Coding Questions VIII - 2024

Find the longest sequence of zeros in binary representation of an integer (Max count of 0s in between 1s).
9 (1001) => 2, 529 (1000010001) => 44, 20 (10100) => 1, 15 (1111) =>0, and 32 (100000) => 0.
def binaryGap(n):
# convert an int to an array of integers (0 and 1)
bits = []
while n > 0:
bits.append(n % 2)
n = n // 2
# reverse the list : for n = 20 bits = [0,0,1,0,1] => [1,0,1,0,0]
bits = bits[::-1]
# get max gap
count = 0
mxgap = 0
for b in bits:
if b == 1:
mxgap = max(count, mxgap)
count = 0
else:
count += 1
return bits,mxgap
numbs = [9, 529, 20, 15, 32]
for n in numbs:
bits, mxgap = binaryGap(n)
print("%d => %s mxgap = %d" %(n,bits,mxgap))
Output:
9 => [1, 0, 0, 1] mxgap = 2 529 => [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1] mxgap = 4 20 => [1, 0, 1, 0, 0] mxgap = 1 15 => [1, 1, 1, 1] mxgap = 0 32 => [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] mxgap = 0
[1,2,3] => [() (1,) (2,) (3,) (1,2) (1,3) (2,3) (1,2,3)]
import itertools
a = [1,2,3]
ans = []
for r in range(0,len(a)+1):
nexts = itertools.combinations(a,r)
for n in nexts:
ans.append(n)
print(ans) # [() (1,) (2,) (3,) (1,2) (1,3) (2,3) (1,2,3)]
['ABC', 'D', 'EF'] => [A, D, E, B, F, C]:
a = ['ABC','D','EF']
# construct a dictionary - { string: current length }
# {'ABC': 3, 'D': 1, 'EF': 2}
da = { x:len(x) for x in a }
# get max length of the strings
mx = max(da.values())
ans = []
# loop with max length
for i in range(mx):
# loop the dictionary
for k,v in da.items():
if v > 0:
# append a char starting from the first one
ans.append(k[-v])
v -= 1
da[k] = v
print(ans)
Output:
['ABC', 'D', 'EF'] => ['A', 'D', 'E', 'B', 'F', 'C']
'ABCDEFG', 3, 'x' --> ['ABC','DEF', 'Gxx']
def block(a,n,mark):
ans = []
count = len(a) // n # full string count
nleft = len(a) % n # length of partial string
nmark = n - nleft # number of 'x's to fill
# full string
for i in range(count):
ans.append(a[i*n:(i+1)*n])
# partial string
ans.append(a[count*n:count*n+nleft]+nmark*'x')
return ans
a = 'ABCDEFG'
n = 3
mark = 'x'
answer = block(a,n,mark)
print(answer) # ['ABC','DEF', 'Gxx']
[1,2,3,4,5] => [1,3,6,10,15]
def accumulate(a):
ans = [a[0]]
for i in range(1,len(a)):
ans.append(a[i-1]+a[i])
return ans
a = [1,2,3,4,5]
ans = accumulate(a)
print(ans) # [1,3,6,10,15]
Given list of strings, ['ABC', 'DEF'], write a function that produces A B C D E F, fn (iterable).
The following code is an example of the generator function:
def chain_from_iterable(a):
for s in a:
for c in s:
yield c
a = ['ABC','DEF']
# chain_from_iterable(a) is a generator function.
for x in chain_from_iterable(a):
print(x, end=' ') # A B C D E F
A return sends a specified value back to its caller while yield produces a sequence of values.
In other words, The difference is that while a return statement terminates a function entirely,
yield statement pauses the function saving all its states and later continues from there on successive calls.
We may want to use yield when we want to iterate over a sequence instead of storing the entire sequence in memory.
The yield is using a generator and a generator function is defined like a normal function but with the yield keyword rather than return.
So, whenever the body of a def contains yield, the function automatically becomes a generator function.
Make an iterator that filters elements from data returning only those that have a corresponding element in selectors that evaluates to True. Stops when either the data or selectors iterables has been exhausted.
compress('ABCDEF', [1,0,1,0,1,1]) => ACEF
def compress(data, selector): return (d for d,s in zip(data, selector) if s) a = 'ABCDEF' bit = [1,0,1,0,1,1] for x in compress(a,bit): print(x, end='') # ACEF
Note that the "compress()" returns a generator, (d for d,s in zip(data, selector) if s).
To return just a list and process it, we do the following:
def compress(data, selector): return [d for d,s in zip(data, selector) if s] a = 'ABCDEF' bit = [1,0,1,0,1,1] d = ''.join(compress(a,bit)) print(d) # ACEF
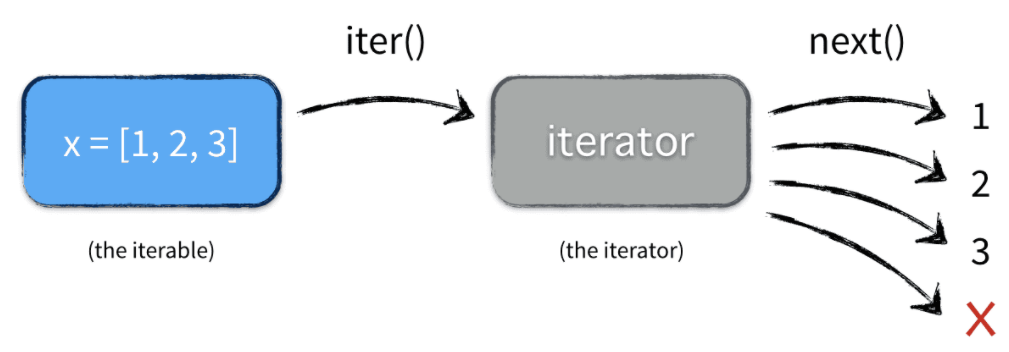
Make an iterator that drops elements from the iterable as long as the predicate is true; afterwards, returns every element. Note, the iterator does not produce any output until the predicate first becomes false, so it may have a lengthy start-up time.
def dropwhile(predicate, a):
# dropwhile(lambda x: x<5, [1,4,6,4,1]) --> 6 4 1
iterator = iter(a)
for x in iterator:
if not predicate(x): # if x > 5
yield x
break;
for x in iterator:
yield x
pred = lambda x: x<5
a = [1,4,6,4,1]
for x in dropwhile(pred,a):
print(x, end = ' ') # 6 4 1
Note that within the generator function, we need to convert the iterable to an iterator via iter(iterator) so that the generator keeps the track of the iterator
(to resume the iteration where it left off at the break).
Write a function that does 'AAAABBBCCD' --> AAAA BBB CC D
def groupby(a):
prev = a[0]
for c in a:
# yield a blank if a new char
if c != prev:
yield ' '
# otherwise, just yield the char
yield c
prev = c
x = ['ABC', 'ABCDD', 'AAAABBBCCD']
new_x = []
for e in x:
out = ''
for c in groupby(e):
out += c
new_x.append(out)
print("%s \n => %s" %(x,new_x))
Output:
['ABC', 'ABCDD', 'AAAABBBCCD'] => ['A B C', 'A B C DD', 'AAAA BBB CC D']
Write a generator function, product('ABCD', '12') that yields A1, A2, B1...D2 one by one:
def product(*args):
ar = list(args)
pools = [list(p) for p in ar]
print('args = %s' %(args,))
print('pools = %s' %pools)
for p0 in pools[0]:
for p1 in pools[1]:
yield p0+p1 # A1, A2, B1...D2 one by one
a = 'ABCD'
b = '12'
for p in product(a,b):
print(p, end=' ')
Output:
args = ('ABCD', '12')
pools = [['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'], ['1', '2']]
A1 A2 B1 B2 C1 C2 D1 D2
Actually, we can use a list comprehension if not for the yield requirement:
a = 'ABCD' b = '12' c = [ x+y for x in a for y in b ]
'ABCD' => AB AC AD BA BC BD CA CB CD DA DB DC
a = 'ABCD'
x = list(a)
n = len(x)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if i != j:
print(x[i]+x[j], end=' ')
Output:
AB AC AD BA BC BD CA CB CD DA DB DC
With a list comprehension, we can do it as the following:
a = 'ABCD' b = ' '.join([ x+y for x in a for y in a if x != y ]) print(b)
Output:
AB AC AD BA BC BD CA CB CD DA DB DC
Make an iterator that computes the function using arguments obtained from the iterable.
Used instead of map() when argument parameters are already grouped in tuples from a single iterable (the data has been "pre-zipped").
def starmap(fn,iterable):
for arg in iterable:
# unpacking a tuple into two arguments
yield fn(*arg)
x = [(2,5),(3,2),(10,3)]
for e in starmap(pow,x):
print(e)
Output:
32 9 1000
Note the difference between map() and starmap() parallels the distinction between
function(a,b) and function(*c) (itertools.starmap(function, iterable)).
Make an iterator that aggregates elements from each of the iterables.
zip_longest('ABCD', 'xy', fillvalue='-') => Ax By C- D-
If the iterables are of uneven length, missing values are filled-in with fillvalue in the StopIterator section.
Iteration continues until the longest iterable is exhausted.
def zip_longest(*args, fillvalue=None):
iterators = [iter(it) for it in args]
num = len(iterators)
while True:
values = []
for i, it in enumerate(iterators):
try:
value = next(it)
print("value=%s" %value)
except StopIteration:
num -= 1
if not num:
return
iterators[i] = iter(fillvalue)
value = fillvalue
values.append(value)
yield tuple(values)
for s in zip_longest('ABCD','xy',fillvalue='-'):
print(s[0]+s[1])
Output:
Ax By C- D-
Ref: itertools.zip_longest(*iterables, fillvalue=None).
-
def sum(a, b): """ sum(4, 3) 7 sum(-4, 5) 1 """ return a + b -
def sum(a, b): """ >>> sum(4, 3) 7 >>> sum(-4, 5) 1 """ return a + b -
def sum(a, b): """ # >>> sum(4, 3) # 7 # >>> sum(-4, 5) # 1 """ return a + b -
def sum(a, b): ### >>> sum(4, 3) 7 >>> sum(-4, 5) 1 ### return a + b
Ans. #2
Ref: doctest — Test interactive Python examples
What would this expression return?
college = ['Freshman', 'Sophomore', 'Junior', 'Senior'] c = list(enumerate(college, 2021)) print(c)
Ans:
[(2021, 'Freshman'), (2022, 'Sophomore'), (2023, 'Junior'), (2024, 'Senior')]
The enumerate() code should look like this:
def enumerate(sequence, start=0):
n = start
for elem in sequence:
yield n, elem
n += 1
[('yellow', 1), ('blue', 2), ('yellow', 3), ('blue', 4), ('red', 1)] => [('blue', [2, 4]), ('red', [1]), ('yellow', [1, 3])]:
from collections import defaultdict
s = [('yellow', 1), ('blue', 2), ('yellow', 3), ('blue', 4), ('red', 1)]
d = defaultdict(list)
for k,v in s:
d[k].append(v)
sd = sorted(d.items())
print(sd)
Output:
[('blue', [2, 4]), ('red', [1]), ('yellow', [1, 3])]
(Note) If we try to access a key in a dictionary that doesn't exist,
defaultdict will create a new key for us instead of throwing a KeyError.
Ref: defaultdict objects
- self means that no other arguments are required to be passed into the method.
- There is no real purpose for the self method; it's just historic computer science jargon that Python keeps to stay consistent with other programming languages.
- self refers to the instance whose method was called.
- self refers to the class that was inherited from to create the object using self.
Ans: #3
Suppose we have the following class with instance method foo():
# a.py
class A:
message = "class message"
@classmethod
def cfoo(cls):
print(cls.message)
def foo(self, msg):
self.message = msg
print(self.message)
def __str__(self):
return self.message
Because the method foo() is designed to process instances, we normally call the method through instance:
>>> from a import A
>>> a = A()
>>> a.foo('instance call')
instance call
When we call the method, the Python automatically replace the self with the instance object, a, and then the msg gets the string passed at the call which is 'instance call'.
(Note) Instance methods can modify the state of an instance or the state of its parent class.
from collections import namedtuple
Point = namedtuple('Point', ['x', 'y'])
p = Point(10,20)
print("p[0]+p[1]=%s" %(p[0]+p[1]))
x,y = p
print("x = %s y = %s" %(x,y))
print("p = ", p)
Output:
p[0]+p[1]=30 x = 10 y = 20 p = Point(x=10, y=20)
- We can assign a name to each of the namedtuple members and refer to them that way, similarly to how we would access keys in dictionary.
- Each member of a namedtuple object can be indexed to directly, just like in a regular tuple.
- namedtuple are just as memory efficient as regular tuples.
What does calling namedtuple on a collection type return?
Ans: a tuple subclass with iterable named fields
Given the following three list, how would we create a new list that matches the desired output printed below?
fruits = ['Apples', 'Oranges', 'Bananas']
quantities = [5, 3, 4]
prices = [1.50, 2.25, 0.89]
# Desired output
[('Apples', 5, 1.50),
('Oranges', 3, 2.25),
('Bananas', 4, 0.89)]
The code should look like this:
fruits = ['Apples', 'Oranges', 'Bananas'] quantities = [5, 3, 4] prices = [1.50, 2.25, 0.89] z = list(zip(fruits, quantities, prices)) print(z)
- A set is an unordered collection of unique items.
- A list is an ordered collection of non-unique items.
The __init__ method is a constructor method that is called automatically whenever a new object is created from a class.
It sets the initial state of a new object.
What statement about a class methods is true?
- A class method is a regular function that belongs to a class, but it must return None.
- A class method can modify the state of the class, but they can't directly modify the state of an instance that inherits from that class.
- A class method is similar to a regular function, but a class method doesn't take any arguments.
- A class method hold all of the data for a particular class.
Ans: #2
(Note) The idea of class method is very similar to instance method, only difference being that instead of passing the instance hiddenly as a first parameter, we're now passing the class itself as a first parameter.
class MyMethods:
def i_method(self,x):
print(self,x)
@staticmethod
def s_method(x):
print(x)
@classmethod
def c_method(cls,x):
print(cls,x)
obj = MyMethods()
obj.i_method(1)
obj.s_method(3)
obj.c_method(5)
Output:
<__main__.MyMethods object at 0x1038dc0a0> 1 3 <class '__main__.MyMethods'> 5
Since we're passing only a class to the method, no instance is involved. This means that it can't directly modify the state of an instance.
- Permutations
['AB', 'AC', 'BA', 'BC', 'CA', 'CB'] - Multiset Permutations
['AA', 'AB', 'AC', 'BA', 'BB', 'BC', 'CA', 'CB', 'CC'] - Combinations
['AB', 'AC', 'BC'] - Combinations with repeatition
['AA', 'AB', 'AC', 'BB', 'BC', 'CC']
The code using itertools should look like this:
import itertools
a = ['A','B','C']
def merge(input):
ans = []
for x in input:
ans.append(x[0]+x[1])
return ans
print("Permutations")
pm = list(itertools.permutations(a,2))
print(merge(pm))
print("Multiset Permutations")
pd = list(itertools.product(a,repeat=2))
print(merge(pd))
print("Combinations")
cb = list(itertools.combinations(a,2))
print(merge(cb))
print("Combinations with Repetition")
cbr = list(itertools.combinations_with_replacement(a,2))
print(merge(cbr))
Sort the following list of dictionaries by 'age':
animals = [
{'type': 'Crow', 'name': 'clair', 'age': 16},
{'type': 'Elephant', 'name': 'ivory', 'age': 4},
{'type': 'Lion', 'name': 'Leo', 'age': 7},
]
import operator
animals = [
{'type': 'Crow', 'name': 'clair', 'age': 16},
{'type': 'Elephant', 'name': 'ivory', 'age': 4},
{'type': 'Lion', 'name': 'Leo', 'age': 7},
]
# using lambda for key
sd = sorted(animals, key = lambda x: x['age'])
print(sd)
# using operator.itemgetter for key
sd2 = sorted(animals, key = operator.itemgetter('age'))
print(sd2)
Output:
[{'type': 'Elephant', 'name': 'ivory', 'age': 4}, {'type': 'Lion', 'name': 'Leo', 'age': 7}, {'type': 'Crow', 'name': 'clair', 'age': 16}]
[{'type': 'Elephant', 'name': 'ivory', 'age': 4}, {'type': 'Lion', 'name': 'Leo', 'age': 7}, {'type': 'Crow', 'name': 'clair', 'age': 16}]
Write a function returning a list of unique words.
def uniq_words(ws):
wset = set()
for w in ws.split():
wset.add(w)
return list(wset)
sentence = "There is no strife no prejudice no national conflict in outer space as yet"
print(uniq_words(sentence))
Output:
['national', 'There', 'is', 'in', 'yet', 'as', 'strife', 'outer', 'prejudice', 'conflict', 'space', 'no']
Note that we're not using a list to processing if a word is already in the list. Rather we're using set() from the onset.
"Sets are significantly faster when it comes to determining if an object is present in the set (as in x in s),
but are slower than lists when it comes to iterating over their contents."- Check the efficiencies (list vs set) from
Python Sets vs Lists
Hash functions take an arbitrary amount of data and return a fixed-length bit string. The output of the function is called secure hash or message digest.
Hash functions are widely used in cryptography.
We want to write a function that hashes a file (lorem.txt) and return the secure hash:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur. Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident, sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit anim id est laborum.
The code should look like this:
import hashlib
def hashing(fname):
m = hashlib.sha256()
with open("lorem.txt", "rb") as f:
line = f.readline()
m.update(line)
# return(m.digest())
return(m.hexdigest())
secure_hash = hashing("lorem.txt")
print(secure_hash)
Output:
ea7ead7f16fd6b4d2314312bab772ea74aae2700f0c243171d89bf9b1e75c2e1
Note that the hash functions are meant to be one-way. So, we cannot convert the output back to the original text.
If we use digest() instead of hexdigest() method for the hash objet m,
we'll get the following output:
b"\xea~\xad\x7f\x16\xfdkM#\x141+\xabw.\xa7J\xae'\x00\xf0\xc2C\x17\x1d\x89\xbf\x9b\x1eu\xc2\xe1"
We can read certain amount of byte one at a time. For example, 512 bytes per read, the code should look like this:
import hashlib
def hashing(fname):
m = hashlib.sha256()
with open("lorem.txt", "rb") as f:
chunk = 0
while chunk != b'':
chunk = f.read(512)
m.update(chunk)
return(m.hexdigest())
secure_hash = hashing("lorem.txt")
print(secure_hash)
Output:
6ef2bb967fcd5de4d5d0c1be2226496d89a1d15c6343e11cdf8c216a337517df
Methods of io.TextIOWrapper:
f.read(): reads whole file and returns a string
>>> with open('lorem.txt','r') as f: ... f.read() ... 'Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit, \nsed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. \nUt enim ad minim veniam, \nquis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. \nDuis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur. \nExcepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident,\nsunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit anim id est laborum.\n'f.readline(): reads a line one by one attaching '\n' at the end of the line
>>> f = open('lorem.txt','r') >>> f.readline() 'Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit, \n' >>> f.readline() 'sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. \n' >>> f.readline() 'Ut enim ad minim veniam, \n'f.readlines(): reads all lines as a list. Same aslist(f)
>>> f = open('lorem.txt','r') >>> f.readlines() ['Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit, \n', 'sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. \n', 'Ut enim ad minim veniam, \n', 'quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. \n', 'Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur. \n', 'Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident,\n', 'sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit anim id est laborum.\n']
Here is the code using the methods of io.TextIOWrapper:
fname = 'csv.txt'
with open(fname,'r') as f:
print("-- for line in f --")
for line in f:
print(line)
print()
with open(fname,'r') as f:
print("-- read() --")
s = f.read()
print(s)
print()
with open(fname,'r') as f:
print("-- f.readlines() --")
s = f.readlines()
print(s)
print()
with open(fname,'r') as f:
print("-- f.readline() --")
while True:
s = f.readline()
if not s:
break;
print(s, end='')
print()
Input (csv.txt):
Los Angeles,34°03′N,118°15′W New York City,40°42′46″N,74°00′21″W Paris,48°51′24″N,2°21′03″E
Output:
-- for line in f -- Los Angeles,34°03′N,118°15′W New York City,40°42′46″N,74°00′21″W Paris,48°51′24″N,2°21′03″E -- read() -- Los Angeles,34°03′N,118°15′W New York City,40°42′46″N,74°00′21″W Paris,48°51′24″N,2°21′03″E -- f.readlines() -- ['Los Angeles,34°03′N,118°15′W\n', 'New York City,40°42′46″N,74°00′21″W\n', 'Paris,48°51′24″N,2°21′03″E\n'] -- f.readline() -- Los Angeles,34°03′N,118°15′W New York City,40°42′46″N,74°00′21″W Paris,48°51′24″N,2°21′03″E
If we want to get the number of bytes of a string, we can use encode() method of string:
>>> s = "12345 7"
>>> s.encode('utf-8')
b'12345 7'
>>> len(s.encode('utf-8'))
7
where the utf stands for Unicode Transformation Format and the 8 means 8 bits.
Input: csv.txt:
Los Angeles,34°03′N,118°15′W New York City,40°42′46″N,74°00′21″W Paris,48°51′24″N,2°21′03″E
Code:
import csv
with open('csv.txt', 'r') as f:
reader = csv.reader(f, delimiter=',')
for row in reader:
print(row)
Output:
['Los Angeles', '34°03′N', '118°15′W'] ['New York City', '40°42′46″N', '74°00′21″W'] ['Paris', '48°51′24″N', '2°21′03″E']
Input (capital.txt):
Abc d Ef Ghi Jkl mn Opq rstuv Wxyz
Code:
with open('capital.txt','r') as f:
count = sum(1 for line in f for c in line if c.isupper())
print(count) # output => 6
What's the difference between is and ==?
ischecks if the two are referencing the same object==checks if the two are the same value
So, a = [1,2,3] and b = [1,2,3]. Then, a is b : False while a == b : True:
>>> a = [1,2,3] >>> b = [1,2,3] >>> a is b False >>> a == b True
Note: integers are a little different:
>>> small_a = 100 >>> small_b = 100 >>> small_a is small_b True >>> small_b == small_b True >>> big_a = 257 >>> big_b = 257 >>> big_a is big_b False >>> big_a == big_b True
Actually, in Python, numbers from -5 up to and including 256 have singleton instances. That means Python creates singletons for the most commonly used integers!
The code (https://www.interviewcake.com/python-interview-questions ):
import copy
question_template = {
"title": "default title",
"question": "default question",
"answer": "default answer",
"hints": []
}
def make_new_question(title, question, answer, hints=None):
# new_q = copy.copy(question_template)
new_q = copy.deepcopy(question_template)
# always require title, question, answer
new_q["title"] = title
new_q["question"] = question
new_q["answer"] = answer
# sometimes there aren't hints, that's fine. Otherwise, add them:
if hints is not None:
new_q["hints"].extend(hints)
return new_q
question_1 = make_new_question("title1", "question1", "answer1", ["q1 hint1", "q1 hint2"])
question_2 = make_new_question("title2", "question2", "answer2")
question_3 = make_new_question("title3", "question3", "answer3", ["q3 hint1"])
print(question_1)
print(question_2)
print(question_3)
Output:
{'title': 'title1', 'question': 'question1', 'answer': 'answer1', 'hints': ['q1 hint1', 'q1 hint2']}
{'title': 'title2', 'question': 'question2', 'answer': 'answer2', 'hints': []}
{'title': 'title3', 'question': 'question3', 'answer': 'answer3', 'hints': ['q3 hint1']}
If we use copy.copy() which is doing a shallow copy, we get a wrong output:
{'title': 'title1', 'question': 'question1', 'answer': 'answer1', 'hints': ['q1 hint1', 'q1 hint2', 'q3 hint1']}
{'title': 'title2', 'question': 'question2', 'answer': 'answer2', 'hints': ['q1 hint1', 'q1 hint2', 'q3 hint1']}
{'title': 'title3', 'question': 'question3', 'answer': 'answer3', 'hints': ['q1 hint1', 'q1 hint2', 'q3 hint1']}
iterator = [i for i in range(1, 4)] matrix = [[y+3*(x-1) for y in iterator] for x in iterator]
Given a list of binary numbers, write a function that converts it to an integer and returns True if the integer is the power of 2:
import collections
def toDec(b):
# converts b to dec
dec = 0
for i,c in enumerate(b):
dec += int(c)*2**(len(b)-1-i)
return dec
def powerOf2(b):
# counts 0s and 1s
d = collections.defaultdict(int)
for bit in b:
d[bit] += 1
# returns dec, True if only one '1', otherwise False
return d['1'] == 1
bin = ['00000001', '00000011', '00000100', '00000101','00000111',
'00001000', '00001001', '00010000', '00100000', '01000000',
'10000000','11111111']
for b in bin:
print(b,toDec(b), powerOf2(b))
Output:
00000001 1 True 00000011 3 False 00000100 4 True 00000101 5 False 00000111 7 False 00001000 8 True 00001001 9 False 00010000 16 True 00100000 32 True 01000000 64 True 10000000 128 True 11111111 255 False
Write a code to read public data returned from URL, and parse the JSON to dictionary object.
urllib:
from urllib.request import urlopen
url = "http://date.jsontest.com"
webUrl = urlopen(url)
if (webUrl.getcode() == 200):
data = webUrl.read().decode('utf-8')
print(f'data = {data}')
else:
raise ConnectionError("Error {} from server, cannot retrieve results ".format(str(webUrl.getcode())))
Output:
data = {
"date": "04-30-2021",
"milliseconds_since_epoch": 1619742724035,
"time": "12:32:04 AM"
}
requests:
import json
import requests
from requests.exceptions import HTTPError
try:
url = 'http://date.jsontest.com'
response = requests.get(url)
# If the response was successful, no Exception will be raised
response.raise_for_status()
data = response.content
print(f'data = {data}')
jd = json.loads(data)
print(f'type(jd) = {type(jd)}')
print(f'jd = {jd}')
except HTTPError as http_err:
print(f'HTTP error occurred: {http_err}') # Python 3.6
except Exception as err:
print(f'Other error occurred: {err}') # Python 3.6
else:
print('Success!')
Output:
data = b'{\n "date": "04-30-2021",\n "milliseconds_since_epoch": 1619742814896,\n "time": "12:33:34 AM"\n}\n'
type(jd) = <class 'dict'>
jd = {'date': '04-30-2021', 'milliseconds_since_epoch': 1619742814896, 'time': '12:33:34 AM'}
Success!
Ref: json.load(s) & json.dump(s)
Given an input file (games.txt) that indicates the results of a series of matches. The results are of the form A M B N which means that team A beat team B by the score of M to N.
o 14 i 6 l 17 h 12 j 13 d 8 i 5 n 4 ...
Write a program that reads in this file and outputs the following statistics:
- The average margin of victory across all games.
- The team that has the largest average margin of victory.
- The team that has the largest average losing margin.
- Find the teams with the top 10 largest average margins of victory.
- The top 10 largest average losing margin.
import collections
import operator
# games log list
games = []
with open("game.txt","r") as f:
for line in f:
games.append(line.split())
# margins
s = 0
for g in games:
s += abs(int(g[1])-int(g[3]))
average_margin = s / len(games)
print("average_margin = %s" %average_margin)
# dictionaries of teams - winners & losers
w = collections.defaultdict(list)
for g in games:
k,v = g[0],int(g[1])-int(g[3])
w[k].append(round(v,2))
winners = dict(w)
l = collections.defaultdict(list)
for g in games:
k,v = g[2],int(g[3])-int(g[1])
l[k].append(round(v,2))
losers = dict(l)
# find a team with largest margin of victory
# loop through winners dict
mx = 0
team = None
w_margin = {}
for k,v in winners.items():
av = sum(v)/len(v)
w_margin[k] = round(av,2)
if av > mx:
team = k
mx = av
print("The team with the largest average margin of victory is '%s' with a av-margin of %f " %(team, mx))
# find a team with largest margin of lost
# loop through winners dict
mn = 0
l_team = None
l_margin = {}
for k,v in losers.items():
av = sum(v)/len(v)
l_margin[k] = round(av,2)
if av < mn:
team = k
mn = av
print("The team with the largest average margin of lost is '%s' with a av-margin of %f " %(team, mn))
w10 = sorted(w_margin.items(), key = operator.itemgetter(1), reverse = True)
print("top 10 = %s" %w10[:10])
l10 = sorted(l_margin.items(), key = operator.itemgetter(1), reverse = False)
print("bottom 10 = %s" %l10[:10])
Output:
average_margin = 6.245
The team with the largest average margin of victory is 'e' with a av-margin of 10.000000
The team with the largest average margin of lost is 'o' with a av-margin of -8.555556
top 10 = [('e', 10.0), ('f', 8.5), ('c', 8.5), ('k', 8.25), ('v', 7.85), ('m', 7.8), ('w', 7.7), ('g', 6.8), ('r', 6.75), ('j', 6.5)]
bottom 10 = [('o', -8.56), ('t', -8.5), ('e', -8.27), ('s', -8.0), ('q', -7.6), ('g', -7.36), ('v', -7.17), ('l', -7.16), ('c', -6.75), ('m', -6.71)]
Pawn race is a game for two people, played on an ordinary 8 × 8 chessboard. The first player has a white pawn, the second one - a black pawn. Initially the pawns are placed somewhere on the board so that the 1st and the 8th rows are not occupied. Players take turns to make a move.
White pawn moves upwards, black one moves downwards. The following moves are allowed:
- one-cell move on the same vertical in the allowed direction
- two-cell move on the same vertical in the allowed direction, if the pawn is standing on the 2nd (for the white pawn) or the 7th (for the black pawn) row. Note that even with the two-cell move a pawn can't jump over the opponent's pawn
- capture move one cell forward in the allowed direction and one cell to the left or to the right.
Actually, the code is available from Python: Pawn race
Virtually the same, here is my code:
def file_rank(x):
"""given position(x), returns column & row"""
return ord(x[0])-ord('a'), int(x[1])
def capture(w_rank, w_file, b_rank, b_file, ):
"""return True if can be captured"""
return abs(b_file - w_file) == 1 and \
abs(w_rank - b_rank) == 1 and \
w_rank < b_rank
def pawn_chess(white, black, to_move):
"""return a winner for an input : w_position, b_position, turn"""
w_file, w_rank = file_rank(white)
b_file, b_rank = file_rank(black)
# if on the same file while black is on a higher rank,
# they'll bump and will not be able to pass each other
if(w_file == b_file and b_rank > w_rank):
return 'draw'
# loop through all other cases
while True:
# if can capture the piece: return a winner
if capture(w_rank, w_file, b_rank, b_file):
return "white" if to_move == 'w' else "black"
# w to move
if to_move == 'w':
# if rank !=2 or can be captured with advance 2, then just advance 1
if w_rank != 2 or capture(w_rank + 2, w_file, b_rank, b_file):
w_rank += 1
# advance 2
else:
w_rank += 2
# b to move
if to_move == 'b':
# if rank !=7 or can be captured with advance 2, then just advance 1
if b_rank != 7 or capture(w_rank, w_file, b_rank - 2, b_file ):
b_rank -= 1
# otherwise, advance 2
else:
b_rank -= 2
# if a pawn is on a promotion square: return a winner
if w_rank == 8 or b_rank == 1:
return "white" if to_move == 'w' else "black"
# take turns
to_move = 'w' if to_move == 'b' else 'b'
# play the game
white, black, toMove = "e2", "e7",'w'
print(white, black, toMove, ' : ', pawn_chess(white, black, toMove))
white, black, toMove = "e3", "d7",'b'
print(white, black, toMove, ' : ', pawn_chess(white, black, toMove))
white, black, toMove = "a7", "h2",'w'
print(white, black, toMove, ' : ', pawn_chess(white, black, toMove))
Output:
e2 e7 w : draw e3 d7 b : black a7 h2 w : white
Write a code to decode a string, for example, 'a1b2z3' => 'abbzzz', 'k2b1y4' => 'kkbzzzz':
def decode(s):
decoded_str = ""
i = 0
while i < len(s):
ch = s[i]
i += 1
count = 0
while i < len(s) and s[i].isdigit():
count = 10 * count + int(s[i])
i += 1
decoded_str += ch*int(count)
return decoded_str
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "a1b2z3"
print(f"{s} => {decode(s)}")
s = "k2b1y4"
print(f"{s} => {decode(s)}")
s = "w10b1z4"
print(f"{s} => {decode(s)}")
Output:
a1b2z3 => abbzzz k2b1y4 => kkbyyyy w10b1z4 => wwwwwwwwwwbzzzz
We can make a class and make the code as @staticmethod:
class Decoder:
@staticmethod
def decode(s):
i = 0
decoded_str = ""
while i < len(s):
ch = s[i]
i += 1
count = 0
while i < len(s) and s[i].isdigit():
count = 10*count + int(s[i])
i += 1
decoded_str += ch*count
return decoded_str, len(decoded_str)
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "z1y2x3"
decoded, decoded_length = Decoder.decode(s)
print(f"s = {s}, decoded = {decoded}, decoded_length = {decoded_length}")
s = "x4y2z10"
decoded, decoded_length = Decoder.decode(s)
print(f"s = {s}, decoded = {decoded}, decoded_length = {decoded_length}")
Note that the @staticmethod decorator indicates that the decode method is a static method,
providing class-level functionality without requiring an instance of the class.
Being a static method, decode can be called on the class itself (Decoder.decode('a1b2z3')) without needing to create an instance of the Decoder class. Since it's a static method, it doesn't have access to instance-specific attributes or methods. In this case, it doesn't matter whether an instance of Decoder is created or not; the method behaves the same.
Output:
s = z1y2x3, decoded = zyyxxx, decoded_length = 6 s = x4y2z10, decoded = xxxxyyzzzzzzzzzz, decoded_length = 16
- Python Coding Questions I
- Python Coding Questions II
- Python Coding Questions III
- Python Coding Questions IV
- Python Coding Questions V
- Python Coding Questions VI
- Python Coding Questions VII
- Python Coding Questions VIII
- Python Coding Questions IX
- Python Coding Questions X
List of codes Q & A
- Merging two sorted list
- Get word frequency - initializing dictionary
- Initializing dictionary with list
- map, filter, and reduce
- Write a function f() - yield
- What is __init__.py?
- Build a string with the numbers from 0 to 100, "0123456789101112..."
- Basic file processing: Printing contents of a file - "with open"
- How can we get home directory using '~' in Python?
- The usage of os.path.dirname() & os.path.basename() - os.path
- Default Libraries
- range vs xrange
- Iterators
- Generators
- Manipulating functions as first-class objects
- docstrings vs comments
- using lambdda
- classmethod vs staticmethod
- Making a list with unique element from a list with duplicate elements
- What is map?
- What is filter and reduce?
- *args and **kwargs
- mutable vs immutable
- Difference between remove, del and pop on lists
- Join with new line
- Hamming distance
- Floor operation on integers
- Fetching every other item in the list
- Python type() - function
- Dictionary Comprehension
- Sum
- Truncating division
- Python 2 vs Python 3
- len(set)
- Print a list of file in a directory
- Count occurrence of a character in a Python string
- Make a prime number list from (1,100)
- Reversing a string - Recursive
- Reversing a string - Iterative
- Reverse a number
- Output?
- Merging overlapped range
- Conditional expressions (ternary operator)
- Packing Unpacking
- Function args
- Unpacking args
- Finding the 1st revision with a bug
- Which one has higher precedence in Python? - NOT, AND , OR
- Decorator(@) - with dollar sign($)
- Multi-line coding
- Recursive binary search
- Iterative binary search
- Pass by reference
- Simple calculator
- iterator class that returns network interfaces
- Converting domain to ip
- How to count the number of instances
- Python profilers - cProfile
- Calling a base class method from a child class that overrides it
- How do we find the current module name?
- Why did changing list 'newL' also change list 'L'?
- Constructing dictionary - {key:[]}
- Colon separated sequence
- Converting binary to integer
- 9+99+999+9999+...
- Calculating balance
- Regular expression - findall
- Chickens and pigs
- Highest possible product
- Implement a queue with a limited size
- Copy an object
- Filter
- Products
- Pickle
- Overlapped Rectangles
- __dict__
- Fibonacci I - iterative, recursive, and via generator
- Fibonacci II - which method?
- Fibonacci III - find last two digits of Nth Fibonacci number
- Write a Stack class returning Max item at const time A
- Write a Stack class returning Max item at const time B
- Finding duplicate integers from a list - 1
- Finding duplicate integers from a list - 2
- Finding duplicate integers from a list - 3
- Reversing words 1
- Parenthesis, a lot of them
- Palindrome / Permutations
- Constructing new string after removing white spaces
- Removing duplicate list items
- Dictionary exercise
- printing numbers in Z-shape
- Factorial
- lambda
- lambda with map/filter/reduce
- Number of integer pairs whose difference is K
- iterator vs generator
- Recursive printing files in a given directory
- Bubble sort
- What is GIL (Global Interpreter Lock)?
- Word count using collections
- Pig Latin
- List of anagrams from a list of words
- lamda with map, filer and reduce functions
- Write a code sending an email using gmail
- histogram 1 : the frequency of characters
- histogram 2 : the frequency of ip-address
- Creating a dictionary using tuples
- Getting the index from a list
- Looping through two lists side by side
- Dictionary sort with two keys : primary / secondary keys
- Writing a file downloaded from the web
- Sorting csv data
- Reading json file
- Sorting class objects
- Parsing Brackets
- Printing full path
- str() vs repr()
- Missing integer from a sequence
- Polymorphism
- Product of every integer except the integer at that index
- What are accessors, mutators, and @property?
- N-th to last element in a linked list
- Implementing linked list
- Removing duplicate element from a list
- List comprehension
- .py vs .pyc
- Binary Tree
- Print 'c' N-times without a loop
- Quicksort
- Dictionary of list
- Creating r x c matrix
- Transpose of a matrix
- str.isalpha() & str.isdigit()
- Regular expression
- What is Hashable? Immutable?
- Convert a list to a string
- Convert a list to a dictionary
- List - append vs extend vs concatenate
- Use sorted(list) to keep the original list
- list.count()
- zip(list,list) - join elements of two lists
- zip(list,list) - weighted average with two lists
- Intersection of two lists
- Dictionary sort by value
- Counting the number of characters of a file as One-Liner
- Find Armstrong numbers from 100-999
- Find GCF (Greatest common divisor)
- Find LCM (Least common multiple)
- Draws 5 cards from a shuffled deck
- Dictionary order by value or by key
- Regular expression - re.split()
- Regular expression : re.match() vs. re.search()
- Regular expression : re.match() - password check
- Regular expression : re.search() - group capturing
- Regular expression : re.findall() - group capturin
- Prime factors : n = products of prime numbers
- Valid IPv4 address
- Sum of strings
- List rotation - left/right
- shallow/deep copy
- Converting integer to binary number
- Creating a directory and a file
- Creating a file if not exists
- Invoking a python file from another
- Sorting IP addresses
- Word Frequency
- Printing spiral pattern from a 2D array - I. Clock-wise
- Printing spiral pattern from a 2D array - II. Counter-Clock-wise
- Find a minimum integer not in the input list
- I. Find longest sequence of zeros in binary representation of an integer
- II. Find longest sequence of zeros in binary representation of an integer - should be surrounded with 1
- Find a missing element from a list of integers
- Find an unpaired element from a list of integers
- Prefix sum : Passing cars
- Prefix sum : count the number of integers divisible by k in range [A,B]
- Can make a triangle?
- Dominant element of a list
- Minimum perimeter
- MinAbsSumOfTwo
- Ceiling - Jump Frog
- Brackets - Nested parentheses
- Brackets - Nested parentheses of multiple types
- Left rotation - list shift
- MaxProfit
- Stack - Fish
- Stack - Stonewall
- Factors or Divisors
- String replace in files 1
- String replace in files 2
- Using list as the default_factory for defaultdict
- Leap year
- Capitalize
- Log Parsing
- Getting status_code for a site
- 2D-Array - Max hourglass sum
- New Year Chaos - list
- List (array) manipulation - list
- Hash Tables: Ransom Note
- Count Triplets with geometric progression
- Strings: Check if two strings are anagrams
- Strings: Making Anagrams
- Strings: Alternating Characters
- Special (substring) Palindrome
- String with the same frequency of characters
- Common Child
- Fraudulent Activity Notifications
- Maximum number of toys
- Min Max Riddle
- Poisonous Plants with Pesticides
- Common elements of 2 lists - Complexity
- Get execution time using decorator(@)
- Conver a string to lower case and split using decorator(@)
- Python assignment and memory location
- shallow copy vs deep copy for compound objects (such as a list)
- Generator with Fibonacci
- Iterator with list
- Second smallest element of a list
- *args, **kargs, and positional args
- Write a function, fn('x','y',3) that returns ['x1', 'y1', 'x2', 'y2', 'x3', 'y3']
- sublist or not
- any(), all()
- Flattening a list
- Select an element from a list
- Circularly identical lists
- Difference between two lists
- Reverse a list
- Split a list with a step
- Break a list and make chunks of size n
- Remove duplicate consecutive elements from a list
- Combination of elements from two lists
- Adding a sublist
- Replace the first occurence of a value
- Sort the values of the first list using the second list
- Transpose of a matrix (nested list)
- Binary Gap
- Powerset
- Round Robin
- Fixed-length chunks or blocks
- Accumulate
- Dropwhile
- Groupby
- Simple product
- Simple permutation
- starmap(fn, iterable)
- zip_longest(*iterables, fillvalue=None)
- What is the correct way to write a doctest?
- enumerate(iterable, start=0)
- collections.defaultdict - grouping a sequence of key-value pairs into a dictionary of lists
- What is the purpose of the 'self' keyword when defining or calling instance methods?
- collections.namedtuple(typename, field_names, *, rename=False, defaults=None, module=None)
- zipped
- What is key difference between a set and a list?
- What does a class's init() method do?
- Class methods
- Permutations and combinations of ['A','B','C']
- Sort list of dictionaries by values
- Return a list of unique words
- hashlib
- encode('utf-8')
- Reading in CSV file
- Count capital letters in a file
- is vs ==
- Create a matrix : [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
- Binary to integer and check if it's the power of 2
- urllib.request.urlopen() and requests
- Game statistics
- Chess - pawn race
- Decoding a string
- Determinant of a matrix - using numpy.linalg.det()
- Revenue from shoe sales - using collections.Counter()
- Rangoli
- Unique characters
- Valid UID
- Permutations of a string in lexicographic sorted order
- Nested list
- Consecutive digit count
- Find a number that occurs only once
- Sorting a two-dimensional array
- Reverse a string
- Generate random odd numbers in a range
- Shallow vs Deep copy
- Transpose matrix
- Are Arguments in Python Passed by Value or by Reference?
- re: Is a string alphanumeric?
- reversed()
- Caesar's cipher, or shift cipher, Caesar's code, or Caesar shift
- Every other words
- re: How can we check if an email address is valid or not?
- re: How to capture temperatures of a text
- re.split(): How to split a text.
- How can we merge two dictionaries?
- How can we combine two dictionaries?
- What is the difference between a generator and a list?
- Pairs of a given array A whose sum value is equal to a target value N
- Adding two integers without plus
- isinstance() vs type()
- What is a decorator?
- In Python slicing, what does my_list[-3:2:-2] slice do?
- Revisit sorting dict - counting chars in a text file
- re: Transforming a date format using re.sub
- How to replace the newlines in csv file with tabs?
- pandas.merge
- How to remove duplicate charaters from a string?
- Implement a class called ComplexNumber
- Find a word frequency
- Get the top 3 most frequent characters of a string
- Just seen and ever seen
- Capitalizing the full name
- Counting Consequitive Characters
- Calculate Product of a List of Integers Provided using input()
- How many times a substring appears in a string
- Hello, first_name last_name
- String validators
- Finding indices that a char occurs in a list
- itertools combinations
Python tutorial
Python Home
Introduction
Running Python Programs (os, sys, import)
Modules and IDLE (Import, Reload, exec)
Object Types - Numbers, Strings, and None
Strings - Escape Sequence, Raw String, and Slicing
Strings - Methods
Formatting Strings - expressions and method calls
Files and os.path
Traversing directories recursively
Subprocess Module
Regular Expressions with Python
Regular Expressions Cheat Sheet
Object Types - Lists
Object Types - Dictionaries and Tuples
Functions def, *args, **kargs
Functions lambda
Built-in Functions
map, filter, and reduce
Decorators
List Comprehension
Sets (union/intersection) and itertools - Jaccard coefficient and shingling to check plagiarism
Hashing (Hash tables and hashlib)
Dictionary Comprehension with zip
The yield keyword
Generator Functions and Expressions
generator.send() method
Iterators
Classes and Instances (__init__, __call__, etc.)
if__name__ == '__main__'
argparse
Exceptions
@static method vs class method
Private attributes and private methods
bits, bytes, bitstring, and constBitStream
json.dump(s) and json.load(s)
Python Object Serialization - pickle and json
Python Object Serialization - yaml and json
Priority queue and heap queue data structure
Graph data structure
Dijkstra's shortest path algorithm
Prim's spanning tree algorithm
Closure
Functional programming in Python
Remote running a local file using ssh
SQLite 3 - A. Connecting to DB, create/drop table, and insert data into a table
SQLite 3 - B. Selecting, updating and deleting data
MongoDB with PyMongo I - Installing MongoDB ...
Python HTTP Web Services - urllib, httplib2
Web scraping with Selenium for checking domain availability
REST API : Http Requests for Humans with Flask
Blog app with Tornado
Multithreading ...
Python Network Programming I - Basic Server / Client : A Basics
Python Network Programming I - Basic Server / Client : B File Transfer
Python Network Programming II - Chat Server / Client
Python Network Programming III - Echo Server using socketserver network framework
Python Network Programming IV - Asynchronous Request Handling : ThreadingMixIn and ForkingMixIn
Python Coding Questions I
Python Coding Questions II
Python Coding Questions III
Python Coding Questions IV
Python Coding Questions V
Python Coding Questions VI
Python Coding Questions VII
Python Coding Questions VIII
Python Coding Questions IX
Python Coding Questions X
Image processing with Python image library Pillow
Python and C++ with SIP
PyDev with Eclipse
Matplotlib
Redis with Python
NumPy array basics A
NumPy Matrix and Linear Algebra
Pandas with NumPy and Matplotlib
Celluar Automata
Batch gradient descent algorithm
Longest Common Substring Algorithm
Python Unit Test - TDD using unittest.TestCase class
Simple tool - Google page ranking by keywords
Google App Hello World
Google App webapp2 and WSGI
Uploading Google App Hello World
Python 2 vs Python 3
virtualenv and virtualenvwrapper
Uploading a big file to AWS S3 using boto module
Scheduled stopping and starting an AWS instance
Cloudera CDH5 - Scheduled stopping and starting services
Removing Cloud Files - Rackspace API with curl and subprocess
Checking if a process is running/hanging and stop/run a scheduled task on Windows
Apache Spark 1.3 with PySpark (Spark Python API) Shell
Apache Spark 1.2 Streaming
bottle 0.12.7 - Fast and simple WSGI-micro framework for small web-applications ...
Flask app with Apache WSGI on Ubuntu14/CentOS7 ...
Fabric - streamlining the use of SSH for application deployment
Ansible Quick Preview - Setting up web servers with Nginx, configure enviroments, and deploy an App
Neural Networks with backpropagation for XOR using one hidden layer
NLP - NLTK (Natural Language Toolkit) ...
RabbitMQ(Message broker server) and Celery(Task queue) ...
OpenCV3 and Matplotlib ...
Simple tool - Concatenating slides using FFmpeg ...
iPython - Signal Processing with NumPy
iPython and Jupyter - Install Jupyter, iPython Notebook, drawing with Matplotlib, and publishing it to Github
iPython and Jupyter Notebook with Embedded D3.js
Downloading YouTube videos using youtube-dl embedded with Python
Machine Learning : scikit-learn ...
Django 1.6/1.8 Web Framework ...
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization