Coding Questions V - 2024

What is Hashable?
Let's start with the key in dictionary. The key of a dictionary should be unique. Internally, the key is transformed by a hash function and become an index to a memory where the value is stored. Suppose, if the key is changed, then it will be pointing somewhere else and we lose the original value the the old key was pointing.
In Python, we can say that the key should be hashable. That's why we always use hashable objects as keys. Hashable objects are integers, floats, strings, tuples, and frozensets.
Immutable object will not change after it has been created, especially in any way that changes the hash value of that object. Objects used as hash keys must be immutable so their hash values remain unchanged. Note that all hashable objects are also immutable objects.
Mutable objects are lists, dictoroaries, and sets.
Don't be surprised at the following code using tuple as a key for a dictionary:
d={}
t1 = (1,2)
t2 = (3,4,5)
d[t1] = 2
d[t2] = 3
print d[t1], d[t2]
Output:
2 3
We rarely use a tuple as a key, but there is no problem because tuple is hashable.
If we use a list as a key, we get the following error:
print d[list(range(2))] TypeError: unhashable type: 'list'
An object is hashable if it has a hash value which never changes during its lifetime (it needs a __hash__() method), and can be compared to other objects (it needs an __eq__() or __cmp__() method). Hashable objects which compare equal must have the same hash value.
Hashability makes an object usable as a dictionary key and a set member, because these data structures use the hash value internally.
All of Python's immutable built-in objects are hashable, while no mutable containers (such as lists or dictionaries) are. Objects which are instances of user-defined classes are hashable by default; they all compare unequal, and their hash value is their id().
-from Python glossary
t = tuple([0,1,2,3]) print(t)
Output:
(0, 1, 2, 3)
# list of strings
L = ["Imagination", "is", "more", "important", "than", "knowledge"]
print(' '.join(L))
# list of integers
N = [0,1,2,3]
print(''.join(str(n) for n in N))
Output:
Imagination is more important than knowledge 0123
number = ['eins','zwei','drei',1,2,3] print(dict(zip(number[:3], number[3:])))
Output:
{'drei': 3, 'eins': 1, 'zwei': 2}
To get the same output from this list, ['eins',1,'zwei',2,'drei',3]:
number = ['eins',1,'zwei',2,'drei',3] print(dict(zip(number[0::2], number[1::2])))
Specially, for this zigzag (on-and-off) type, we can use iter() method, and create list iterator object:
number = ['eins',1,'zwei',2,'drei',3] i = iter(number) print(type(i)) print(dict(zip(i,i)))
We'll get the same output:
<type 'listiterator'>
{'drei': 3, 'eins': 1, 'zwei': 2}
While the append() and extend() methods modify the original list, the concatenate ('+') creates a new list:
a = [1,2] b = [3,4,5] c = a.append(b) # modifying a print(a, c) a = [1,2] b = [3,4,5] c = a.extend(b) # modifying a print(a, c) a = [1,2] b = [3,4,5] c = a + b # creating a new list print(a, c)
Output:
[1, 2, [3, 4, 5]] None [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] None [1, 2] [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
The sorted() function returns a new sorted list.
We can also use the list.sort() method. It modifies the list in-place (and returns None to avoid confusion).
Usually it's less convenient than sorted() -
but if we don't need the original list, list.sort() is slightly more efficient.
a = [3, 2, 1] a2 = sorted(a) print(a, a2) a3 = a.sort() print(a, a3)
Output:
[3, 2, 1] [1, 2, 3] [1, 2, 3] None
The list.sort() method is only defined for lists.
In contrast, the sorted() function accepts any iterable.
Note that both list.sort() and sorted() have a key parameter
to specify a function (or other callable) to be called on each list element prior to making comparisons:
from operator import itemgetter, attrgetter
guest = [
('john', 'A', 15, 170),
('clair', 'B', 44, 240),
('bell', 'D', 74, 111),
('dave', 'C', 10, 164) ]
print(sorted(guest, key = lambda x:x[0]))
print(sorted(guest, key = itemgetter(1)))
class Guest:
def __init__(self, name, grade, age, weight):
self.name = name
self.grade = grade
self.age = age
self.weight = weight
def __repr__(self):
return repr( (self.name, self.grade, self.age, self.weight) )
g_object = [
Guest('john', 'A', 15, 170),
Guest('clair', 'B', 44, 240),
Guest('bell', 'D', 74, 111),
Guest('dave', 'C', 10, 164),
]
print(sorted(g_object, key = lambda g: g.age))
print(sorted(g_object, key = attrgetter('weight')))
Output:
[('bell', 'D', 74, 111), ('clair', 'B', 44, 240), ('dave', 'C', 10, 164), ('john', 'A', 15, 170)]
[('john', 'A', 15, 170), ('clair', 'B', 44, 240), ('dave', 'C', 10, 164), ('bell', 'D', 74, 111)]
[('dave', 'C', 10, 164), ('john', 'A', 15, 170), ('clair', 'B', 44, 240), ('bell', 'D', 74, 111)]
[('bell', 'D', 74, 111), ('dave', 'C', 10, 164), ('john', 'A', 15, 170), ('clair', 'B', 44, 240)]
We have a list : [1,1,2,3,4,5,6,6,6]. Print how many 6s in the list in one-liner:
print([1,1,2,3,4,5,6,6,6].count(6))
There is a Counter() method which is faster:
from collections import Counter L = [1,1,2,3,4,5,6,6,6] print(Counter(L))
Output:
Counter({6: 3, 1: 2, 2: 1, 3: 1, 4: 1, 5: 1})
So, we can pass the number as a key to the dictionary to get its count. For example, pass 6 as a key:
print Counter([1,1,2,3,4,5,6,6,6])[6] # we get 3
We can write a simple version of the Counter() like this:
def myCounter(L):
import operator
# initialize dict with 0
d = dict.fromkeys(L,0)
# or
# d = {x:0 for x in L}
for l in L:
d[l] += 1
# return sorted (by vaule) dict descending order
return sorted(d.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
# or using labmda
# return sorted(d.items(), key = lambda x:x[1], reverse=True)
L = [1,1,2,3,4,5,6,6,6]
print(myCounter(L))
Given two lists, a = ['l','m','n'] and b = ['p','q','r']. Write a code to crete a list, ['lp', 'mq', 'nr'].
As a preview, the following code shows how the zip(list,list) works:
#!/usr/local/bin/python
a = ['l','m','n']
b = ['p','q','r']
c = [(x,y) for x,y in zip(a,b)]
print(c) # ==> [('l', 'p'), ('m', 'q'), ('n', 'r')]
d = [[x,y] for x,y in zip(a,b)]
print(d) # ==> [['l', 'p'], ['m', 'q'], ['n', 'r']]
Our code should look like this:
#!/usr/local/bin/python j = [''.join([x,y]) for x,y in zip(a,b)] # or # j = [x+y for x,y in zip(a,b)] print(j)
Output:
['lp', 'mq', 'nr']
Note that join() takes a list!
We have two lists: [values] and [weights]. This sample shows how to use zip to calculate weighted average:
weights = [0.5, 0.8, 0.7, 0.8, 1.0] values = [10, 20, 10, 10, 30] average = sum([weight[i] * values[i] for i in range(len(weight))])/sum(values) zip_average = sum ([x * y for x,y in zip(weights,values)]) / sum(values) print average, zip_average # 0.825 0.825
Note that the sum(list) takes a list, and the zip(list,list) takes two lists.
Here we can use two approach: filter() and list comprehension:
a = [1,2,3,5,7,9] b = [2,3,5,6,7,8] print filter(lambda x: x in a, b) # prints out [2, 3, 5, 7]
Note that we can do the same with list comprehension:
a = [1,2,3,5,7,9] b = [2,3,5,6,7,8] print [x for x in a if x in b] # prints out [2, 3, 5, 7]
With set():
a = [1,2,3,5,7,9] b = [2,3,5,6,7,8] j = list(set(a) & set(b)) print(j) # ==> [2, 3, 5, 7]
In this section, initially a list of character is given. From the list, we make a dictionary {char, count}, and print out the dictionary sorted by the value (count).
a = ['a','a','c','c','b','c']
# d = dict.fromkeys(a,0)
# or
d = {x:0 for x in a}
print(d)
for ch in a:
d[ch] += 1
print(d)
sorted_d = sorted(d.items(), key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True)
print(sorted_d)
Output:
{'a': 0, 'c': 0, 'b': 0}
{'a': 2, 'c': 3, 'b': 1}
[('c', 3), ('a', 2), ('b', 1)]
We can also use operator.itemgetter() to sort dictionary:
inventory = {'apple': 3, 'banana': 2, 'pear': 5, 'orange': 1}
s = sorted(inventory.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(0))
print(s)
Output:
[('apple', 3), ('banana', 2), ('orange', 1), ('pear', 5)]
The file given: "input.txt" is "abcdefgHIJKLMOPQrstuvwxyz". We need to count the Capitals only. One line of code:
print(len([s for s in open("input.txt","r").read() if s.isupper()]))
Output:
9
Actually, more readable code looks something like this:
with open("input.txt","r") as f:
print(len([s for s in f.read() if s.isupper()]))
Write a program that computes all Armstrong numbers in the range of 0 and 999. An Armstrong number is a number such that the sum of its digits raised to the third power is equal to the number itself. For example, 371 is an Armstrong number, since 3**3 + 7**3 + 1**3 = 371.
Hint: use floor (//)
def isArmstrong(n):
temp = n
sum = 0
while temp > 0:
sum += (temp % 10)**3
temp //= 10
if n == sum:
return True
return False
n = 1000
print([i for i in range(0,n) if isArmstrong(i)])
Output:
[0, 1, 153, 370, 371, 407]
def GCF(n1,n2):
n = min(n1,n2)
while True:
if n1 % n == 0 and n2 % n == 0:
return n
n -= 1
n1 = 80; n2 = 240
print(GCF(n1,n2))
Output:
80
def LCM(n1,n2):
n = max(n1,n2)
while True:
if n % n1 == 0 and n % n2 == 0:
return n
n += 1
n1 = 24; n2 = 36
print(LCM(n1,n2))
Output:
72
Write a code to shuffle a deck of card and draw 5 cards.
import itertools, random deck = list(itertools.product(range(1,14),['Space','Diamond','Club','Heart'])) random.shuffle(deck) hands = list(deck[i] for i in range(5)) print(hands)
Output:
[(2, 'Club'), (11, 'Diamond'), (8, 'Diamond'), (13, 'Heart'), (2, 'Diamond')]
Example:
# 'AAAABBBCCDAABBB' --> [A, B, C, D] (Ever seen)
# 'AAAABBBCCDAABBB' --> [A, B, C, D, A, B] (Just seen)
s1 = 'AAAABBBCCDAABBB'
s2 = 'AAAABBBCCDAABBB'
ever_seen = [s1[0]]
for v in s1[1:]:
if v != ever_seen[-1] and v not in ever_seen:
ever_seen.append(v)
print(ever_seen)
just_seen = [s2[0]]
for v in s2[1:]:
if v != just_seen[-1]:
just_seen.append(v)
print(just_seen)
Output:
['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'] ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'A', 'B']
Given a list, list items as the most frequent at top:
mylist = ['a','b','b','d','b','c','d','a','d','d']
d = {}.fromkeys(mylist,0)
# or
d = {k:0 for k in mylist}
for m in mylist:
d[m] += 1
print('initial d = %s' %d)
import operator
# descending : reverse=True
d2 = sorted(d.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
print('order by value: %s' %d2)
d2 = sorted(d.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(0), reverse=True)
print('order by key: %s' %d2)
Output:
initial d = {'a': 2, 'b': 3, 'd': 4, 'c': 1}
order by value: [('d', 4), ('b', 3), ('a', 2), ('c', 1)]
order by key: [('d', 4), ('c', 1), ('b', 3), ('a', 2)]
Note: the itemgetter() can be used like this (specifying the sort order):
import operator
st = [('Tom',19,80), ('John',20,90), ('Jony',17,91), ('Jony',17,93), ('Json',21,85)]
print(sorted(st, key = operator.itemgetter(0,1,2)))
Output:
[('John', 20, 90), ('Jony', 17, 91), ('Jony', 17, 93), ('Json', 21, 85), ('Tom', 19, 80)]
Take an input string parameter and determine if exactly 3 question marks exist between every pair of numbers that add up to 10. If so, return true, otherwise return false.
'''
"arrb6???4xxbl5???eee5" => true
"4???1??bc9" => false
"acc?7??sss?3rr4??????5" => true
"5??aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa?5?5" => false
"9b???1???9??k?1???9" => true
"3?6???4?j?1???9" => true
"aa6?9" => false
'''
sslist = ["arrb6???4xxbl5???eee5", "4???1??bc9", "acc?7??sss?3rr4??????5",
"5??aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa?5?5", "9b???1???9??k?1???9", "3?6???4?j?1???9", "aa6?9"]
def qmark(ss):
print(ss)
# index : the location of digits
index = [i for i, s in enumerate(ss) if s.isdigit()]
print('index=%s' %index)
# index_tuple : [(start1, end1), ... ]
index_tuple = [(index[i], index[i+1]) for i in range(len(index)-1)]
print('index_tuple=%s' %index_tuple)
# truth : list of 'True' or 'False'.
# To pass, all items should be 'True', Empty list means failure
truth = []
for t in index_tuple:
sum = int(ss[t[0]]) + int(ss[t[1]])
if sum == 10:
if ss[t[0]:t[1]].count("?") != 3:
truth.append('F')
else:
truth.append('T')
if len(truth) == 0:
return False
elif 'F' in truth:
return False
else:
return True
for ss in sslist:
print(qmark(ss))
print()
The output:
arrb6???4xxbl5???eee5 index=[4, 8, 13, 20] index_tuple=[(4, 8), (8, 13), (13, 20)] True 4???1??bc9 index=[0, 4, 9] index_tuple=[(0, 4), (4, 9)] False acc?7??sss?3rr4??????5 index=[4, 11, 14, 21] index_tuple=[(4, 11), (11, 14), (14, 21)] True 5??aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa?5?5 index=[0, 23, 25] index_tuple=[(0, 23), (23, 25)] False 9b???1???9??k?1???9 index=[0, 5, 9, 14, 18] index_tuple=[(0, 5), (5, 9), (9, 14), (14, 18)] True 3?6???4?j?1???9 index=[0, 2, 6, 10, 14] index_tuple=[(0, 2), (2, 6), (6, 10), (10, 14)] True aa6?9 index=[2, 4] index_tuple=[(2, 4)] False
We can split a string with string.split(). But when we need to split a string with multiple delimiters, we may want to use regular expression, re.split().
For example with the following string:
"Is life a joke? Does it not make you cry? Life is not a joke! Those who live know. It is sometimes a yoke!"
We want to split the string with three delimiters: '?', '!', and '.'
The string now has multiple sentences.
We should write a code the maximum number of words for those sentences.
Here is the code:
def solution(S):
import re
sentences = re.split(r'[.!?]', S)
print(sentences)
mx = 0
for sn in sentences:
mx = max (mx, len(sn.split()))
return mx
S = '''Is life a joke? Does it not make you cry? Life is not a joke! My be or may be not at all.'''
print(solution(S))
Output:
['Is life a joke', ' Does it not make you cry', ' Life is not a joke', ' My be or may be not at all', ''] 8
Note that in the re.split() we used r (raw) which signals Python not to interpret backslashes and special meta-characters in the string (literally, ignore if there are any special character, for example, dot(.), meta character). Also, we used square bracket, '[]', to tell Python to match any characters in the bracket.
Another example for a given string: '1. First part 2. Second part 3. Third part'. How to split the string to ['First part', 'Second part', 'Third part']?
input_string = '1. First part 2. Second part 3. Third part'
strings = re.split('\d\. ', input_string)
print(strings)
Output:
['', 'First part ', 'Second part ', 'Third part']
Both method accept pattern and string and returns a match object on success or None if no match is found.
The following code prints out the 'count' for a given pattern, 'back':
import re
filename = ['backup.txt','text.back','backup2.txt', 'file.back']
pattern = r'back'
count = 0
for file in filename:
if re.match(pattern, file):
print('matched: %s' %file)
count += 1
print('count=%d' %count)
Output:
matched: backup.txt matched: backup2.txt count=2
Note that re.match() is very similar to re.search(), and the difference is that re.match() will start looking for matches at the beginning of the string.
So, we can get the same result from re.search() if we use ^ before the pattern:
import re
filename = ['backup.txt','text.back','backup2.txt', 'file.back']
pattern = r'back'
count = 0
print('pattern=%s' %pattern)
for file in filename:
if re.match(pattern, file):
print('re.match() - matched: %s' %file)
count += 1
print('count=%d' %count)
pattern = r'back'
count = 0
print('pattern=%s' %pattern)
for file in filename:
if re.search(pattern, file):
print('re.search() - matched: %s' %file)
count += 1
print('count=%d' %count)
pattern = r'^back'
count = 0
print('pattern=%s' %pattern)
for file in filename:
result = re.search(pattern, file)
if result:
print('re.search() - matched: %s' %result.group())
count += 1
print('count=%d' %count)
Output:
pattern=back re.match() - matched: backup.txt re.match() - matched: backup2.txt count=2 pattern=back re.search() - matched: backup.txt re.search() - matched: text.back re.search() - matched: backup2.txt re.search() - matched: file.back count=4 pattern=^back re.search() - matched: back re.search() - matched: back count=2
The match object has group() method which contains the matching text in the string.
'''
1. At least 1 letter between [a-z]
2. At least 1 number between [0-9]
1. At least 1 letter between [A-Z]
3. At least 1 character from [@#$%^&+=]
4. Minimum length of transaction password: 6
'''
import re
def pass_check(password):
if re.match(r"^(?=.*[\d])(?=.*[A-Z])(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[@#$])[\w\d@#$]{6,}$", password):
return password
else:
return None
password = ['ABd1234@1','abcdef', '3Fa1#', '2w3E*', '2We3345']
pass_ok = []
for p in password:
pass_ok.append(pass_check(p))
print(pass_ok)
Output:
['ABd1234@1', None, None, None, None]
Note:
- (?=...)
Matches if ... matches next, but doesn't consume any of the string. This is called a positive lookahead assertion. For example, Isaac (?=Asimov) will match 'Isaac ' only if it's followed by 'Asimov'.
Note that if we use '!' instead of '=', we call it negative lookahead. For example, Isaac (?!Asimov) will match 'Isaac ' if it's not followed by 'Asimov'.
import re result = re.match(r'Issac (?=Asimov)', 'Issac Asimov 1920-1992') if result: print(result.group(0)) else: print('no match') result = re.match(r'Issac (?!Asimov)', 'Issac Asimov 1920-1992') if result: print(result.group(0)) else: print('no match')
Output:
Issac no match
- \d
Matches any decimal digit
import re
# . (dot) : matches any character except newline
# \w : matches any word character i.e letters, alphanumeric, digits and underscore ('_')
# + : matches one or more of the preceding character (greedy match)
patterns = [r'\w@\w', r'\w+@\w+', r'[\w.-]+@[\w.]+']
for p in patterns:
match = re.search(p, 'ki.hong-777@yahoo.com')
if match:
print('pattern = %s, match.group() = %s' %(p, match.group()))
else:
print('No match')
Output:
pattern = \w@\w, match.group() = 7@y pattern = \w+@\w+, match.group() = 777@yahoo pattern = [\w.-]+@[\w.]+, match.group() = ki.hong-777@yahoo.com
Group capturing allows us to extract parts from the matching string. We can create groups using parentheses ().
Using the capturing capability, we can extract username and host name from the email address in the above example. To do this we need to add () around username and host name like this:
r'([\w.-]+)@([\w.]+)'
The code:
import re
# . (dot) : matches any character except newline
# \w : matches any word character i.e letters, alphanumeric, digits and underscore ('_')
# + : matches one or more of the preceding character (greedy match)
patterns = [r'([\w.-]+)@([\w.]+)']
for p in patterns:
match = re.search(p, 'ki.hong-777@yahoo.com')
if match:
print('pattern = %s, match.group() = %s' %(p, match.group()))
print('group(1) = %s, group(2) = %s' %(match.group(1),match.group(2)))
else:
print('No match')
We can also use group capturing with findall(). When group capturing is applied, findall() returns a list of tuples where tuples will contain the matching groups:
import re
# + : matches one or more of the preceding character (greedy match)
# \d : matches a single digit
pattern = r'(\d{3})-(\d+)-(\d\d\d\d)'
numbers = ['123-456-7890', '3210-6540-09870']
print('pattern = %s' %pattern)
for n in numbers:
match = re.findall(pattern, n)
if match:
for m in match:
print('number = %s, m = %s' %(n,m))
else:
print('No match')
Output:
pattern = (\d{3})-(\d+)-(\d\d\d\d)
number = 123-456-7890, m = ('123', '456', '7890')
number = 3210-6540-09870, m = ('210', '6540', '0987')
We used three patterns to illustrate the difference. The \d{3} picks up 3 digits preceding '-', \d+ gets any umber of digits before '-', and \d\d\d\d takes 4 digits as specified.
Write a function to find all the prime factors of a given integer. The function must return a list containing all the prime factors, sorted in ascending order.
import math
def prime_factors(n):
pf = []
while n % 2 == 0:
pf.append(2)
n = int(n/2)
for i in range(3, int(n/2), 2):
while n % i == 0:
pf.append(i)
n = n/i
return pf
numbers = [2,5,12,34,135,741,5068,40356,362925,3628855,39916866,479001678]
for n in numbers:
print('%s: %s' %(n, prime_factors(n)))
Output:
2: [2] 5: [] 12: [2, 2] 34: [2] 135: [3, 3, 3, 5] 741: [3, 13, 19] 5068: [2, 2, 7, 181] 40356: [2, 2, 3, 3, 19, 59] 362925: [3, 3, 5, 5, 1613] 3628855: [5, 557, 1303] 39916866: [2, 3, 11, 604801] 479001678: [2, 3, 79833613]
Create a function that takes a string (IPv4 address in standard dot-decimal format) and returns True if the IP is valid or False if it's not.
# "1.2.3.4" => True
# "1.2.3" => False
# "1.2.3.4.5" => False
# "123.45.67.89" => True
# "123.456.78.90" => False
# "123.045.067.089" => False
def valid(ip):
n4 = ip.split('.')
if len(n4) != 4:
return False
for n in n4:
if n[0] == '0' or int(n) > 255:
return False
return True
ips = ["1.2.3.4", "1.2.3", "1.2.3.4.5", "123.45.67.89", "123.456.78.90", "123.045.067.089"]
for ip in ips:
print('%s => %s' %(ip,valid(ip)))
Output:
1.2.3.4 => True 1.2.3 => False 1.2.3.4.5 => False 123.45.67.89 => True 123.456.78.90 => False 123.045.067.089 => False
Write a program to replace each string with an integer value in a given list of strings. The replacement integer value should be a sum of Ascii values of each character of the corresponding string.
countries =['Denmark', 'Estonia', 'Finland', 'France', 'Germany', 'Greece', 'Hungary', 'Ireland', 'Italy'] ord_sum = [] for country in countries: ord_sum.append(sum([ord(c) for c in country])) print(ord_sum)
Output:
[706, 723, 700, 591, 723, 587, 734, 703, 515]
Write a left and right rotations of a list. For example, rotation(l, 2) should convert a = [1,2,3,4,5] should print out [3,4,5,1,2], which is a left rotation. For right rotation, the 2nd parameter can be given as -2 instead of +2.
def rotation(a,n): return a[n:] + a[:n] a = [1,2,3,4,5] # left print(rotation(a,1)) print(rotation(a,2)) # right print(rotation(a,-1)) print(rotation(a,-2))
Output:
[2, 3, 4, 5, 1] [3, 4, 5, 1, 2] [5, 1, 2, 3, 4] [4, 5, 1, 2, 3]
For more complete (general) solution, please check Left rotation - list shift
The keyword here is reference!
We copy to make a duplicate data. But this copy function only makes the copy of reference that means if we change the new object then this will change the original as well.
So, we may want to use deep copy so that we can create a new object with original one and can modify the newly created object separately.
Note that the deep copy makes execution of the program slower due to making certain copies for each object that is been called.
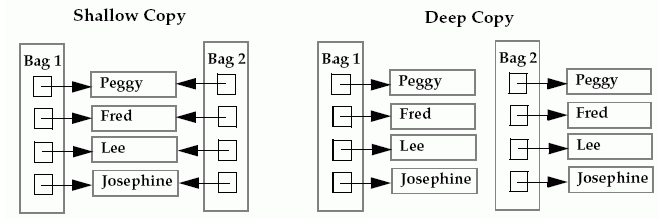
Picture credit: trying to do a shallow copy on list in python
When a child element of a list changes, the element of the copied list also changes. To make the original and copied ones remain independent, we can use copy.deepcopy().
import copy
x = [1,2,[1,2]]
y = x
print('x=%s, y=%s' %(x,y))
x[2][0] = '?'
print('x=%s, y=%s' %(x,y))
x2 = [1,2,[1,2]]
y2 = copy.copy(x2)
print('x2=%s, y2=%s' %(x2,y2))
x2[2][0] = '?'
print('x2=%s, y2=%s' %(x2,y2))
x3 = [1,2,[1,2]]
y3 = copy.deepcopy(x3)
print('x3=%s, y3=%s' %(x3,y3))
x3[2][0] = '?'
print('x3=%s, y3=%s' %(x3,y3))
Output:
x=[1, 2, [1, 2]], y=[1, 2, [1, 2]] x=[1, 2, ['?', 2]], y=[1, 2, ['?', 2]] x2=[1, 2, [1, 2]], y2=[1, 2, [1, 2]] x2=[1, 2, ['?', 2]], y2=[1, 2, ['?', 2]] x3=[1, 2, [1, 2]], y3=[1, 2, [1, 2]] x3=[1, 2, ['?', 2]], y3=[1, 2, [1, 2]]
Note that for the deepcopied y3[2][0]=1, not affected from the x3[2][0]='?'
Note also that y = x is the same as y = copy.copy(x).
Another example: shallow copy vs deep copy.
def binary(n):
b = []
while n > 0:
b.append(str(n % 2))
n = n // 2
return b[::-1]
n = 21
bb = binary(n)
print(bb)
print(''.join(bb))
Output:
['1', '0', '1', '0', '1'] 10101
Or we can just use bin():
n = 21 print(bin(n)) print(bin(n)[2:])
Output:
0b10101 10101
Binary => int:
int(0b1111) # => 15 int(0B1111) # => 15
Write a code to create a directory with name "Temporary" and create a file "myfile.txt" in the new directory "Temporary".
import os
filename = os.path.expanduser('~/Documents/TEST/Temporary/myfile.txt')
dirname = os.path.dirname(filename)
if not os.path.exists(dirname):
os.makedirs(dirname)
with open(filename,'w') as f:
f.write("test")
List all the files from a given path and verify the file "myfile.txt" file exists or not? If the file does not exist create it.
import os
path = os.path.expanduser('~/Documents/TEST/Temporary')
fname = "myfile.txt"
print(path)
for root, dirnames, filenames in os.walk(path):
files = [f for f in filenames]
if not fname in files:
with open(os.path.join(path, fname), 'w') as f:
f.write("test...")
Create a hello.py file and run this program by invoking it in another python file.
# hello.py
print("hello, python!")
def hello_1():
print('hello-1')
def hello_2():
print('hello-2')
# call_hello.py
import hello
hello.hello_1()
hello.hello_2()
We can run it "python call_hello.py", and the output:
hello, python! hello-1 hello-2
import operator
ips = ['5.4.3.2', '1.2.3.4', '5.4.1.2', '1.2.4.5']
# [['5', '4', '3', '2'], [], ...]
splitted = [(ip.split('.')) for ip in ips]
# [[['1', '2', '3', '4'], [], ...]]
sorted_splitted = sorted(splitted, key=operator.itemgetter(0,1,2,3), reverse=False)
# inserting dot('.')s
sorted_ips = ['.'.join(s) for s in sorted_splitted]
print('%s => %s' %(ips,sorted_ips))
Output:
['5.4.3.2', '1.2.3.4', '5.4.1.2', '1.2.4.5'] => ['1.2.3.4', '1.2.4.5', '5.4.1.2', '5.4.3.2']
For a given text, we want to get the frequency of the words. The most frequent one at the top.
text=""" bands which have connected them with another, and to assume among the powers of the earth, the separate and equal station to which the Laws of Nature and of Nature's God entitle them, a decent respect to the opinions of mankind requires that they should declare the causes which impel them to the separation. """
First, we need to process the text excluding some characters:
words = text.replace('-',' ').replace(',',' ').replace('.',' ').replace('\n',' ').lower().split()
print(words)
The modified input text should look like this:
['bands', 'which', 'have', 'connected', 'them', 'with', 'another', 'and', 'to', 'assume', 'among', 'the', 'powers', 'of', 'the', 'earth', 'the', 'separate', 'and', 'equal', 'station', 'to', 'which', 'the', 'laws', 'of', 'nature', 'and', 'of', "nature's", 'god', 'entitle', 'them', 'a', 'decent', 'respect', 'to', 'the', 'opinions', 'of', 'mankind', 'requires', 'that', 'they', 'should', 'declare', 'the', 'causes', 'which', 'impel', 'them', 'to', 'the', 'separation']
Here are some of the implementations:
d = {}.fromkeys(words,0)
for w in words:
d[w] += 1
s = sorted(d.items(), key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True)
print(s)
import operator
d = {}
for w in words:
d[w] = d.get(w,0)+1
s = sorted(d.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
print(s)
import collections d = collections.Counter(words) # descending #d = sorted(collections.Counter(words), reverse=True) # ascending print(d)
d = {}
for w in words:
if w not in d:
d[w] = 0
d[w] += 1
mylist = [(k, d[k]) for k in sorted(d, key=d.get, reverse=True)]
print(mylist)
The outputs should look like this:
[('the', 7), ('to', 4), ('of', 4), ('which', 3), ('them', 3), ('and', 3), ('bands', 1), ('have', 1), ('connected', 1), ('with', 1), ('another', 1), ('assume', 1), ('among', 1), ('powers', 1), ('earth', 1), ('separate', 1), ('equal', 1), ('station', 1), ('laws', 1), ('nature', 1), ("nature's", 1), ('god', 1), ('entitle', 1), ('a', 1), ('decent', 1), ('respect', 1), ('opinions', 1), ('mankind', 1), ('requires', 1), ('that', 1), ('they', 1), ('should', 1), ('declare', 1), ('causes', 1), ('impel', 1), ('separation', 1)]
With a given query string, we want to make a dictionary for the parameters. Note that the url has two identical key, "userEmail", and we want to keep both of the emails.
url = "https://bogotobogo.com/?userId=1&userName=Bob&userEmail=foo@gmail.com&userEmail=bar@yahoo.com"
from collections import defaultdict
parm_dict = defaultdict(list)
par_list = url.split('?')[1].split('&')
print(par_list)
for p in par_list:
k,v = p.split('=')
parm_dict[k].append(v)
print(parm_dict)
Output:
['userId=1', 'userName=Bob', 'userEmail=foo@gmail.com', 'userEmail=bar@yahoo.com']
defaultdict(<class 'list'>, {'userId': ['1'], 'userName': ['Bob'], 'userEmail': ['foo@gmail.com', 'bar@yahoo.com']})
Print numbers in spiral pattern (clock-wise) for a given 2D array.
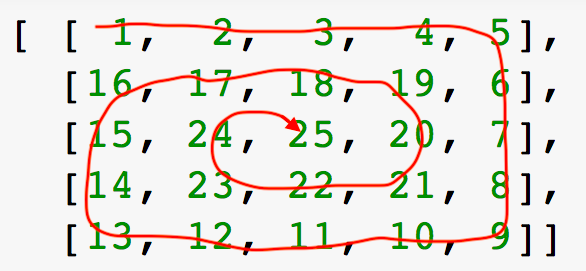
# clock-wise spiral
def spiral(re, ce, a):
rs = 0; cs = 0
# rs : starting row index
# rd : ending row index
# cs : starting column index
# ce : ending column index
while (rs < re and cs < ce):
# printing the 1st row of the remaining rows
for c in range(cs, ce):
print(a[rs][c],end=" ")
rs += 1
# printing the last column of the remaining columns
for r in range(rs, re):
print(a[r][ce-1],end=" ")
ce -= 1
# printing the last row of the remaining rows
if rs < re:
for c in range(ce-1, cs-1, -1):
print(a[re-1][c],end=" ")
re -= 1
# printing the first column of the remaining columns
if cs < ce:
for r in range(re-1, rs-1, -1):
print(a[r][c],end=" ")
cs += 1
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Case 1 : 4 x 6 grid
row = 4
column = 6
arr = [ [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
[16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 7],
[15, 24, 23, 22, 21, 8],
[14, 13, 12, 11, 10, 9]]
spiral(4, 6, arr)
print()
# Case 2 - 5 x 5 grid
row = 5
column = 5
arr = [ [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[16, 17, 18, 19, 6],
[15, 24, 25, 20, 7],
[14, 23, 22, 21, 8],
[13, 12, 11, 10, 9]]
spiral(5, 5, arr)
Output:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
Print numbers in spiral pattern (coundter-clock-wise) for a given 2D array.

# counter-clock-wise spiral
def spiral(re, ce, a):
rs = 0; cs = 0
# rs : starting row index
# rd : ending row index
# cs : starting column index
# ce : ending column index
while (rs < re and cs < ce):
# printing the 1st column of the remaining columns
for r in range(rs, re):
print(a[r][cs],end=" ")
cs += 1
# printing the last row of the remaining rows
for c in range(cs, ce):
print(a[re-1][c],end=" ")
re -= 1
# printing the last column of the remaining columns
if cs < ce:
for r in range(re-1, rs-1, -1):
print(a[r][ce-1],end=" ")
ce -= 1
# printing the first row of the remaining rows
if rs < re:
for c in range(ce-1, cs-1, -1):
print(a[r][c],end=" ")
rs += 1
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Case 1 : 4 x 6 grid
row = 4
column = 6
arr = [ [1, 15, 13, 14, 13, 12],
[2, 16, 23, 22, 21, 11],
[3, 17, 18, 19, 20, 10],
[4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]]
spiral(4, 6, arr)
print()
# Case 2 - 5 x 5 grid
row = 5
column = 5
arr = [ [1, 16, 15, 14, 13],
[2, 17, 24, 23, 12],
[3, 18, 25, 22, 11],
[4, 19, 20, 21, 10],
[5, 6, 7, 8, 9]]
spiral(5, 5, arr)
Output:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 13 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
Print out a minimum integer (should be greater than 0) not in the input list of integers. The size of the list could be up to N = 100000.
N = 100000
def my_integer(a):
a = set(a)
i = 1
while (i <= N):
if i not in a and i >= 1:
return i
i += 1
a = [1, 2, 7, 5, 4, 1, 3]
print(my_integer(a))
a = [1, 2, 3]
print(my_integer(a))
a =[2]
print(my_integer(a))
a = [x for x in range(-5,5,2)]
print(my_integer(a))
import random
a = [random.randint(-N//2, N//2) for x in range(N//2)]
print(my_integer(a))
a = [random.randint(-2, 2) for x in range(10)]
print(my_integer(a))
Output:
6 4 1 2 4 3
def binary(n):
b = []
while n > 0:
b.append(n%2)
n = n // 2
return b
def mxlength(a):
count = 0
mx = 0
for index, e in enumerate(a):
if e == 0:
count += 1
mx = max(mx, count)
else:
count = 0
return mx
for x in range(20):
b = binary(x)
print('%s : b=%s, mx=%s' %(x, b, mxlength(b)))
Output:
0 : b=[], mx=0 1 : b=[1], mx=0 2 : b=[0, 1], mx=1 3 : b=[1, 1], mx=0 4 : b=[0, 0, 1], mx=2 5 : b=[1, 0, 1], mx=1 6 : b=[0, 1, 1], mx=1 7 : b=[1, 1, 1], mx=0 8 : b=[0, 0, 0, 1], mx=3 9 : b=[1, 0, 0, 1], mx=2 10 : b=[0, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 11 : b=[1, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 12 : b=[0, 0, 1, 1], mx=2 13 : b=[1, 0, 1, 1], mx=1 14 : b=[0, 1, 1, 1], mx=1 15 : b=[1, 1, 1, 1], mx=0 16 : b=[0, 0, 0, 0, 1], mx=4 17 : b=[1, 0, 0, 0, 1], mx=3 18 : b=[0, 1, 0, 0, 1], mx=2 19 : b=[1, 1, 0, 0, 1], mx=2
The difference from the previous case is that the 0-block should be surrounded with 1s. So, the number 16 = [1,0,0,0,0] should have max = 0 not 4 because it's missing '1' at the end.
def binary(n):
b = []
while n > 0:
b.append(n%2)
n = n // 2
return b
def mxlength(b):
count = 0
mx = 0
total = 0
for index, bit in enumerate(b):
if bit == 0:
# exclude the 0-block with starting and ending with 0
if index == 0 or index == len(b)-1:
count = 0
total = 0
# for each bit, calculate the sum of the bits before and after the index
else:
count += 1
total = total + b[index-1]+b[index+1]
# legitimate 0-block's total should be 2
if total == 2:
mx = max(mx, count)
else:
count = 0
total = 0
return mx
for x in range(100):
b = binary(x)
print('%s : b=%s, mx=%s' %(x, b, mxlength(b)))
Output:
0 : b=[], mx=0 1 : b=[1], mx=0 2 : b=[0, 1], mx=0 3 : b=[1, 1], mx=0 4 : b=[0, 0, 1], mx=0 5 : b=[1, 0, 1], mx=1 6 : b=[0, 1, 1], mx=0 7 : b=[1, 1, 1], mx=0 8 : b=[0, 0, 0, 1], mx=0 9 : b=[1, 0, 0, 1], mx=2 10 : b=[0, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 11 : b=[1, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 12 : b=[0, 0, 1, 1], mx=0 13 : b=[1, 0, 1, 1], mx=1 14 : b=[0, 1, 1, 1], mx=0 15 : b=[1, 1, 1, 1], mx=0 16 : b=[0, 0, 0, 0, 1], mx=0 17 : b=[1, 0, 0, 0, 1], mx=3 18 : b=[0, 1, 0, 0, 1], mx=2 19 : b=[1, 1, 0, 0, 1], mx=2 20 : b=[0, 0, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 21 : b=[1, 0, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 22 : b=[0, 1, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 23 : b=[1, 1, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 24 : b=[0, 0, 0, 1, 1], mx=0 25 : b=[1, 0, 0, 1, 1], mx=2 26 : b=[0, 1, 0, 1, 1], mx=1 27 : b=[1, 1, 0, 1, 1], mx=1 28 : b=[0, 0, 1, 1, 1], mx=0 29 : b=[1, 0, 1, 1, 1], mx=1 30 : b=[0, 1, 1, 1, 1], mx=0 31 : b=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1], mx=0 32 : b=[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1], mx=0 33 : b=[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1], mx=4 34 : b=[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1], mx=3 35 : b=[1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1], mx=3 36 : b=[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1], mx=2 37 : b=[1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1], mx=2 38 : b=[0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1], mx=2 39 : b=[1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1], mx=2 40 : b=[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 41 : b=[1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1], mx=2 42 : b=[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 43 : b=[1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 44 : b=[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 45 : b=[1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 46 : b=[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 47 : b=[1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 48 : b=[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1], mx=0 49 : b=[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1], mx=3 50 : b=[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1], mx=2 51 : b=[1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1], mx=2 52 : b=[0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1], mx=1 53 : b=[1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1], mx=1 54 : b=[0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1], mx=1 55 : b=[1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1], mx=1 56 : b=[0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1], mx=0 57 : b=[1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1], mx=2 58 : b=[0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1], mx=1 59 : b=[1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1], mx=1 60 : b=[0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1], mx=0 61 : b=[1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1], mx=1 62 : b=[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], mx=0 63 : b=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], mx=0 64 : b=[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1], mx=0 65 : b=[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1], mx=5 66 : b=[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1], mx=4 67 : b=[1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1], mx=4 68 : b=[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1], mx=3 69 : b=[1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1], mx=3 70 : b=[0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1], mx=3 71 : b=[1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1], mx=3 72 : b=[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1], mx=2 73 : b=[1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1], mx=2 74 : b=[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1], mx=2 75 : b=[1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1], mx=2 76 : b=[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1], mx=2 77 : b=[1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1], mx=2 78 : b=[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1], mx=2 79 : b=[1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1], mx=2 80 : b=[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 81 : b=[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1], mx=3 82 : b=[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1], mx=2 83 : b=[1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1], mx=2 84 : b=[0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 85 : b=[1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 86 : b=[0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 87 : b=[1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 88 : b=[0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 89 : b=[1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1], mx=2 90 : b=[0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 91 : b=[1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 92 : b=[0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 93 : b=[1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 94 : b=[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 95 : b=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1], mx=1 96 : b=[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1], mx=0 97 : b=[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1], mx=4 98 : b=[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1], mx=3 99 : b=[1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1], mx=3
Note that the returned list from the function (binary()) should be reversed for the bits to represent the real binary value. In our case, however, it gives us the right answer.
A list consisting of N different integers is given. The array contains integers in the range [1..(N + 1)], which means that exactly one element is missing.
Let's try to find the missing element.
def missing(a):
exists = [False]*(len(A)+1)
for item in a:
exists[item-1] = True
for index, e in enumerate(exists):
if e == False:
return index+1
a = [1,2,3,5,6]
print(missing(a))
Output:
4
A non-empty list a consisting of N integers is given. The list contains an odd number of elements, and each element of the list can be paired with another element that has the same value, except for one element that is left unpaired.
For example, given a = [1,2,3,1,2], the output should be '3'.
The following solution gives us the right answer, but it's O(n^2):
def unpaired(a):
for e in a:
if a.count(e) % 2 == 1:
return e
return None
a = [1,2,3,1,2]
unpaired(a)
Another try which looks ok - (O(N logN)) and traverse(O(N)):
def unpaired(a):
d = dict.fromkeys(a,0)
print(d)
for x in a:
d[x] += 1
print(d)
odd = []
for k,v in d.items():
if v % 2 == 1:
odd.append(k)
return k
return k
a = [9,3,9,3,9,7,9]
print(unpaired(a))
Here we have a final solution: sort the list first ( O(N logN) ), and traverse( O(N) ) the elements with step 2:
def unpaired(a):
if len(a) == 1:
return a[0]
a = sorted(a)
for i in range(0,len(a),2):
if i+1 == len(a):
return a[i]
if a[i] != a[i+1]:
return a[i]
a = [1,2,3,5,6,10,1,2,6,3,5]
print(unpaired(a))
import random
N = 1000000
a = [random.randint(1,N) for x in range(N//2)]
print(unpaired(a))
Output:
10 2
- Python Coding Questions I
- Python Coding Questions II
- Python Coding Questions III
- Python Coding Questions IV
- Python Coding Questions V
- Python Coding Questions VI
- Python Coding Questions VII
- Python Coding Questions VIII
- Python Coding Questions IX
- Python Coding Questions X
List of codes Q & A
- Merging two sorted list
- Get word frequency - initializing dictionary
- Initializing dictionary with list
- map, filter, and reduce
- Write a function f() - yield
- What is __init__.py?
- Build a string with the numbers from 0 to 100, "0123456789101112..."
- Basic file processing: Printing contents of a file - "with open"
- How can we get home directory using '~' in Python?
- The usage of os.path.dirname() & os.path.basename() - os.path
- Default Libraries
- range vs xrange
- Iterators
- Generators
- Manipulating functions as first-class objects
- docstrings vs comments
- using lambdda
- classmethod vs staticmethod
- Making a list with unique element from a list with duplicate elements
- What is map?
- What is filter and reduce?
- *args and **kwargs
- mutable vs immutable
- Difference between remove, del and pop on lists
- Join with new line
- Hamming distance
- Floor operation on integers
- Fetching every other item in the list
- Python type() - function
- Dictionary Comprehension
- Sum
- Truncating division
- Python 2 vs Python 3
- len(set)
- Print a list of file in a directory
- Count occurrence of a character in a Python string
- Make a prime number list from (1,100)
- Reversing a string - Recursive
- Reversing a string - Iterative
- Reverse a number
- Output?
- Merging overlapped range
- Conditional expressions (ternary operator)
- Packing Unpacking
- Function args
- Unpacking args
- Finding the 1st revision with a bug
- Which one has higher precedence in Python? - NOT, AND , OR
- Decorator(@) - with dollar sign($)
- Multi-line coding
- Recursive binary search
- Iterative binary search
- Pass by reference
- Simple calculator
- iterator class that returns network interfaces
- Converting domain to ip
- How to count the number of instances
- Python profilers - cProfile
- Calling a base class method from a child class that overrides it
- How do we find the current module name?
- Why did changing list 'newL' also change list 'L'?
- Constructing dictionary - {key:[]}
- Colon separated sequence
- Converting binary to integer
- 9+99+999+9999+...
- Calculating balance
- Regular expression - findall
- Chickens and pigs
- Highest possible product
- Implement a queue with a limited size
- Copy an object
- Filter
- Products
- Pickle
- Overlapped Rectangles
- __dict__
- Fibonacci I - iterative, recursive, and via generator
- Fibonacci II - which method?
- Fibonacci III - find last two digits of Nth Fibonacci number
- Write a Stack class returning Max item at const time A
- Write a Stack class returning Max item at const time B
- Finding duplicate integers from a list - 1
- Finding duplicate integers from a list - 2
- Finding duplicate integers from a list - 3
- Reversing words 1
- Parenthesis, a lot of them
- Palindrome / Permutations
- Constructing new string after removing white spaces
- Removing duplicate list items
- Dictionary exercise
- printing numbers in Z-shape
- Factorial
- lambda
- lambda with map/filter/reduce
- Number of integer pairs whose difference is K
- iterator vs generator
- Recursive printing files in a given directory
- Bubble sort
- What is GIL (Global Interpreter Lock)?
- Word count using collections
- Pig Latin
- List of anagrams from a list of words
- lamda with map, filer and reduce functions
- Write a code sending an email using gmail
- histogram 1 : the frequency of characters
- histogram 2 : the frequency of ip-address
- Creating a dictionary using tuples
- Getting the index from a list
- Looping through two lists side by side
- Dictionary sort with two keys : primary / secondary keys
- Writing a file downloaded from the web
- Sorting csv data
- Reading json file
- Sorting class objects
- Parsing Brackets
- Printing full path
- str() vs repr()
- Missing integer from a sequence
- Polymorphism
- Product of every integer except the integer at that index
- What are accessors, mutators, and @property?
- N-th to last element in a linked list
- Implementing linked list
- Removing duplicate element from a list
- List comprehension
- .py vs .pyc
- Binary Tree
- Print 'c' N-times without a loop
- Quicksort
- Dictionary of list
- Creating r x c matrix
- Transpose of a matrix
- str.isalpha() & str.isdigit()
- Regular expression
- What is Hashable? Immutable?
- Convert a list to a string
- Convert a list to a dictionary
- List - append vs extend vs concatenate
- Use sorted(list) to keep the original list
- list.count()
- zip(list,list) - join elements of two lists
- zip(list,list) - weighted average with two lists
- Intersection of two lists
- Dictionary sort by value
- Counting the number of characters of a file as One-Liner
- Find Armstrong numbers from 100-999
- Find GCF (Greatest common divisor)
- Find LCM (Least common multiple)
- Draws 5 cards from a shuffled deck
- Dictionary order by value or by key
- Regular expression - re.split()
- Regular expression : re.match() vs. re.search()
- Regular expression : re.match() - password check
- Regular expression : re.search() - group capturing
- Regular expression : re.findall() - group capturin
- Prime factors : n = products of prime numbers
- Valid IPv4 address
- Sum of strings
- List rotation - left/right
- shallow/deep copy
- Converting integer to binary number
- Creating a directory and a file
- Creating a file if not exists
- Invoking a python file from another
- Sorting IP addresses
- Word Frequency
- Printing spiral pattern from a 2D array - I. Clock-wise
- Printing spiral pattern from a 2D array - II. Counter-Clock-wise
- Find a minimum integer not in the input list
- I. Find longest sequence of zeros in binary representation of an integer
- II. Find longest sequence of zeros in binary representation of an integer - should be surrounded with 1
- Find a missing element from a list of integers
- Find an unpaired element from a list of integers
- Prefix sum : Passing cars
- Prefix sum : count the number of integers divisible by k in range [A,B]
- Can make a triangle?
- Dominant element of a list
- Minimum perimeter
- MinAbsSumOfTwo
- Ceiling - Jump Frog
- Brackets - Nested parentheses
- Brackets - Nested parentheses of multiple types
- Left rotation - list shift
- MaxProfit
- Stack - Fish
- Stack - Stonewall
- Factors or Divisors
- String replace in files 1
- String replace in files 2
- Using list as the default_factory for defaultdict
- Leap year
- Capitalize
- Log Parsing
- Getting status_code for a site
- 2D-Array - Max hourglass sum
- New Year Chaos - list
- List (array) manipulation - list
- Hash Tables: Ransom Note
- Count Triplets with geometric progression
- Strings: Check if two strings are anagrams
- Strings: Making Anagrams
- Strings: Alternating Characters
- Special (substring) Palindrome
- String with the same frequency of characters
- Common Child
- Fraudulent Activity Notifications
- Maximum number of toys
- Min Max Riddle
- Poisonous Plants with Pesticides
- Common elements of 2 lists - Complexity
- Get execution time using decorator(@)
- Conver a string to lower case and split using decorator(@)
- Python assignment and memory location
- shallow copy vs deep copy for compound objects (such as a list)
- Generator with Fibonacci
- Iterator with list
- Second smallest element of a list
- *args, **kargs, and positional args
- Write a function, fn('x','y',3) that returns ['x1', 'y1', 'x2', 'y2', 'x3', 'y3']
- sublist or not
- any(), all()
- Flattening a list
- Select an element from a list
- Circularly identical lists
- Difference between two lists
- Reverse a list
- Split a list with a step
- Break a list and make chunks of size n
- Remove duplicate consecutive elements from a list
- Combination of elements from two lists
- Adding a sublist
- Replace the first occurence of a value
- Sort the values of the first list using the second list
- Transpose of a matrix (nested list)
- Binary Gap
- Powerset
- Round Robin
- Fixed-length chunks or blocks
- Accumulate
- Dropwhile
- Groupby
- Simple product
- Simple permutation
- starmap(fn, iterable)
- zip_longest(*iterables, fillvalue=None)
- What is the correct way to write a doctest?
- enumerate(iterable, start=0)
- collections.defaultdict - grouping a sequence of key-value pairs into a dictionary of lists
- What is the purpose of the 'self' keyword when defining or calling instance methods?
- collections.namedtuple(typename, field_names, *, rename=False, defaults=None, module=None)
- zipped
- What is key difference between a set and a list?
- What does a class's init() method do?
- Class methods
- Permutations and combinations of ['A','B','C']
- Sort list of dictionaries by values
- Return a list of unique words
- hashlib
- encode('utf-8')
- Reading in CSV file
- Count capital letters in a file
- is vs ==
- Create a matrix : [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
- Binary to integer and check if it's the power of 2
- urllib.request.urlopen() and requests
- Game statistics
- Chess - pawn race
- Decoding a string
- Determinant of a matrix - using numpy.linalg.det()
- Revenue from shoe sales - using collections.Counter()
- Rangoli
- Unique characters
- Valid UID
- Permutations of a string in lexicographic sorted order
- Nested list
- Consecutive digit count
- Find a number that occurs only once
- Sorting a two-dimensional array
- Reverse a string
- Generate random odd numbers in a range
- Shallow vs Deep copy
- Transpose matrix
- Are Arguments in Python Passed by Value or by Reference?
- re: Is a string alphanumeric?
- reversed()
- Caesar's cipher, or shift cipher, Caesar's code, or Caesar shift
- Every other words
- re: How can we check if an email address is valid or not?
- re: How to capture temperatures of a text
- re.split(): How to split a text.
- How can we merge two dictionaries?
- How can we combine two dictionaries?
- What is the difference between a generator and a list?
- Pairs of a given array A whose sum value is equal to a target value N
- Adding two integers without plus
- isinstance() vs type()
- What is a decorator?
- In Python slicing, what does my_list[-3:2:-2] slice do?
- Revisit sorting dict - counting chars in a text file
- re: Transforming a date format using re.sub
- How to replace the newlines in csv file with tabs?
- pandas.merge
- How to remove duplicate charaters from a string?
- Implement a class called ComplexNumber
- Find a word frequency
- Get the top 3 most frequent characters of a string
- Just seen and ever seen
- Capitalizing the full name
- Counting Consequitive Characters
- Calculate Product of a List of Integers Provided using input()
- How many times a substring appears in a string
- Hello, first_name last_name
- String validators
- Finding indices that a char occurs in a list
- itertools combinations
Python tutorial
Python Home
Introduction
Running Python Programs (os, sys, import)
Modules and IDLE (Import, Reload, exec)
Object Types - Numbers, Strings, and None
Strings - Escape Sequence, Raw String, and Slicing
Strings - Methods
Formatting Strings - expressions and method calls
Files and os.path
Traversing directories recursively
Subprocess Module
Regular Expressions with Python
Regular Expressions Cheat Sheet
Object Types - Lists
Object Types - Dictionaries and Tuples
Functions def, *args, **kargs
Functions lambda
Built-in Functions
map, filter, and reduce
Decorators
List Comprehension
Sets (union/intersection) and itertools - Jaccard coefficient and shingling to check plagiarism
Hashing (Hash tables and hashlib)
Dictionary Comprehension with zip
The yield keyword
Generator Functions and Expressions
generator.send() method
Iterators
Classes and Instances (__init__, __call__, etc.)
if__name__ == '__main__'
argparse
Exceptions
@static method vs class method
Private attributes and private methods
bits, bytes, bitstring, and constBitStream
json.dump(s) and json.load(s)
Python Object Serialization - pickle and json
Python Object Serialization - yaml and json
Priority queue and heap queue data structure
Graph data structure
Dijkstra's shortest path algorithm
Prim's spanning tree algorithm
Closure
Functional programming in Python
Remote running a local file using ssh
SQLite 3 - A. Connecting to DB, create/drop table, and insert data into a table
SQLite 3 - B. Selecting, updating and deleting data
MongoDB with PyMongo I - Installing MongoDB ...
Python HTTP Web Services - urllib, httplib2
Web scraping with Selenium for checking domain availability
REST API : Http Requests for Humans with Flask
Blog app with Tornado
Multithreading ...
Python Network Programming I - Basic Server / Client : A Basics
Python Network Programming I - Basic Server / Client : B File Transfer
Python Network Programming II - Chat Server / Client
Python Network Programming III - Echo Server using socketserver network framework
Python Network Programming IV - Asynchronous Request Handling : ThreadingMixIn and ForkingMixIn
Python Coding Questions I
Python Coding Questions II
Python Coding Questions III
Python Coding Questions IV
Python Coding Questions V
Python Coding Questions VI
Python Coding Questions VII
Python Coding Questions VIII
Python Coding Questions IX
Python Coding Questions X
Image processing with Python image library Pillow
Python and C++ with SIP
PyDev with Eclipse
Matplotlib
Redis with Python
NumPy array basics A
NumPy Matrix and Linear Algebra
Pandas with NumPy and Matplotlib
Celluar Automata
Batch gradient descent algorithm
Longest Common Substring Algorithm
Python Unit Test - TDD using unittest.TestCase class
Simple tool - Google page ranking by keywords
Google App Hello World
Google App webapp2 and WSGI
Uploading Google App Hello World
Python 2 vs Python 3
virtualenv and virtualenvwrapper
Uploading a big file to AWS S3 using boto module
Scheduled stopping and starting an AWS instance
Cloudera CDH5 - Scheduled stopping and starting services
Removing Cloud Files - Rackspace API with curl and subprocess
Checking if a process is running/hanging and stop/run a scheduled task on Windows
Apache Spark 1.3 with PySpark (Spark Python API) Shell
Apache Spark 1.2 Streaming
bottle 0.12.7 - Fast and simple WSGI-micro framework for small web-applications ...
Flask app with Apache WSGI on Ubuntu14/CentOS7 ...
Fabric - streamlining the use of SSH for application deployment
Ansible Quick Preview - Setting up web servers with Nginx, configure enviroments, and deploy an App
Neural Networks with backpropagation for XOR using one hidden layer
NLP - NLTK (Natural Language Toolkit) ...
RabbitMQ(Message broker server) and Celery(Task queue) ...
OpenCV3 and Matplotlib ...
Simple tool - Concatenating slides using FFmpeg ...
iPython - Signal Processing with NumPy
iPython and Jupyter - Install Jupyter, iPython Notebook, drawing with Matplotlib, and publishing it to Github
iPython and Jupyter Notebook with Embedded D3.js
Downloading YouTube videos using youtube-dl embedded with Python
Machine Learning : scikit-learn ...
Django 1.6/1.8 Web Framework ...
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization