Network Programming - Server & Client A : Basics

Please visit http://www.bogotobogo.com/cplusplus/sockets_server_client.php for general concept for Network programming, TCP/IP/, socket, etc.
In the following code, the server sends the current time string to the client:
# server.py
import socket
import time
# create a socket object
serversocket = socket.socket(
socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# get local machine name
host = socket.gethostname()
port = 9999
# bind to the port
serversocket.bind((host, port))
# queue up to 5 requests
serversocket.listen(5)
while True:
# establish a connection
clientsocket,addr = serversocket.accept()
print("Got a connection from %s" % str(addr))
currentTime = time.ctime(time.time()) + "\r\n"
clientsocket.send(currentTime.encode('ascii'))
clientsocket.close()
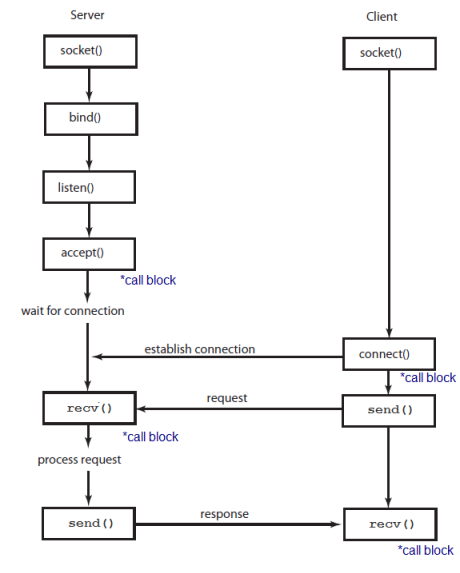
Here is the summary of the key functions from socket - Low-level networking interface:
- socket.socket(): Create a new socket using the given address family, socket type and protocol number.
- socket.bind(address): Bind the socket to address.
- socket.listen(backlog): Listen for connections made to the socket. The backlog argument specifies the maximum number of queued connections and should be at least 0; the maximum value is system-dependent (usually 5), the minimum value is forced to 0.
- socket.accept(): The return value is a pair (conn, address) where conn is a new socket object usable to send and receive data on the connection, and address is the address bound to the socket on the other end of the connection.
At accept(), a new socket is created that is distinct from the named socket. This new socket is used solely for communication with this particular client.
For TCP servers, the socket object used to receive connections is not the same socket used to perform subsequent communication with the client. In particular, the accept() system call returns a new socket object that's actually used for the connection. This allows a server to manage connections from a large number of clients simultaneously. - socket.send(bytes[, flags]): Send data to the socket. The socket must be connected to a remote socket. Returns the number of bytes sent. Applications are responsible for checking that all data has been sent; if only some of the data was transmitted, the application needs to attempt delivery of the remaining data.
- socket.colse(): Mark the socket closed. all future operations on the socket object will fail. The remote end will receive no more data (after queued data is flushed). Sockets are automatically closed when they are garbage-collected, but it is recommended to close() them explicitly.
Note that the server socket doesn't receive any data. It just produces client sockets. Each clientsocket is created in response to some other client socket doing a connect() to the host and port we're bound to. As soon as we've created that clientsocket, we go back to listening for more connections.
# client.py
import socket
# create a socket object
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# get local machine name
host = socket.gethostname()
port = 9999
# connection to hostname on the port.
s.connect((host, port))
# Receive no more than 1024 bytes
tm = s.recv(1024)
s.close()
print("The time got from the server is %s" % tm.decode('ascii'))
The output from the run should look like this:
$ python server.py &
Got a connection from ('127.0.0.1', 54597)
$ python client.py
The time got from the server is Wed Jan 29 19:14:15 2014
Note from http://docs.python.org/2/howto/sockets.html:
"If you need fast IPC between two processes on one machine, you should look into whatever form of shared memory the platform offers. A simple protocol based around shared memory and locks or semaphores is by far the fastest technique."
"If you do decide to use sockets, bind the 'server' socket to 'localhost'. On most platforms, this will take a shortcut around a couple of layers of network code and be quite a bit faster."
In Python 3, all strings are Unicode. For more info, visit Character Encoding.
So, if any kind of text string is to be sent across the network, it needs to be
encoded.This is why the server is using the encode('ascii') method on the data it
transmits. Likewise, when a client receives network data, that data is first received as raw
unencoded bytes. If you print it out or try to process it as text, we're unlikely to get
what we expected. Instead, we need to decode it first.This is why the client code is
using decode('ascii') on the result.
This is an echo server: the server that echoes back all data it receives to a client that sent it.
Server:
# echo_server.py
import socket
host = '' # Symbolic name meaning all available interfaces
port = 12345 # Arbitrary non-privileged port
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.bind((host, port))
s.listen(1)
conn, addr = s.accept()
print('Connected by', addr)
while True:
data = conn.recv(1024)
if not data: break
conn.sendall(data)
conn.close()
Client:
# echo_client.py
import socket
host = socket.gethostname()
port = 12345 # The same port as used by the server
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect((host, port))
s.sendall(b'Hello, world')
data = s.recv(1024)
s.close()
print('Received', repr(data))
Note that the server does not sendall()/recv() on the socket it is listening on but on the new socket returned by accept().
$ python echo_server.py
('Connected by', ('127.0.0.1', 57750))
$ python echo_client.py
('Received', "'Hello, world'")
Python Network Programming
Network Programming - Server & Client A : Basics
Network Programming - Server & Client B : File Transfer
Network Programming II - Chat Server & Client
Network Programming III - SocketServer
Network Programming IV - SocketServer Asynchronous request
Python tutorial
Python Home
Introduction
Running Python Programs (os, sys, import)
Modules and IDLE (Import, Reload, exec)
Object Types - Numbers, Strings, and None
Strings - Escape Sequence, Raw String, and Slicing
Strings - Methods
Formatting Strings - expressions and method calls
Files and os.path
Traversing directories recursively
Subprocess Module
Regular Expressions with Python
Regular Expressions Cheat Sheet
Object Types - Lists
Object Types - Dictionaries and Tuples
Functions def, *args, **kargs
Functions lambda
Built-in Functions
map, filter, and reduce
Decorators
List Comprehension
Sets (union/intersection) and itertools - Jaccard coefficient and shingling to check plagiarism
Hashing (Hash tables and hashlib)
Dictionary Comprehension with zip
The yield keyword
Generator Functions and Expressions
generator.send() method
Iterators
Classes and Instances (__init__, __call__, etc.)
if__name__ == '__main__'
argparse
Exceptions
@static method vs class method
Private attributes and private methods
bits, bytes, bitstring, and constBitStream
json.dump(s) and json.load(s)
Python Object Serialization - pickle and json
Python Object Serialization - yaml and json
Priority queue and heap queue data structure
Graph data structure
Dijkstra's shortest path algorithm
Prim's spanning tree algorithm
Closure
Functional programming in Python
Remote running a local file using ssh
SQLite 3 - A. Connecting to DB, create/drop table, and insert data into a table
SQLite 3 - B. Selecting, updating and deleting data
MongoDB with PyMongo I - Installing MongoDB ...
Python HTTP Web Services - urllib, httplib2
Web scraping with Selenium for checking domain availability
REST API : Http Requests for Humans with Flask
Blog app with Tornado
Multithreading ...
Python Network Programming I - Basic Server / Client : A Basics
Python Network Programming I - Basic Server / Client : B File Transfer
Python Network Programming II - Chat Server / Client
Python Network Programming III - Echo Server using socketserver network framework
Python Network Programming IV - Asynchronous Request Handling : ThreadingMixIn and ForkingMixIn
Python Coding Questions I
Python Coding Questions II
Python Coding Questions III
Python Coding Questions IV
Python Coding Questions V
Python Coding Questions VI
Python Coding Questions VII
Python Coding Questions VIII
Python Coding Questions IX
Python Coding Questions X
Image processing with Python image library Pillow
Python and C++ with SIP
PyDev with Eclipse
Matplotlib
Redis with Python
NumPy array basics A
NumPy Matrix and Linear Algebra
Pandas with NumPy and Matplotlib
Celluar Automata
Batch gradient descent algorithm
Longest Common Substring Algorithm
Python Unit Test - TDD using unittest.TestCase class
Simple tool - Google page ranking by keywords
Google App Hello World
Google App webapp2 and WSGI
Uploading Google App Hello World
Python 2 vs Python 3
virtualenv and virtualenvwrapper
Uploading a big file to AWS S3 using boto module
Scheduled stopping and starting an AWS instance
Cloudera CDH5 - Scheduled stopping and starting services
Removing Cloud Files - Rackspace API with curl and subprocess
Checking if a process is running/hanging and stop/run a scheduled task on Windows
Apache Spark 1.3 with PySpark (Spark Python API) Shell
Apache Spark 1.2 Streaming
bottle 0.12.7 - Fast and simple WSGI-micro framework for small web-applications ...
Flask app with Apache WSGI on Ubuntu14/CentOS7 ...
Fabric - streamlining the use of SSH for application deployment
Ansible Quick Preview - Setting up web servers with Nginx, configure enviroments, and deploy an App
Neural Networks with backpropagation for XOR using one hidden layer
NLP - NLTK (Natural Language Toolkit) ...
RabbitMQ(Message broker server) and Celery(Task queue) ...
OpenCV3 and Matplotlib ...
Simple tool - Concatenating slides using FFmpeg ...
iPython - Signal Processing with NumPy
iPython and Jupyter - Install Jupyter, iPython Notebook, drawing with Matplotlib, and publishing it to Github
iPython and Jupyter Notebook with Embedded D3.js
Downloading YouTube videos using youtube-dl embedded with Python
Machine Learning : scikit-learn ...
Django 1.6/1.8 Web Framework ...
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization