Image Histogram

"An image histogram is a type of histogram that acts as a graphical representation of the tonal distribution in a digital image. It plots the number of pixels for each tonal value. By looking at the histogram for a specific image a viewer will be able to judge the entire tonal distribution at a glance." - Image histogram.
- Histogram is a graphical representation of the intensity distribution of an image.
- Histogram quantifies the number of pixels for each intensity value.
Here is a simple code for just loading the image:
import cv2
import numpy as np
gray_img = cv2.imread('images/SunsetGoldenGate.jpg', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
cv2.imshow('GoldenGate',gray_img)
while True:
k = cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xFF
if k == 27: break # ESC key to exit
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
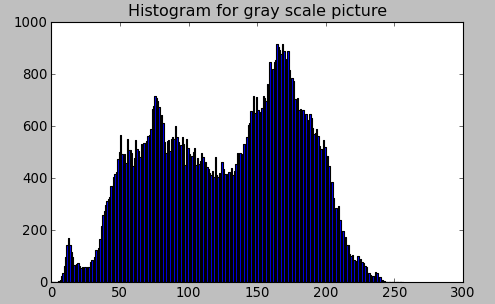
The code for histogram looks like this:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
gray_img = cv2.imread('images/GoldenGateSunset.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
cv2.imshow('GoldenGate',gray_img)
hist = cv2.calcHist([gray_img],[0],None,[256],[0,256])
plt.hist(gray_img.ravel(),256,[0,256])
plt.title('Histogram for gray scale picture')
plt.show()
while True:
k = cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xFF
if k == 27: break # ESC key to exit
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Note: This is how ravel() works, and it's equivalent of reshape(-1).
>>> x = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]) >>> print np.ravel(x) [1 2 3 4 5 6] >>> x.reshape(-1) array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
Before using that function, we need to understand some terminologies related with histograms.
- bins :The histogram above shows the number of pixels for every pixel value, from 0 to 255. In fact, we used 256 values (bins) to show the above histogram. It could be 8, 16, 32 etc. OpenCV uses histSize to refer to bins.
- dims : It is the number of parameters for which we collect the data. In our case, we collect data based on intensity value. So, in our case, it is 1.
- range : It is the range of intensity values we want to measure. Normally, it is [0,256], ie all intensity values.
OpenCV comes with an in-built cv2.calcHist() function for histogram. So, it's time to look into the specific parameters related to the cv2.calcHist() function.
cv2.calcHist(images, channels, mask, histSize, ranges[, hist[, accumulate]])
In the code, we used:
hist = cv2.calcHist([gray_img],[0],None,[256],[0,256])
The parameters are:
- images: source image of type uint8 or float32. it should be given in as a list, ie, [gray_img].
- channels: it is also given in as a list []. It the index of channel for which we calculate histogram. For example, if input is grayscale image, its value is [0]. For color image, you can pass [0],[1] or [2] to calculate histogram of blue,green or red channel, respectively.
- mask: mask image. To find histogram of full image, it is set as None. However, if we want to get histogram of specific region of image, we should create a mask image for that and give it as mask.
- histSize: this represents our BIN count. Need to be given in []. For full scale, we pass [256].
- ranges: Normally, it is [0,256].
NumPy also provides us a function for histogram, np.histogram(). So, we can use NumPy fucntion instead of OpenCV function:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
gray_img = cv2.imread('images/GoldenGateSunset.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
cv2.imshow('GoldenGate',gray_img)
#hist = cv2.calcHist([gray_img],[0],None,[256],[0,256])
hist,bins = np.histogram(gray_img,256,[0,256])
plt.hist(gray_img.ravel(),256,[0,256])
plt.title('Histogram for gray scale picture')
plt.show()
while True:
k = cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xFF
if k == 27: break # ESC key to exit
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Other parts of the code remain untouched, and it gives us the same histogram.
Let's draw RGB histogram:
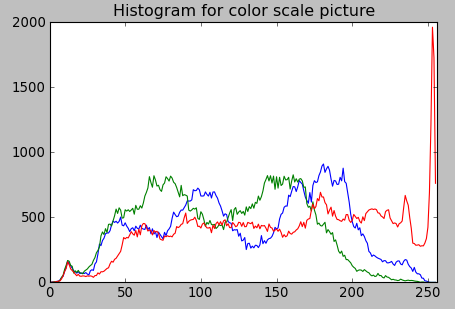
The code:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('images/GoldenGateSunset.png', -1)
cv2.imshow('GoldenGate',img)
color = ('b','g','r')
for channel,col in enumerate(color):
histr = cv2.calcHist([img],[channel],None,[256],[0,256])
plt.plot(histr,color = col)
plt.xlim([0,256])
plt.title('Histogram for color scale picture')
plt.show()
while True:
k = cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xFF
if k == 27: break # ESC key to exit
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization