GoLang Tutorial - Go Application Authentication II (JWT Authentication)
Continued from Go Application Authentication I (BasicAuth, Bearer-Token-Based Authentication).
A JSON Web Token (JWT) is a compact and self-contained way for securely transmitting information between two parties as a JSON object. This information can be verified and trusted because it is digitally signed. JWTs can be used to authenticate users, share information between applications, and more.
While both JWT-based authentication and bearer token authentication serve the purpose of authenticating users, they differ in how the tokens are generated and how the server verifies these tokens. JWTs provide a standardized format for the token, including a signed payload with user claims, enabling stateless authentication and easier information extraction on the server side. Bearer tokens, on the other hand, are simpler and often used in session-based authentication.
There are three parts in a JWT:
- Header: The header contains information about the token, such as the signing algorithm and token type.
{ "alg": "HS256", "typ": "JWT" } - Payload: The payload contains the claims of the token, such as the user's ID, name, and email address.
{ "sub": "1234567890", "name": "John Doe", "iat": 1516239022 }Claims are statements about the user or resource that the token is for. They are typically key-value pairs, such as:
iss: The issuer of the token,
sub: The subject of the token,
aud: The audience of the token,
exp: The expiration time of the token,
iat: The issued-at time of the token,
jti: The unique identifier of the token
- Signature: The signature is used to verify the authenticity of the token.
It is created by signing the header and payload using a secret key.
HMACSHA256( base64UrlEncode(header) + "." + base64UrlEncode(payload), secret )
The following Go code demonstrates a simple web server using the Gin web framework, implementing a basic form of authentication using JSON Web Tokens (JWT).
main.go:
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/golang-jwt/jwt/v4"
"net/http"
"strings"
"time"
)
var jwtKey = []byte("my_secret_key")
var tokens []string
type Claims struct {
Username string `json:"username"`
jwt.RegisteredClaims
}
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.POST("/login", gin.BasicAuth(gin.Accounts{
"admin": "secret",
}), func(c *gin.Context) {
token, _ := generateJWT()
tokens = append(tokens, token)
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"token": token,
})
})
r.GET("/resource", func(c *gin.Context) {
bearerToken := c.Request.Header.Get("Authorization")
reqToken := strings.Split(bearerToken, " ")[1]
claims := &Claims{}
tkn, err := jwt.ParseWithClaims(reqToken, claims, func(token *jwt.Token) (interface{}, error) {
return jwtKey, nil
})
if err != nil {
if err == jwt.ErrSignatureInvalid {
c.JSON(http.StatusUnauthorized, gin.H{
"message": "unauthorized",
})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{
"message": "bad request",
})
return
}
if !tkn.Valid {
c.JSON(http.StatusUnauthorized, gin.H{
"message": "unauthorized",
})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"data": "resource data",
})
})
r.Run() // Listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080
}
func generateJWT() (string, error) {
expirationTime := time.Now().Add(5 * time.Minute)
claims := &Claims{
Username: "username",
RegisteredClaims: jwt.RegisteredClaims{
ExpiresAt: jwt.NewNumericDate(expirationTime),
},
}
token := jwt.NewWithClaims(jwt.SigningMethodHS256, claims)
return token.SignedString(jwtKey)
}
- package main: This line indicates that this Go file belongs to the main package. In Go, the main package is special, and it is the entry point for the executable programs.
- import:
import ( "github.com/gin-gonic/gin" "github.com/golang-jwt/jwt/v4" "net/http" "strings" "time" )Here, the code imports the following packages:- gin: A web framework for Go.
- jwt: A library for working with JSON Web Tokens (JWT).
- net/http: Standard Go HTTP package.
- strings: Package for string manipulation.
- time: Package for handling time-related operations.
- Global variables:
var jwtKey = []byte("my_secret_key") var tokens []stringThe code defines a global variable jwtKey to store the secret key used for signing and verifying JWTs. This key should be kept confidential and not exposed to unauthorized users. The tokens slice is to store generated JWTs. - Claims struct:
type Claims struct { Username string `json:"username"` jwt.RegisteredClaims }The code defines a structure Claims (payload) to represent the claims contained in a JWT. This structure includes a Username field and a set of standard claims provided by the jwt package. - main function:
func main() { r := gin.Default() // ... r.Run() // Listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080 }Initializes a Gin router (r).
The // ... section defines the endpoints and handlers.
r.Run(): Starts the server and listens on 0.0.0.0:8080 - /login endpoint:
r.POST("/login", gin.BasicAuth(gin.Accounts{ "admin": "secret", }), func(c *gin.Context) { // ... })The /login endpoint handles basic authentication requests. It validates the provided credentials and, if valid, generates a JWT for the user. The generated JWT is added to a global list of active tokens and returned to the client in the response body. - protected /resource endpoint:
r.GET("/resource", func(c *gin.Context) { // ... })The /resource endpoint protects a resource that can only be accessed by users who have a valid JWT. Checks the Authorization header for a valid JWT, validates it, and responds with resource data if successful. - Handling JWT in /resource endpoint:
bearerToken := c.Request.Header.Get("Authorization") reqToken := strings.Split(bearerToken, " ")[1] claims := &Claims{} tkn, err := jwt.ParseWithClaims(reqToken, claims, func(token *jwt.Token) (interface{}, error) { return jwtKey, nil }) if err != nil { // ... } // ...It extracts the JWT from the Authorization header of the request.
Parses and validates the JWT using the secret key (jwtKey), and checks if it has expired.
If the JWT is valid, responds with "resource data"; otherwise, returns an unauthorized or bad request message. - generateJWT function:
func generateJWT() (string, error) { // ... }Generates a new JWT with a predefined expiration time (5 minutes in this example). Uses the secret key (jwtKey) for signing the token.
$ go mod init example.com
go: creating new go.mod: module example.com
go: to add module requirements and sums:
go mod tidy
$ go mod tidy
go: finding module for package github.com/golang-jwt/jwt/v4
go: finding module for package github.com/gin-gonic/gin
go: downloading github.com/golang-jwt/jwt v3.2.2+incompatible
go: downloading github.com/golang-jwt/jwt/v4 v4.5.0
go: found github.com/gin-gonic/gin in github.com/gin-gonic/gin v1.9.1
go: found github.com/golang-jwt/jwt/v4 in github.com/golang-jwt/jwt/v4 v4.5.0
$ go run main.go
[GIN-debug] [WARNING] Creating an Engine instance with the Logger and Recovery middleware already attached.
[GIN-debug] [WARNING] Running in "debug" mode. Switch to "release" mode in production.
- using env: export GIN_MODE=release
- using code: gin.SetMode(gin.ReleaseMode)
[GIN-debug] POST /login --> main.main.func1 (4 handlers)
[GIN-debug] GET /resource --> main.main.func2 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] [WARNING] You trusted all proxies, this is NOT safe. We recommend you to set a value.
Please check https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/gin-gonic/gin#readme-don-t-trust-all-proxies for details.
[GIN-debug] Environment variable PORT is undefined. Using port :8080 by default
[GIN-debug] Listening and serving HTTP on :8080
...
We can test the endpoint using the Thunder HTTP Client:
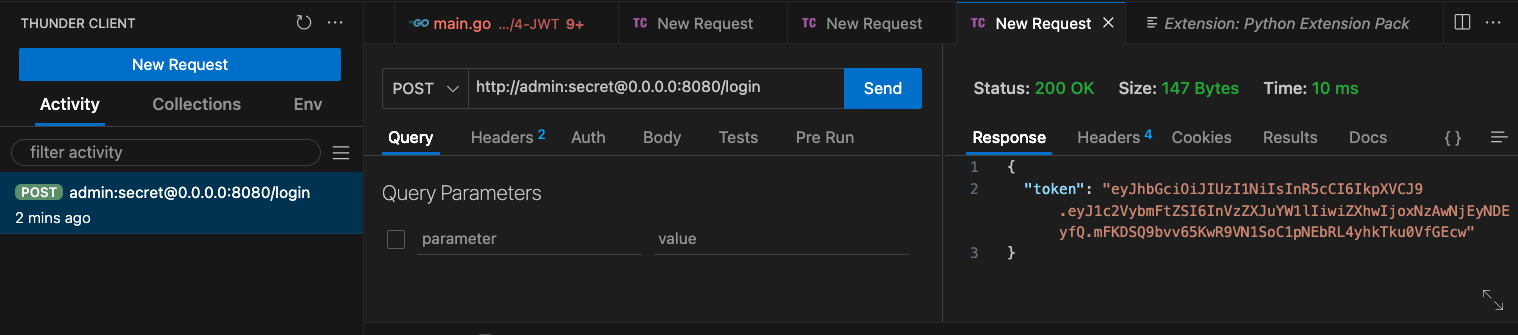
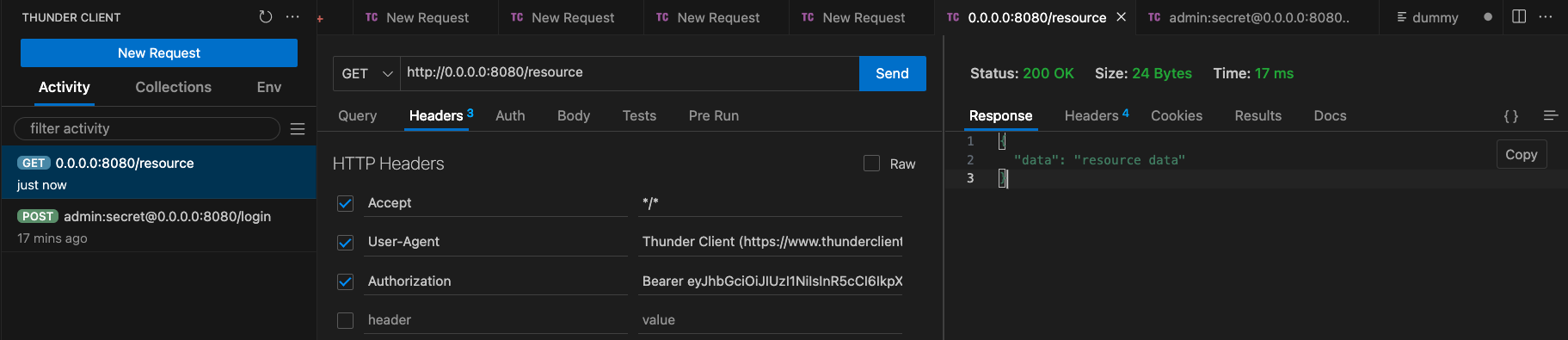
As mentioned previously, JWT-based authentication shares similarities with bearer token authentication. However, the generation and verification processes for the token differ. In our implementation, we rely on the golang-jwt package to handle both the generation and verification of JWT tokens
Source: https://github.com/Einsteinish/go_tutorial/tree/main/authentication
Go Tutorial
- GoLang Tutorial - HelloWorld
- Calling code in an external package & go.mod / go.sum files
- Workspaces
- Workspaces II
- Visual Studio Code
- Data Types and Variables
- byte and rune
- Packages
- Functions
- Arrays and Slices
- A function taking and returning a slice
- Conditionals
- Loops
- Maps
- Range
- Pointers
- Closures and Anonymous Functions
- Structs and receiver methods
- Value or Pointer Receivers
- Interfaces
- Web Application Part 0 (Introduction)
- Web Application Part 1 (Basic)
- Web Application Part 2 (Using net/http)
- Web Application Part 3 (Adding "edit" capability)
- Web Application Part 4 (Handling non-existent pages and saving pages)
- Web Application Part 5 (Error handling and template caching)
- Web Application Part 6 (Validating the title with a regular expression)
- Web Application Part 7 (Function Literals and Closures)
- Building Docker image and deploying Go application to a Kubernetes cluster (minikube)
- Serverless Framework (Serverless Application Model-SAM)
- Serverless Web API with AWS Lambda
- Arrays vs Slices with an array left rotation sample
- Variadic Functions
- Goroutines
- Channels ("<-")
- Channels ("<-") with Select
- Channels ("<-") with worker pools
- Defer
- GoLang Panic and Recover
- String Formatting
- JSON
- SQLite
- Modules 0: Using External Go Modules from GitHub
- Modules 1 (Creating a new module)
- Modules 2 (Adding Dependencies)
- AWS SDK for Go (S3 listing)
- Linked List
- Binary Search Tree (BST) Part 1 (Tree/Node structs with insert and print functions)
- Go Application Authentication I (BasicAuth, Bearer-Token-Based Authentication)
- Go Application Authentication II (JWT Authentication)
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization