(Batch) gradient descent algorithm

Gradient descent is an optimization algorithm that works by efficiently searching the parameter space, intercept($\theta_0$) and slope($\theta_1$) for linear regression, according to the following rule:
\[\begin{aligned} \theta := \theta -\alpha \frac{\delta}{\delta \theta}J(\theta). \end{aligned} \]Note that we used '$:=$' to denote an assign or an update.
The \(J(\theta)\) is known as the cost function and \(\alpha\) is the learning rate, a free parameter. In this tutorial, we're going to use a least squares cost function defined as following:
\[\begin{aligned} J(\theta) = \frac{1}{2m}\sum_{i=1}^m (h_\theta(x^{(i)})-y^{(i)})^2, \end{aligned} \]where \(m\) is the total number of training examples and $h_\theta(x^{(i)})$ is the hypothesis function defined like this:
\[\begin{aligned} h_\theta(x^{(i)}) = \theta_0 + \theta_1 x^{(i)} \end{aligned} \]where the super script $(i)$ is used to denote the $i^{th}$ sample (we'll save subscripts for the index to a feature when we deal with multi-features).
We need derivatives for both $\theta_0$ and $\theta_1$:
\[\begin{aligned} \frac{\partial}{\partial \theta_0}J(\theta_0, \theta_1) = \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^m (h_\theta(x^{(i)})-y^{(i)}) \end{aligned} \] \[\begin{aligned} = \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^m (\theta_0 + \theta_1 x^{(i)}-y^{(i)}) \end{aligned} \] \[\begin{aligned} \frac{\partial}{\partial \theta_1}J(\theta_0, \theta_1) = \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^m (h_\theta(x^{(i)})-y^{(i)})x^{(i)} \end{aligned} \] \[\begin{aligned} = \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^m (\theta_0 + \theta_1 x^{(i)}-y^{(i)})x^{(i)} \end{aligned} \]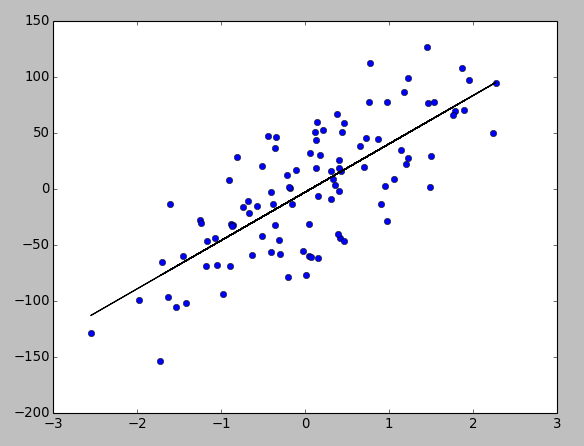
The following code runs until it converges or reaches iteration maximum. We get $\theta_0$ and $\theta_1$ as its output:
import numpy as np
import random
import sklearn
from sklearn.datasets.samples_generator import make_regression
import pylab
from scipy import stats
def gradient_descent(alpha, x, y, ep=0.0001, max_iter=10000):
converged = False
iter = 0
m = x.shape[0] # number of samples
# initial theta
t0 = np.random.random(x.shape[1])
t1 = np.random.random(x.shape[1])
# total error, J(theta)
J = sum([(t0 + t1*x[i] - y[i])**2 for i in range(m)])
# Iterate Loop
while not converged:
# for each training sample, compute the gradient (d/d_theta j(theta))
grad0 = 1.0/m * sum([(t0 + t1*x[i] - y[i]) for i in range(m)])
grad1 = 1.0/m * sum([(t0 + t1*x[i] - y[i])*x[i] for i in range(m)])
# update the theta_temp
temp0 = t0 - alpha * grad0
temp1 = t1 - alpha * grad1
# update theta
t0 = temp0
t1 = temp1
# mean squared error
e = sum( [ (t0 + t1*x[i] - y[i])**2 for i in range(m)] )
if abs(J-e) <= ep:
print 'Converged, iterations: ', iter, '!!!'
converged = True
J = e # update error
iter += 1 # update iter
if iter == max_iter:
print 'Max interactions exceeded!'
converged = True
return t0,t1
if __name__ == '__main__':
x, y = make_regression(n_samples=100, n_features=1, n_informative=1,
random_state=0, noise=35)
print 'x.shape = %s y.shape = %s' %(x.shape, y.shape)
alpha = 0.01 # learning rate
ep = 0.01 # convergence criteria
# call gredient decent, and get intercept(=theta0) and slope(=theta1)
theta0, theta1 = gradient_descent(alpha, x, y, ep, max_iter=1000)
print ('theta0 = %s theta1 = %s') %(theta0, theta1)
# check with scipy linear regression
slope, intercept, r_value, p_value, slope_std_error = stats.linregress(x[:,0], y)
print ('intercept = %s slope = %s') %(intercept, slope)
# plot
for i in range(x.shape[0]):
y_predict = theta0 + theta1*x
pylab.plot(x,y,'o')
pylab.plot(x,y_predict,'k-')
pylab.show()
print "Done!"
Output:
x.shape = (100, 1) y.shape = (100,) Converged, iterations: 641 !!! theta0 = [-2.81943944] theta1 = [ 43.1387759] intercept = -2.84963639461 slope = 43.2042438802
The regression line in the picture above confirms we got the right result from our Gradient Descent algorithm. Also, the sciPy's stats.linregress reassures (intercept and slope values) the correctness of our outcome (theta0 and theta1).
We need to be a little bit careful when we updates $\theta_0$ and $\theta_1$. First, we calculate the temporary $\theta_0$ and $\theta_1$ with old $\theta_0$ and $\theta_1$, and then we get new $\theta_0$ and $\theta_1$ from $temp0$ and $temp1$:
\[\begin{aligned} temp0 := \theta_0 -\alpha \frac{\partial}{\partial \theta_0}J(\theta_0, \theta_1) \end{aligned} \] \[\begin{aligned} temp1 := \theta_1 -\alpha \frac{\partial}{\partial \theta_1}J(\theta_0, \theta_1) \end{aligned} \] \[\begin{aligned} \theta_0 := temp0 \end{aligned} \] \[\begin{aligned} \theta_1 := temp1. \end{aligned} \]The following code is almost the same as the code we used in the previous section but simpler since it utilized numPy better. It runs until it reaches iteration maximum. We get $\theta_0$ and $\theta_1$ as its output:
import numpy as np
import random
from sklearn.datasets.samples_generator import make_regression
import pylab
from scipy import stats
def gradient_descent_2(alpha, x, y, numIterations):
m = x.shape[0] # number of samples
theta = np.ones(2)
x_transpose = x.transpose()
for iter in range(0, numIterations):
hypothesis = np.dot(x, theta)
loss = hypothesis - y
J = np.sum(loss ** 2) / (2 * m) # cost
print "iter %s | J: %.3f" % (iter, J)
gradient = np.dot(x_transpose, loss) / m
theta = theta - alpha * gradient # update
return theta
if __name__ == '__main__':
x, y = make_regression(n_samples=100, n_features=1, n_informative=1,
random_state=0, noise=35)
m, n = np.shape(x)
x = np.c_[ np.ones(m), x] # insert column
alpha = 0.01 # learning rate
theta = gradient_descent_2(alpha, x, y, 1000)
# plot
for i in range(x.shape[1]):
y_predict = theta[0] + theta[1]*x
pylab.plot(x[:,1],y,'o')
pylab.plot(x,y_predict,'k-')
pylab.show()
print "Done!"
Output:
iter 0 | J: 1604.873 iter 1 | J: 1586.636 iter 2 | J: 1568.768 iter 3 | J: 1551.261 ... iter 997 | J: 699.300 iter 998 | J: 699.300 iter 999 | J: 699.300 theta = [ -2.84837957 43.20234847]
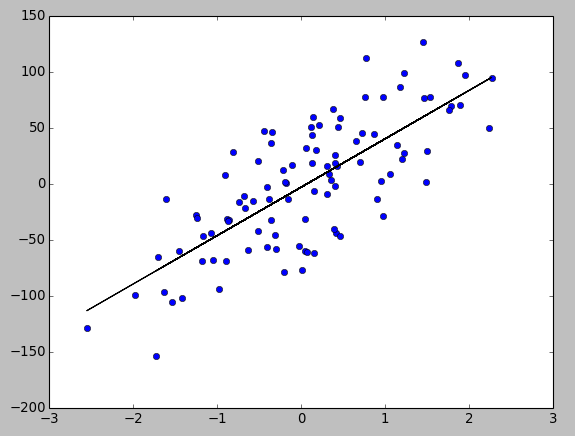
We may also want to see how the batch gradient descent is used for the well known Iris dataset : Single Layer Neural Network - Adaptive Linear Neuron using linear (identity) activation function with batch gradient method
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization