Installing RabbitMQ & Celery
RabbitMQ & Celery Tutorials
Installing RabbitMQ & Celery
Hello World RabbitMQ
Work Queues (Task Queues) : RabbitMQ
Exchanges - Publish/Subscribe : RabbitMQ
Multiple bindings - Routing : RabbitMQ
Queueing Messages using Celery with RabbitMQ Message Broker Server
Before we move on, let's get familiar with a couple of terms.
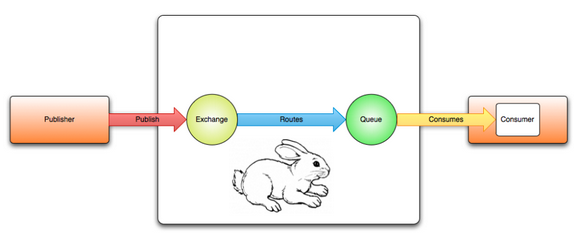
Picture from slides.com.
- RabbitMQ - Message broker server built on the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP). RabbitMQ is written in Erlang. It's responsible queuing up tasks and scheduling them.
- Celery - Task queue that is built on an asynchronous message passing system. Celery is written in Python. It can be used as a wrapper for Python API to interact with RabbitMQ.
- Celeryd - Part of the Celery package and it is the worker that actually runs the task.
- Producer (Publisher) - A program that sends messages.
- Consumer - A program that mostly waits to receive messages.
RabbitMQ and Celery work together to execute a code sometime later when resources are available.
This video explains RabbitMQ's basic concepts very well.
- It starts with Publisher/Message Broker (Queue)/Consumer.
- It also explains how the Queue works.
- It addresses how we can guarantee the delivery of message (reliable delivery):
- The Broker send confirmation to the Producer when it successfully stored the message received.
- The Consumer send Ack to the Broker when it processed the message. At the Acknowledgement from the Consumer, the Broker removes the stored message from the queue.
- When the message system may fail : potential message duplication.
- We can scale the Consumers.
- Then, the video introduces the Exchange which is required by Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP).
- We have three types of bindings which tells routing behavior from Exchange to the queues
- Fanout Exchange - ALWAYS deliver messages to binded queues REGARDLESS of bindings
- Direct Exchange - ONLY delivers messages to binded queues WHEN routing-key MATCHES bindings
- Topic Exchange - can use wile card for bindings */#
We'll work on Ubuntu 14.04. RabbitMQ installation on Ubuntu is as simple as this:
$ sudo apt-get install rabbitmq-server
Rabbitmq is set to start automatically after it's installed.
To see the information about the installed RabbitMQ such as version:
$ sudo rabbitmqctl status
Status of node rabbit@k ...
[{pid,5135},
{running_applications,[{rabbit,"RabbitMQ","3.2.4"},
{mnesia,"MNESIA CXC 138 12","4.11"},
{os_mon,"CPO CXC 138 46","2.2.14"},
{xmerl,"XML parser","1.3.5"},
{sasl,"SASL CXC 138 11","2.3.4"},
{stdlib,"ERTS CXC 138 10","1.19.4"},
{kernel,"ERTS CXC 138 10","2.16.4"}]},
{os,{unix,linux}},
{erlang_version,"Erlang R16B03 (erts-5.10.4) [source] [64-bit] [smp:2:2] [async-threads:30] [kernel-poll:true]\n"},
{memory,[{total,35396072},
{connection_procs,2704},
{queue_procs,5408},
{plugins,0},
{other_proc,13384560},
{mnesia,60688},
{mgmt_db,0},
{msg_index,28112},
{other_ets,761752},
{binary,8632},
{code,16522377},
{atom,594537},
{other_system,4027302}]},
{vm_memory_high_watermark,0.4},
{vm_memory_limit,1487224832},
{disk_free_limit,50000000},
{disk_free,439562670080},
{file_descriptors,[{total_limit,924},
{total_used,3},
{sockets_limit,829},
{sockets_used,1}]},
{processes,[{limit,1048576},{used,123}]},
{run_queue,0},
{uptime,6387}]
...done.
To stop the rabbitmq:
$ sudo rabbitmqctl stop [sudo] password for k: Stopping and halting node rabbit@k ... ...done.
Issue the status command again to see that it's really stopped.
$ sudo rabbitmqctl status
Error: unable to connect to node rabbit@k: nodedown
DIAGNOSTICS
===========
nodes in question: [rabbit@k]
hosts, their running nodes and ports:
- k: [{rabbitmqctl8566,53150}]
current node details:
- node name: rabbitmqctl8566@k
- home dir: /var/lib/rabbitmq
- cookie hash: 37CWzJUtjVqK+RSWTjgfqg==
To start it again, the recommended method is
$ sudo invoke-rc.d rabbitmq-server start * Starting message broker rabbitmq-server
If we check the status again:
$ sudo rabbitmqctl status
Status of node rabbit@k ...
[{pid,8683},
{running_applications,[{rabbit,"RabbitMQ","3.2.4"},
{os_mon,"CPO CXC 138 46","2.2.14"},
{mnesia,"MNESIA CXC 138 12","4.11"},
{xmerl,"XML parser","1.3.5"},
{sasl,"SASL CXC 138 11","2.3.4"},
{stdlib,"ERTS CXC 138 10","1.19.4"},
{kernel,"ERTS CXC 138 10","2.16.4"}]},
{os,{unix,linux}},
{erlang_version,"Erlang R16B03 (erts-5.10.4) [source] [64-bit] [smp:2:2] [async-threads:30] [kernel-poll:true]\n"},
{memory,[{total,35605480},
{connection_procs,2704},
{queue_procs,5408},
{plugins,0},
{other_proc,13607584},
{mnesia,60128},
{mgmt_db,0},
{msg_index,20888},
{other_ets,755712},
{binary,7488},
{code,16522377},
{atom,594537},
{other_system,4028654}]},
{vm_memory_high_watermark,0.4},
{vm_memory_limit,1487224832},
{disk_free_limit,50000000},
{disk_free,439561547776},
{file_descriptors,[{total_limit,924},
{total_used,3},
{sockets_limit,829},
{sockets_used,1}]},
{processes,[{limit,1048576},{used,123}]},
{run_queue,0},
{uptime,56}]
...done.
We may want to create a directory where we can implement our new system:
$ mkdir ~/TEST/MQ $ cd ~/TEST/MQ
Now we install Celery:
$ sudo apt-get update $ sudo pip install celery $ which celery /usr/local/bin/celery $ celery --version 3.1.13 (Cipater)
We're going to use Celery later after we've done some practice with RabbitMQ!
RabbitMQ & Celery Tutorials
Installing RabbitMQ & Celery
Hello World RabbitMQ
Work Queues (Task Queues) : RabbitMQ
Exchanges - Publish/Subscribe : RabbitMQ
Multiple bindings - Routing : RabbitMQ
Queueing Messages using Celery with RabbitMQ Message Broker Server
Python tutorial
Python Home
Introduction
Running Python Programs (os, sys, import)
Modules and IDLE (Import, Reload, exec)
Object Types - Numbers, Strings, and None
Strings - Escape Sequence, Raw String, and Slicing
Strings - Methods
Formatting Strings - expressions and method calls
Files and os.path
Traversing directories recursively
Subprocess Module
Regular Expressions with Python
Regular Expressions Cheat Sheet
Object Types - Lists
Object Types - Dictionaries and Tuples
Functions def, *args, **kargs
Functions lambda
Built-in Functions
map, filter, and reduce
Decorators
List Comprehension
Sets (union/intersection) and itertools - Jaccard coefficient and shingling to check plagiarism
Hashing (Hash tables and hashlib)
Dictionary Comprehension with zip
The yield keyword
Generator Functions and Expressions
generator.send() method
Iterators
Classes and Instances (__init__, __call__, etc.)
if__name__ == '__main__'
argparse
Exceptions
@static method vs class method
Private attributes and private methods
bits, bytes, bitstring, and constBitStream
json.dump(s) and json.load(s)
Python Object Serialization - pickle and json
Python Object Serialization - yaml and json
Priority queue and heap queue data structure
Graph data structure
Dijkstra's shortest path algorithm
Prim's spanning tree algorithm
Closure
Functional programming in Python
Remote running a local file using ssh
SQLite 3 - A. Connecting to DB, create/drop table, and insert data into a table
SQLite 3 - B. Selecting, updating and deleting data
MongoDB with PyMongo I - Installing MongoDB ...
Python HTTP Web Services - urllib, httplib2
Web scraping with Selenium for checking domain availability
REST API : Http Requests for Humans with Flask
Blog app with Tornado
Multithreading ...
Python Network Programming I - Basic Server / Client : A Basics
Python Network Programming I - Basic Server / Client : B File Transfer
Python Network Programming II - Chat Server / Client
Python Network Programming III - Echo Server using socketserver network framework
Python Network Programming IV - Asynchronous Request Handling : ThreadingMixIn and ForkingMixIn
Python Coding Questions I
Python Coding Questions II
Python Coding Questions III
Python Coding Questions IV
Python Coding Questions V
Python Coding Questions VI
Python Coding Questions VII
Python Coding Questions VIII
Python Coding Questions IX
Python Coding Questions X
Image processing with Python image library Pillow
Python and C++ with SIP
PyDev with Eclipse
Matplotlib
Redis with Python
NumPy array basics A
NumPy Matrix and Linear Algebra
Pandas with NumPy and Matplotlib
Celluar Automata
Batch gradient descent algorithm
Longest Common Substring Algorithm
Python Unit Test - TDD using unittest.TestCase class
Simple tool - Google page ranking by keywords
Google App Hello World
Google App webapp2 and WSGI
Uploading Google App Hello World
Python 2 vs Python 3
virtualenv and virtualenvwrapper
Uploading a big file to AWS S3 using boto module
Scheduled stopping and starting an AWS instance
Cloudera CDH5 - Scheduled stopping and starting services
Removing Cloud Files - Rackspace API with curl and subprocess
Checking if a process is running/hanging and stop/run a scheduled task on Windows
Apache Spark 1.3 with PySpark (Spark Python API) Shell
Apache Spark 1.2 Streaming
bottle 0.12.7 - Fast and simple WSGI-micro framework for small web-applications ...
Flask app with Apache WSGI on Ubuntu14/CentOS7 ...
Fabric - streamlining the use of SSH for application deployment
Ansible Quick Preview - Setting up web servers with Nginx, configure enviroments, and deploy an App
Neural Networks with backpropagation for XOR using one hidden layer
NLP - NLTK (Natural Language Toolkit) ...
RabbitMQ(Message broker server) and Celery(Task queue) ...
OpenCV3 and Matplotlib ...
Simple tool - Concatenating slides using FFmpeg ...
iPython - Signal Processing with NumPy
iPython and Jupyter - Install Jupyter, iPython Notebook, drawing with Matplotlib, and publishing it to Github
iPython and Jupyter Notebook with Embedded D3.js
Downloading YouTube videos using youtube-dl embedded with Python
Machine Learning : scikit-learn ...
Django 1.6/1.8 Web Framework ...
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization