location (IP address) and TCP port. (If we can use anology, IP address is the phone number and the TCP port is the extension).
A socket is an object similar to a file that allows a program to accept incoming connections, make outgoing connections, and send and receive data. Before two machines can communicate, both must create a socket object.
A socket is a resource assigned to the server process. The server creates it using the system call socket(), and it can't be shared with other processes.
There are several different types of socket that determine the structure of the transport layer. The most common types are stream sockets and datagram sockets.
| TCP (Streams) | UDP (Datagrams) |
|---|---|
| Connections | Connectionless sockets We don't have to maintain an open connection as we do with stream sockets. We just build a packet, put an IP header on it with destination information, and send it out. No connection needed: datagram sockets also use IP for routing, but they don't use TCP *note: can be connect()'d if we really want. |
| SOCK_STREAM | SOCK_DGRAM |
| If we output two items into the socket in the order "A, B", they will arrive in the order "A, B" at the opposite end. They will also be error-free. |
If we send a datagram, it may arrive. But it may arrive out of order. If it arrives, however, the data within the packet will be error-free. |
| Why would we use an unreliable protocol? Speed! We just ignore the dropped packets. |
|
| Arbitrary length content | Limited message size |
| Flow control matches sender to receiver | Can send regardless of receiver state |
| Congestion control matches sender to network | Can send regardless of network state |
| http, telnet | tftp (trivial file transfer protocol), dhcpcd (a DHCP client), multiplayer games, streaming audio, video conferencing *note: They use complementary protocol on top of UDP to get more reliability |
- Stream Sockets
Stream sockets provide reliable two-way communication similar to when we call someone on the phone. One side initiates the connection to the other, and after the connection is established, either side can communicate to the other.
In addition, there is immediate confirmation that what we said actually reached its destination.
Stream sockets use a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), which exists on the transport layer of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model. The data is usually transmitted in packets. TCP is designed so that the packets of data will arrive without errors and in sequence.
Webservers, mail servers, and their respective client applications all use TCP and stream socket to communicate. - Datagram Sockets
Communicating with a datagram socket is more like mailing a letter than making a phone call. The connection is one-way only and unreliable.
If we mail several letters, we can't be sure that they arrive in the same order, or even that they reached their destination at all. Datagram sockets use User Datagram Protocol (UDP). Actually, it's not a real connection, just a basic method for sending data from one point to another.
Datagram sockets and UDP are commonly used in networked games and streaming media.
Though in this section, we mainly put focus on applications that maintain connections to their clients, using connection-oriented TCP, there are cases where the overhead of establishing and maintaining a socket connection is unnecessary.
For example, just to get the data, a process of creating a socket, making a connection, reading a single response, and closing the connection, is just too much. In this case, we use UDP.
Services provided by UDP are typically used where a client needs to make a short query of a server and expects a single short response. To access a service from UDP, we need to use the UDP specific system calls, sendto() and recvfrom() instead of read() and write() on the socket.UDP is used by app that doesn't want reliability or bytestreams.
- Voice-over-ip (unreliable) such as conference call. (visit VoIP)
- DNS, RPC (message-oriented)
- DHCP (bootstrapping)
The client-server model distinguishes between applications as well as devices. Network clients make requests to a server by sending messages, and servers respond to their clients by acting on each request and returning results.
For example, let's talk about telnet.
When we connect to a remote host on port 23 with telnet (the client), a program on that host (called telnetd, the server) springs to life. It handles the incoming telnet connection, sets us up with a login prompt, etc.
One server generally supports numerous clients, and multiple servers can be networked together in a pool to handle the increased processing load as the number of clients grows.
Some of the most popular applications on the Internet follow the client-server model including email, FTP and Web services. Each of these clients features a user interface and a client application that allows the user to connect to servers. In the case of email and FTP, users enter a computer name (or an IP address) into the interface to set up connections to the server.
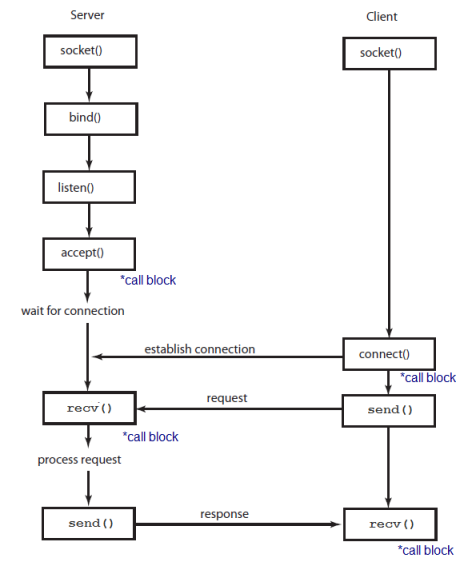
The steps to establish a socket on the server side are:
- Create a socket with the socket() system call.
- The server process gives the socket a name. In linux file system, local sockets are given a filename, under /tmp or /usr/tmp directory. For network sockets, the filename will be a service identifier, port number, to which the clients can make connection. This identifier allows to route incoming connections (which has that the port number) to connect server process. A socket is named using bind() system call.
- The server process then waits for a client to connect to the named socket, which is basically listening for connections with the listen() system call. If there are more than one client are trying to make connections, the listen() system call make a queue.
The machine receiving the connection (the server) must bind its socket object to a known port number. A port is a 16-bit number in the range 0-65535 that's managed by the operating system and used by clients to uniquely identify servers. Ports 0-1023 are reserved by the system and used by common network protocols. -
Accept a connection with the accept() system call. At accept(), a new socket is created that is distinct from the named socket. This new socket is used solely for communication with this particular client.
For TCP servers, the socket object used to receive connections is not the same socket used to perform subsequent communication with the client. In particular, the accept() system call returns a new socket object that's actually used for the connection. This allows a server to manage connections from a large number of clients simultaneously. - Send and receive data.
- The named socket remains for further connections from other clients. A typical web server can take advantage of multiple connections. In other words, it can serve pages to many clients at once. But for a simple server, further clients wait on the listen queue until the server is ready again.
The steps to establish a socket on the client side are:
- Create a socket with the socket() system call.
- Connect the socket to the address of the server using the connect() system call.
- Send and receive data. There are a number of ways to do this, but the simplest is to use the read() and write() system calls.
TCP communication
UDP communication - clients and servers don't establish a connection with each other
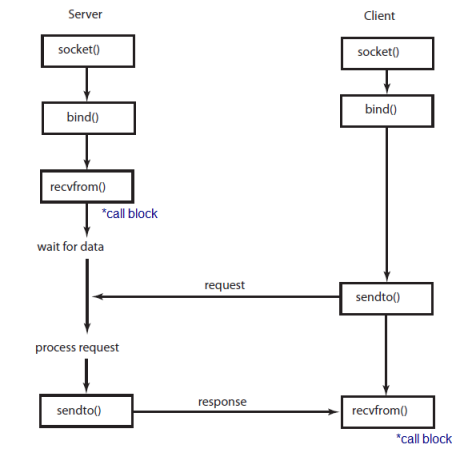
*call block, go to Blocking socket vs non-blocking socket .
Sockets, in C, behaves like files because they use file descriptors to identify themselves. Sockets behave so much like files that we can use the read() and write() to receive and send data using socket file descriptors.
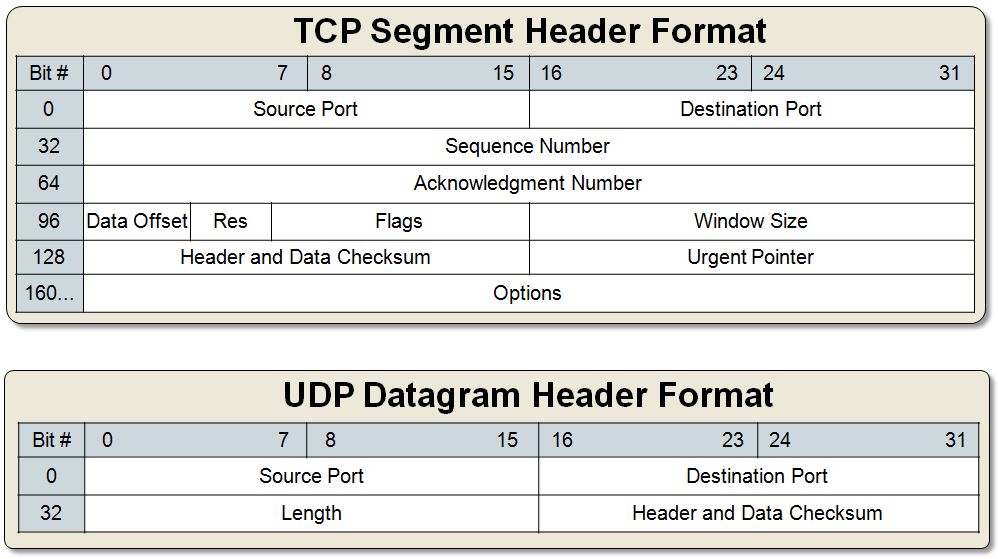
There are several functions, however, specifically designed to handle sockets. These functions have their prototypes defined in /usr/include/sys/sockets.h.int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol)
Used to create a new socket, returns a file descriptor for the socket or -1 on error.
It takes three parameters:
- domain: the protocol family of socket being requested
- type: the type of socket within that family
- and the protocol.
The parameters allow us to say what kind of socket we want (IPv4/IPv6, stream/datagram(TCP/UDP)).
- The protocol family should be AF_INET or AF_INET6
- and the protocol type for these two families is
either SOCK_STREAM for TCP/IP or SOCK_DGRAM for UDP/IP. - The protocol should usually be set to zero to indicate that the default protocol should be used.
int bind(int fd, struct sockaddr *local_addr, socklen_t addr_length)
Once we have a socket, we might have to associate that socket with a port on our local machine.
The port number is used by the kernel to match an incoming packet to a certain process's socket descriptor.
A server will call bind() with the address of the local host and the port on which it will listen for connections.
It takes file descriptor (previously established socket), a pointer to (the address of) a structure containing the details of the address to bind to, the value INADDR_ANY is typically used for this, and the length of the address structure.
The particular structure that needs to be used will depend on the protocol, which is why it is passed by the pointer.
So, this bind() call will bind the socket to the current IP address on port, portno
Returns 0 on success and -1 on error.int listen(int fd, int backlog_queue_size)
Once a server has been bound to an address, the server can then call listen() on the socket.
The parameters to this call are the socket (fd) and the maximum number of queued connections requests up to backlog_queue_size.
Returns 0 on success and -1 on error.int accept(int fd, struct sockaddr *remote_host, socklen_t addr_length)
Accepts an incoming connection on a bound socket. The address information from the remote host is written into the remote_host structure and the actual size of the address structure is written into *addr_length.
In other words, this accept() function will write the connecting client's address info into the address structure.
Then, returns a new socket file descriptor for the accepted connection.
So, the original socket file descriptor can continue to be used for accepting new connections while the new socket file descriptor is used for communicating with the connected client.
This function returns a new socket file descriptor to identify the connected socket or -1 on error.Here is the description from the man page:
"It extracts the first connection request on the queue of pending connections for the listening socket, sockfd, creates a new connected socket, and returns a new file descriptor referring to that socket. The newly created socket is not in the listening state. The original socket sockfd is unaffected by this call".If no pending connections are present on the queue, and the socket is not marked as nonblocking, accept() blocks the caller until a connection is present.
int connect(int fd, struct sockaddr *remote_host, socklen_t addr_length)
Connects a socket (described by file descriptor fd) to a remote host.
Returns 0 on success and -1 on error.This is a blocking call. That's because when we issue a call to connect(), our program doesn't regain control until either the connection is made, or an error occurs. For example, let's say that we're writing a web browser. We try to connect to a web server, but the server isn't responding. So, we now want the connect() API to stop trying to connect by clicking a stop button. But that can't be done. It waits for a return which could be 0 on success or -1 on error.
int send(int fd, void *buffer, size_t n, int flags)
Sends n bytes from *buffer to socket fd.
Returns the number of bytes sent or -1 on error.int receive(int fd, void *buffer, size_t n, int flags)
Reveives n bytes from socket fd into *buffer.
Returns the number of bytes received or -1 on error.This is another blocking call. In other words, when we call recv() to read from a stream, control isn't returned to our program until at least one byte of data is read from the remote site. This process of waiting for data to appear is referred to as blocking. The same is true for the write() and the connect() APIs, etc. When we run those blocking APIs, the connection "blocks" until the operation is complete.
The following server code listens for TCP connections on port 20001. When a client connects, it sends the message "Hello world!", and then it receives data from client.
server.c
/* The port number is passed as an argument */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
void error(const char *msg)
{
perror(msg);
exit(1);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int sockfd, newsockfd, portno;
socklen_t clilen;
char buffer[256];
struct sockaddr_in serv_addr, cli_addr;
int n;
if (argc < 2) {
fprintf(stderr,"ERROR, no port provided\n");
exit(1);
}
// create a socket
// socket(int domain, int type, int protocol)
sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (sockfd < 0)
error("ERROR opening socket");
// clear address structure
bzero((char *) &serv;_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
portno = atoi(argv[1]);
/* setup the host_addr structure for use in bind call */
// server byte order
serv_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
// automatically be filled with current host's IP address
serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
// convert short integer value for port must be converted into network byte order
serv_addr.sin_port = htons(portno);
// bind(int fd, struct sockaddr *local_addr, socklen_t addr_length)
// bind() passes file descriptor, the address structure,
// and the length of the address structure
// This bind() call will bind the socket to the current IP address on port, portno
if (bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) &serv;_addr,
sizeof(serv_addr)) < 0)
error("ERROR on binding");
// This listen() call tells the socket to listen to the incoming connections.
// The listen() function places all incoming connection into a backlog queue
// until accept() call accepts the connection.
// Here, we set the maximum size for the backlog queue to 5.
listen(sockfd,5);
// The accept() call actually accepts an incoming connection
clilen = sizeof(cli_addr);
// This accept() function will write the connecting client's address info
// into the the address structure and the size of that structure is clilen.
// The accept() returns a new socket file descriptor for the accepted connection.
// So, the original socket file descriptor can continue to be used
// for accepting new connections while the new socker file descriptor is used for
// communicating with the connected client.
newsockfd = accept(sockfd,
(struct sockaddr *) &cli;_addr, &clilen;);
if (newsockfd < 0)
error("ERROR on accept");
printf("server: got connection from %s port %d\n",
inet_ntoa(cli_addr.sin_addr), ntohs(cli_addr.sin_port));
// This send() function sends the 13 bytes of the string to the new socket
send(newsockfd, "Hello, world!\n", 13, 0);
bzero(buffer,256);
n = read(newsockfd,buffer,255);
if (n < 0) error("ERROR reading from socket");
printf("Here is the message: %s\n",buffer);
close(newsockfd);
close(sockfd);
return 0;
}
When a socket is created with the socket() function, the domain, type, and protocol of the socket must be specified. The domain refers to the protocol family of the socket.
/* Address families. */ #define AF_UNSPEC PF_UNSPEC #define AF_LOCAL PF_LOCAL #define AF_UNIX PF_UNIX #define AF_FILE PF_FILE #define AF_INET PF_INET #define AF_AX25 PF_AX25 #define AF_IPX PF_IPX #define AF_APPLETALK PF_APPLETALK #define AF_NETROM PF_NETROM #define AF_BRIDGE PF_BRIDGE #define AF_ATMPVC PF_ATMPVC #define AF_X25 PF_X25 #define AF_INET6 PF_INET6 #define AF_ROSE PF_ROSE #define AF_DECnet PF_DECnet #define AF_NETBEUI PF_NETBEUI #define AF_SECURITY PF_SECURITY #define AF_KEY PF_KEY #define AF_NETLINK PF_NETLINK #define AF_ROUTE PF_ROUTE #define AF_PACKET PF_PACKET #define AF_ASH PF_ASH #define AF_ECONET PF_ECONET #define AF_ATMSVC PF_ATMSVC #define AF_SNA PF_SNA #define AF_IRDA PF_IRDA #define AF_PPPOX PF_PPPOX #define AF_WANPIPE PF_WANPIPE #define AF_BLUETOOTH PF_BLUETOOTH #define AF_MAX PF_MAX
A socket can be used to communicate using a variety of protocols, from the standard Internet protocol used when we browse the Web. These families are defined in bits/socket.h, which is automatically included from sys/socket.h.
There are several types of sockets: stream sockets and datagram sockets are the most commonly used. The types of sockets are also defined in /usr/include/bits/socket.h
/* Types of sockets. */
enum __socket_type
{
SOCK_STREAM = 1, /* Sequenced, reliable, connection-based
byte streams. */
#define SOCK_STREAM SOCK_STREAM
SOCK_DGRAM = 2, /* Connectionless, unreliable datagrams
of fixed maximum length. */
#define SOCK_DGRAM SOCK_DGRAM
SOCK_RAW = 3, /* Raw protocol interface. */
#define SOCK_RAW SOCK_RAW
SOCK_RDM = 4, /* Reliably-delivered messages. */
#define SOCK_RDM SOCK_RDM
SOCK_SEQPACKET = 5, /* Sequenced, reliable, connection-based,
datagrams of fixed maximum length. */
#define SOCK_SEQPACKET SOCK_SEQPACKET
SOCK_PACKET = 10 /* Linux specific way of getting packets
at the dev level. For writing rarp and
other similar things on the user level. */
#define SOCK_PACKET SOCK_PACKET
};
The 3rd argument for the socket() function is the protocol, which should always be 0. The specification allows for multiple protocols within a protocol family, so this argument is used to select on of the protocols from the family.
/usr/include/bits/socket.h
/* Protocol families. */ #define PF_UNSPEC 0 /* Unspecified. */ #define PF_LOCAL 1 /* Local to host (pipes and file-domain). */ #define PF_UNIX PF_LOCAL /* Old BSD name for PF_LOCAL. */ #define PF_FILE PF_LOCAL /* Another non-standard name for PF_LOCAL. */ #define PF_INET 2 /* IP protocol family. */ #define PF_AX25 3 /* Amateur Radio AX.25. */ #define PF_IPX 4 /* Novell Internet Protocol. */ #define PF_APPLETALK 5 /* Appletalk DDP. */ #define PF_NETROM 6 /* Amateur radio NetROM. */ #define PF_BRIDGE 7 /* Multiprotocol bridge. */ #define PF_ATMPVC 8 /* ATM PVCs. */ #define PF_X25 9 /* Reserved for X.25 project. */ #define PF_INET6 10 /* IP version 6. */ #define PF_ROSE 11 /* Amateur Radio X.25 PLP. */ #define PF_DECnet 12 /* Reserved for DECnet project. */ #define PF_NETBEUI 13 /* Reserved for 802.2LLC project. */ #define PF_SECURITY 14 /* Security callback pseudo AF. */ #define PF_KEY 15 /* PF_KEY key management API. */ #define PF_NETLINK 16 #define PF_ROUTE PF_NETLINK /* Alias to emulate 4.4BSD. */ #define PF_PACKET 17 /* Packet family. */ #define PF_ASH 18 /* Ash. */ #define PF_ECONET 19 /* Acorn Econet. */ #define PF_ATMSVC 20 /* ATM SVCs. */ #define PF_SNA 22 /* Linux SNA Project */ #define PF_IRDA 23 /* IRDA sockets. */ #define PF_PPPOX 24 /* PPPoX sockets. */ #define PF_WANPIPE 25 /* Wanpipe API sockets. */However, in practice, most protocol families only have one protocol, which means this should usually be set for 0; the first and only protocol in the enumeration of the family.
serv_addr.sin_family = AF_INET; serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY; serv_addr.sin_port = htons(portno);
- sin_family = specifies the address family, usually the constant AF_INET
- sin_addr = holds the IP address returned by inet_addr() to be used in the socket connection.
- sin_port = specifies the port number and must be used with htons() function that converts the host byte order to network byte order so that it can be transmitted and routed properly when opening the socket connection. The reason for this is that computers and network protocols order their bytes in a non-compatible fashion.
The lines above set up the serv_addr structure for use in the bind call.
/* Structure describing a generic socket address. */
struct sockaddr
{
__SOCKADDR_COMMON (sa_); /* Common data: address family and length. */
char sa_data[14]; /* Address data. */
};
The address family is AF_INET, since we are using IPv4 and the sockaddr_in structure. The short integer value for port must be converted into network byte order, so the htons() (Host-to-Network Short) function is used.
The bind() call passes the socket file descriptor, the address structure, and the length of the address structure. This call will bind the socket to the current IP address on port 20001.
if (bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) &serv;_addr,
sizeof(serv_addr)) < 0) error("ERROR on binding");
The listen() call tells the socket to listen for incoming connections, and a subsequent accept() call actually accepts an incoming connection. The listen() function places all incoming connections into a backlog queue until an accept() call accepts the connections. The last argument to the listen() call sets the maximum size for the backlog queue.
listen(sockfd,5);
clilen = sizeof(cli_addr);
newsockfd = accept(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) &cli;_addr, &clilen;);
if (newsockfd < 0) error("ERROR on accept");
The final argument of the accept() is a pointer to the size of the address structure. This is because the accept() function will write the connecting client's address information into the address structure and the size of that structure is clilen. The accept() function returns a new socket file descriptor for the accepted connection:
newsockfd = accept(sockfd,
(struct sockaddr *) &cli;_addr,&clilen;);
This way, the original socket file descriptor can continue to be used for accepting new connections, while the new socket file descriptor is used for communicating with the connected client.
The send() function sends the 13 bytes of the string Hello, world\n" to the new socket that describes the new connection.
send(newsockfd, "Hello, world!\n", 13,0);
To compile, the server.c:
gcc -o server server.c
and to run
./server port#
client.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <netdb.h>
void error(const char *msg)
{
perror(msg);
exit(0);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int sockfd, portno, n;
struct sockaddr_in serv_addr;
struct hostent *server;
char buffer[256];
if (argc < 3) {
fprintf(stderr,"usage %s hostname port\n", argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
portno = atoi(argv[2]);
sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (sockfd < 0)
error("ERROR opening socket");
server = gethostbyname(argv[1]);
if (server == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr,"ERROR, no such host\n");
exit(0);
}
bzero((char *) &serv;_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
serv_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
bcopy((char *)server->h_addr,
(char *)&serv;_addr.sin_addr.s_addr,
server->h_length);
serv_addr.sin_port = htons(portno);
if (connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) &serv;_addr, sizeof(serv_addr)) < 0)
error("ERROR connecting");
printf("Please enter the message: ");
bzero(buffer,256);
fgets(buffer,255,stdin);
n = write(sockfd, buffer, strlen(buffer));
if (n < 0)
error("ERROR writing to socket");
bzero(buffer,256);
n = read(sockfd, buffer, 255);
if (n < 0)
error("ERROR reading from socket");
printf("%s\n", buffer);
close(sockfd);
return 0;
}
To compile
gcc -o client client.c
and to run
./client hostname port#
First, we run server.c as in
$ ./server 20001
Then, on client side
$ ./client myhostname 20001 Please enter the message:
Then, server side has the following message when connected successfully:
$ ./server 20001 server: got connection from 127.0.0.1 port 47173
Then, on client side
$ ./client myhostname 20001 Please enter the message: Hello from client
Then, server side has the following message:
$ ./server 20001 server: got connection from 127.0.0.1 port 47173 Here is the message: Hello from Client
Clent side gets message (Hello, world!) from the server:
$ ./client myhostname 20001 Please enter the message: Hello from Client Hello, world!
To run this codes, we don't need two machines. One is enough!
Continued to Socket - Server & Client 2.
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization