Traversing directories recursively

How to get the home directory in Python?
home = os.path.expanduser("~")
This will ensure it works on all platforms. Or we can do:
from os.path import expanduser
home = expanduser("~")
What is the difference of os.path.basename() and os.path.dirname() functions?
Both functions use the os.path.split(path) function to split the pathname path into a pair; (head, tail).
- path="/foo/bar/item"
- The os.path.dirname(path) function returns the head of the path.
>>> os.path.dirname(path) '/foo/bar'
- The os.path.basename(path) function returns the tail of the path.
>>> os.path.basename(path) 'item'
Note that if we have a slash('/') at the end of the path, we get different result:
- path="/foo/bar/item/"
- The os.path.dirname(path) function returns the head of the path.
>>> os.path.dirname(path) '/foo/bar/item'
- The os.path.basename(path) function returns the tail of the path.
>>> os.path.basename(path) ''
os.walk(top, topdown=True, onerror=None, followlinks=False)
The os.walk() generate the file names in a directory tree by walking the tree either top-down or bottom-up.
For each directory in the tree rooted at directory top, it yields a 3-tuple:
(dirpath, dirnames, filenames)
The dirpath is a string for the path to the directory. The dirnames is a list of the names of the subdirectories in dirpath (excluding '.' and '..'). The filenames is a list of the names of the non-directory files in dirpath.
Note that the names in the lists contain no path components. To get a full path (which begins with top) to a file or directory in dirpath, do os.path.join(dirpath, name).
As a preview, we get the following output from the tree like this:
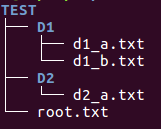
import os path = "./TEST" for root,d_names,f_names in os.walk(path): print root, d_names, f_names
Output:
./TEST ['D1', 'D2'] ['root.txt'] ./TEST/D1 [] ['d1_b.txt', 'd1_a.txt'] ./TEST/D2 [] ['d2_a.txt']
We can make a full path for each file:
import os
path = "./TEST"
fname = []
for root,d_names,f_names in os.walk(path):
for f in f_names:
fname.append(os.path.join(root, f))
print("fname = %s" %fname)
The output:
fname = ['./TEST/root.txt', './TEST/D1/d1_b.txt', './TEST/D1/d1_a.txt', './TEST/D2/d2_a.txt']
As another example, we're going to use the tree below:
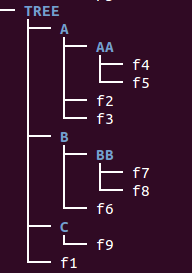
dirpath:
import os
for dirpath, dirs, files in os.walk("."):
print dirpath
Output:
. ./A ./A/AA ./C ./B ./B/BB
dirs:
import os
for dirpath, dirs, files in os.walk("."):
print dirs
Output:
['A', 'C', 'B'] ['AA'] [] [] ['BB'] []
files:
import os
for dirpath, dirs, files in os.walk("."):
print files
Output:
['f1'] ['f3', 'f2'] ['f4', 'f5'] ['f9'] ['f6'] ['f7', 'f8']
Listing files in directories recursively?
Here is the code:
import os
for dirpath, dirs, files in os.walk("."):
path = dirpath.split('/')
print '|', (len(path))*'---', '[',os.path.basename(dirpath),']'
for f in files:
print '|', len(path)*'---', f
Suppose we are now in TREE directory, then the output should look like this:
| --- [ . ] | --- f1 | --- f0.py | ------ [ A ] | ------ f3 | ------ f2 | --------- [ AA ] | --------- f4 | --------- f5 | ------ [ C ] | ------ f9 | ------ [ B ] | ------ f6 | --------- [ BB ] | --------- f7 | --------- f8

How to traverse a directory tree?
One of the answers may be to use os.walk() to recursively traverse directories.
So, in this section, we want to print all file contents recursively using the os.walk():
import os
for dirpath, dirs, files in os.walk("./TREE/"):
for filename in files:
fname = os.path.join(dirpath,filename)
with open(fname) as myfile:
print(myfile.read())
The key here is to use os.path.join() when we read the files. Note that the names in the lists contain no path components. To get a full path (which begins with top) to a file or directory in dirpath, do os.path.join(dirpath, filename).
The output from the code:
inside f1 ... inside f8
Here is another example. It reads in CMakeLists.txt, and generate a csv file with the targets.
import os
home = os.path.expanduser("~")
root_dir = os.path.join(home, "TEST/TF/tf")
cmake_path = os.path.join(root_dir, "CMakeLists.txt")
# make target list
def make_target_list():
target_tag="set(TARGET_NAME"
target_list = []
for dirpath, dirs, files in os.walk(root_dir):
if "CMakeLists.txt" in files:
for f in files:
cmake_path = os.path.join(dirpath, f)
with open(cmake_path,'rb') as lines:
for line in lines:
if target_tag in line:
target = line[line.find(target_tag)+len(target_tag)+1:line.find(")")]
target_list.append(target.strip('"'))
return target_list
# writing csv
def write_csv(t):
import csv
with open('tf.csv', 'wb') as f:
w = csv.writer(f, delimiter=' ')
w.writerow(t)
if __name__ == '__main__':
target = make_target_list()
print target
write_csv(target)
Output:
['assignment-client', 'ice-server', 'plugins', 'octree', 'embedded-webserver', 'audio', 'script-engine', 'entities-renderer', 'render-utils', 'model', 'render', 'animation', 'gpu', 'input-plugins', 'networking', 'fbx', 'ui', 'shared', 'avatars', 'display-plugins', 'entities', 'environment', 'audio-client', 'auto-updater', 'physics', 'gpu-test', 'render-utils-test', 'ui-test', 'shaders-test', 'entities-test', 'interface', 'gvr-interface', 'scribe', 'vhacd-util', 'mtc', 'domain-server']
The csv file looks like this:
$ cat tf.csv assignment-client ice-server plugins octree embedded-webserver audio script-engine entities-renderer render-utils model render animation gpu input-plugins networking fbx ui shared avatars display-plugins entities environment audio-client auto-updater physics gpu-test render-utils-test ui-test shaders-test entities-test interface gvr-interface scribe vhacd-util mtc domain-server
This is almost the same as previous ones.
I need to find files which have more than one unit of Google Ads (I am supposed to have only one of the type per page).
So, during the recursive file traversing, I have to include only (*.php) files not *.png, *.txt, etc. Also, I have to count the occurrence of the Ad-unit in a file. If a file has more than one unit, this code prints out two things : full path and the count.
Here is the code:
import os
for dirpath, dirs, files in os.walk("."):
for filename in files:
fname = os.path.join(dirpath,filename)
if fname.endswith('.php'):
with open(fname) as myfile:
line = myfile.read()
c = line.count('bogo_sq')
if c > 1:
print fname, c
Output sample:
../AngularJS/AngularJS_More_Directives_HTML_DOM.php 2 ../DevOps/AWS/aws_S3_Simple_Storage_Service.php 2 ../Android/android22Threads.php 2 ../python/pytut.php 2
Recently, I switched to https (SSL) from http. But found out, my CSSs were not loading properly, and it broke my pages. It turned out, I was using http, for example, "http://apis.google.com/js/plusone.js". So, I had to browse all files, and replace it to "//apis.google.com/js/plusone.js".
Here is the the script I used for the task:
import os
import sys
import fileinput
path = "../public_html"
# construct full file path recursively
file_list = []
for root,d_names,f_names in os.walk(path):
for f in f_names:
file_list.append(os.path.join(root, f))
print("file_list : %s" %file_list)
search = ['http://netdna', 'http://fonts', 'http://maxcdn', 'http://getbootstrap', 'http://php',
'http://tinymce', 'http://wiki.moxiecode', 'http://www.google', 'http://www.apple',
'http://activex.microsoft', 'http://download.macromedia', 'http://cdn.mathjax'
'http://code.jquery', 'http://w.sharethis', 'http://s7.addthis',
'http://ajax.googleapis', 'http://cdn.mathjax', 'http://d3js.org',
'http://apis.google', 'http://pagead2.googlesyndication']
replace = ['//netdna', '//fonts', '//maxcdn', '//getbootstrap', '//php',
'//tinymce', '//wiki.moxiecode', '//www.google', '//www.apple',
'//activex.microsoft', '//download.macromedia', '//cdn.mathjax'
'//code.jquery','//w.sharethis', '//s7.addthis',
'//ajax.googleapis','//cdn.mathjax','//d3js.org',
'//apis.google', '//pagead2.googlesyndication']
if (len(search) != len(replace)) :
sys.exit("Error: search does not match with replace")
# Loop through files and replace "search" with "replace"
for filename in file_list:
# exclude img/video files
if filename.lower().endswith(('.png', '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.gif', '.bak',
'.mp4', '.ogv', '.mp3', '.ismv', '.ts', '.ismc', '.m3u8',
'.mov', '.avi', '.dv', '.wmv', '.ogg', '.mkv', '.webm',
'.idx', '.tar', '.gz', '.zip', '.pdf', '.svg', '.bz')):
continue
print(filename)
# Read in the file
with open(filename, 'r') as file :
filedata = file.read()
# Replace the target string
for i in range(len(search)):
filedata = filedata.replace(search[i], replace[i])
# Write the file out again
with open(filename, 'w') as file:
file.write(filedata)
I replaced quite a few API calls with something like this: "//apis.google". Just dropped the "http:". I also excluded some files such as media or compressed ones. I did not use in-place replacing since my python version was 2.7
The output (just listing the processed files):
... ../public_html/dj/static/admin/js/jquery.init.js ../public_html/dj/static/admin/js/collapse.js ../public_html/dj/static/admin/js/prepopulate.js ...
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization