GoLang Tutorial - Calling code in an external package & go.mod / go.sum files
Go to https://go.dev/doc/tutorial/getting-started, and the check Call code in an external package section.
example/quote/quote.go:
package main
import "fmt"
import "rsc.io/quote"
func main() {
fmt.Println(quote.Go())
}
$ go mod init example/quote
go: creating new go.mod: module example/quote
go: to add module requirements and sums:
go mod tidy
The command go mod init example/quote is used in Go to initialize a new Go module.
A Go module is a collection of Go packages that are versioned together as a single unit.
This helps manage dependencies and version information for our project.
Breaking down the command go mod init example/quote:
go mod init: This part of the command is telling Go to initialize a new module.example/quote: This is the argument passed to go mod init, and it specifies the module path. The module path is a unique identifier for the module. In this case, it's set to example/quote. The module path is often derived from the repository URL where the code is hosted, but it doesn't have to be. It's a way of naming and identifying our module.
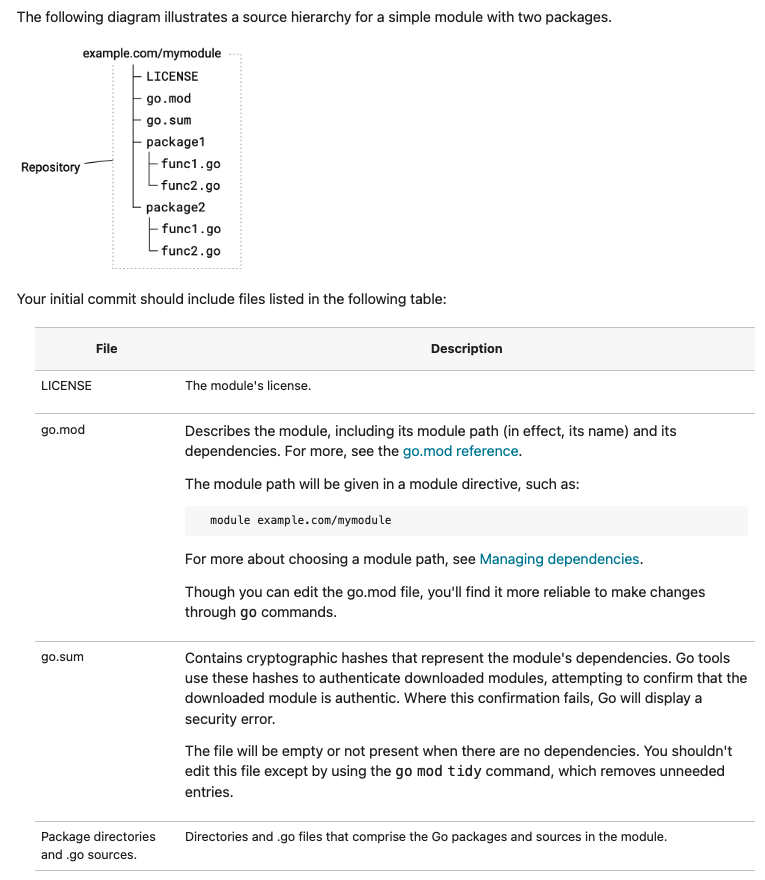
When we run this command in a directory containing Go code, it creates a go.mod file in that directory. The go.mod file contains information about the module, including its path and any dependencies it may have.
For example, after runninggo mod init example/quote, we might get a go.mod file that looks something like this:
module example/quote go 1.21.4
The go 1.21.4 indicates the Go version for which the module is intended.
The go.mod file will also be updated as we add dependencies to our project using the go get command.
$ go mod tidy go: finding module for package rsc.io/quote go: found rsc.io/quote in rsc.io/quote v1.5.2
The go mod tidy command in Go is used to remove any dependencies from our module's go.mod file that are no longer required.
It helps in cleaning up our module's dependency list by removing any entries that are not directly needed by our code.
Here's a brief explanation:
- Dependency Removal:
When we develop a Go project, we might add, update, or remove dependencies. Over time, our go.mod file may accumulate references to dependencies that are no longer used by our code. - Unused Dependencies:
Thego mod tidycommand scans our codebase, identifies the dependencies that are actively being used, and removes any entries in the go.mod file that are no longer necessary. - Modifying go.mod:
After runninggo mod tidy, our go.mod file will be updated to reflect the dependencies actually needed by our project. This is useful for keeping our project's dependency list concise and ensuring that we only include what is necessary.
After running this go mod tidy, our go.mod file will be updated
to only include the dependencies required by our project's code.
$ cat go.mod
module example/quote
go 1.21.4
require rsc.io/quote v1.5.2
require (
golang.org/x/text v0.0.0-20170915032832-14c0d48ead0c // indirect
rsc.io/sampler v1.3.0 // indirect
)
go.sum:
golang.org/x/text v0.0.0-20170915032832-14c0d48ead0c h1:qgOY6WgZOaTkIIMiVjBQcw93ERBE4m30iBm00nkL0i8= golang.org/x/text v0.0.0-20170915032832-14c0d48ead0c/go.mod h1:NqM8EUOU14njkJ3fqMW+pc6Ldnwhi/IjpwHt7yyuwOQ= rsc.io/quote v1.5.2 h1:w5fcysjrx7yqtD/aO+QwRjYZOKnaM9Uh2b40tElTs3Y= rsc.io/quote v1.5.2/go.mod h1:LzX7hefJvL54yjefDEDHNONDjII0t9xZLPXsUe+TKr0= rsc.io/sampler v1.3.0 h1:7uVkIFmeBqHfdjD+gZwtXXI+RODJ2Wc4O7MPEh/QiW4= rsc.io/sampler v1.3.0/go.mod h1:T1hPZKmBbMNahiBKFy5HrXp6adAjACjK9JXDnKaTXpA=
The go.sum file in our Go project is used to provide additional security by recording the expected cryptographic checksums of the content of specific module versions. It acts as a kind of lock file for our dependencies.
- Module Identifier (rsc.io/quote v1.5.2):
This line represents a specific module (in this case, rsc.io/quote) and the version (v1.5.2) our project is using. - Hash (h1:w5fcysjrx7yqtD/aO+QwRjYZOKnaM9Uh2b40tElTs3Y=):
This is the cryptographic hash of the module's content. It ensures that the code we're using hasn't been tampered with. The hash is specific to the content of the module at that version. - go.mod file hash (h1:LzX7hefJvL54yjefDEDHNONDjII0t9xZLPXsUe+TKr0=):
Similar to the module hash, this is the cryptographic hash of the go.mod file for that module version. It helps ensure that the go.mod file hasn't been altered.
When someone else works on the project, the Go tooling checks the go.sum file to verify that the expected cryptographic checksums match the actual checksums of the downloaded modules. If they don't match, it signals a potential security issue or a modification in the module, preventing the use of potentially compromised or altered code.
In summary, the go.sum file helps ensure the integrity and security of our project's dependencies by recording and verifying cryptographic checksums.
Go Tutorial
- GoLang Tutorial - HelloWorld
- Calling code in an external package & go.mod / go.sum files
- Workspaces
- Workspaces II
- Visual Studio Code
- Data Types and Variables
- byte and rune
- Packages
- Functions
- Arrays and Slices
- A function taking and returning a slice
- Conditionals
- Loops
- Maps
- Range
- Pointers
- Closures and Anonymous Functions
- Structs and receiver methods
- Value or Pointer Receivers
- Interfaces
- Web Application Part 0 (Introduction)
- Web Application Part 1 (Basic)
- Web Application Part 2 (Using net/http)
- Web Application Part 3 (Adding "edit" capability)
- Web Application Part 4 (Handling non-existent pages and saving pages)
- Web Application Part 5 (Error handling and template caching)
- Web Application Part 6 (Validating the title with a regular expression)
- Web Application Part 7 (Function Literals and Closures)
- Building Docker image and deploying Go application to a Kubernetes cluster (minikube)
- Serverless Framework (Serverless Application Model-SAM)
- Serverless Web API with AWS Lambda
- Arrays vs Slices with an array left rotation sample
- Variadic Functions
- Goroutines
- Channels ("<-")
- Channels ("<-") with Select
- Channels ("<-") with worker pools
- Defer
- GoLang Panic and Recover
- String Formatting
- JSON
- SQLite
- Modules 0: Using External Go Modules from GitHub
- Modules 1 (Creating a new module)
- Modules 2 (Adding Dependencies)
- AWS SDK for Go (S3 listing)
- Linked List
- Binary Search Tree (BST) Part 1 (Tree/Node structs with insert and print functions)
- Go Application Authentication I (BasicAuth, Bearer-Token-Based Authentication)
- Go Application Authentication II (JWT Authentication)
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization