19. Django 1.8 Server Build - CentOS 7 hosted on VPS - User Authentication 6 (Google login)

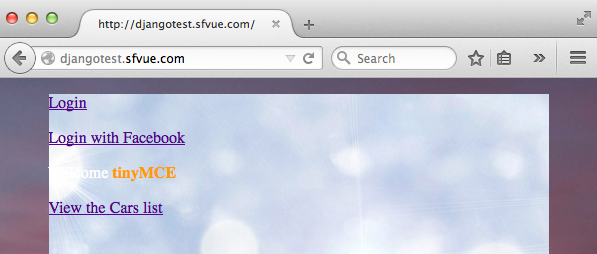
In this tutorial, to the page shown above, we'll make a user to be able to login via Google.
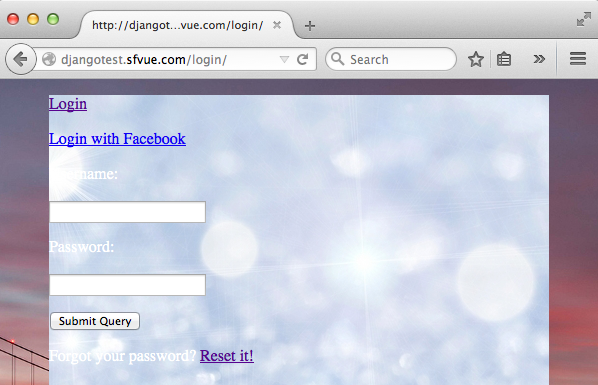
Currently, we only have the following login page we've made:
We need to install python-social-auth:
$ sudo pip install python-social-auth ... Successfully installed python-social-auth oauthlib requests requests-oauthlib PyJWT six
It will be installed in /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/.
We need to update settings.py to include/register the library in our project.
Add the application to INSTALLED_APPS setting, for default Django ORM:
INSTALLED_APPS = (
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'car',
'tinymce',
'pages',
'driver',
'django.contrib.admin',
'social.apps.django_app.default',
)
There's a context processor that will add backends and associations data to template context. Add desired authentication backends to Django's AUTHENTICATION_BACKENDS setting:
TEMPLATE_CONTEXT_PROCESSORS = (
...
'social.apps.django_app.context_processors.backends',
'social.apps.django_app.context_processors.login_redirect',
)
backends context processor will load a backends key in the context with three entries on it:
- associated It's a list of UserSocialAuth instances related with the currently logged in user. Will be empty if there's no current user.
- not_associated A list of available backend names not associated with the current user yet. If there's no user logged in, it will be a list of all available backends.
- backends A list of all available backend names.
Add desired authentication backends to Django's AUTHENTICATION_BACKENDS setting:
AUTHENTICATION_BACKENDS = (
'social.backends.facebook.FacebookOAuth2',
'social.backends.google.GoogleOAuth2',
'social.backends.twitter.TwitterOAuth',
'django.contrib.auth.backends.ModelBackend',
)
Take into account that backends must be defined in AUTHENTICATION_BACKENDS or Django won't pick them when trying to authenticate the user.
We shouldn't miss django.contrib.auth.backends.ModelBackend if we use django.contrib.auth application or users won't be able to login by username / password method.
Since we registered the library in our project, let's update the database:
$ python manage.py makemigrations
Migrations for 'driver':
0002_auto_20150712_1815.py:
- Alter field user on driver
$ python manage.py migrate
Operations to perform:
Synchronize unmigrated apps: staticfiles, car, tinymce, messages, pages
Apply all migrations: sessions, admin, driver, auth, default, contenttypes
Synchronizing apps without migrations:
Creating tables...
Running deferred SQL...
Installing custom SQL...
Running migrations:
Rendering model states... DONE
Applying default.0001_initial... OK
Applying default.0002_add_related_name... OK
Applying default.0003_alter_email_max_length... OK
Applying driver.0002_auto_20150712_1815... OK
Update the Project's urlpatterns in urls.py to include the main auth URLs:
from django.conf.urls import include, url
from django.contrib import admin
from django.conf import settings
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^admin/', include(admin.site.urls)),
url(r'^tinymce/', include('tinymce.urls')),
url(r'^$', 'pages.views.MainHomePage'),
url(r'^cars/$', 'car.views.CarsAll'),
url(r'^cars/(?P<carslug>.*)/$', 'car.views.SpecificCar'),
url(r'^makes/(?P<makeslug>.*)/$', 'car.views.SpecificMake'),
url(r'^media/(?P<path>.*)$', 'django.views.static.serve', {
'document_root': settings.MEDIA_ROOT,
}),
url(r'^register/$', 'driver.views.DriverRegistration'),
url(r'^login/$', 'driver.views.LoginRequest'),
url(r'^logout/$', 'driver.views.LogoutRequest'),
url(r'^resetpassword/passwordsent/$', 'django.contrib.auth.views.password_reset_done'),
url(r'^resetpassword/$', 'django.contrib.auth.views.password_reset',
{'post_reset_redirect' : 'django.contrib.auth.views.password_reset_done'},
name="password_reset"),
url(r'^reset/(?P<uidb64>[0-9A-Za-z]+)/(?P<token>.+)/$', 'django.contrib.auth.views.password_reset_confirm', name='password_reset_confirm'),
url(r'^reset/done/$', 'django.contrib.auth.views.password_reset_complete', name='password_reset_complete'),
url(r'^profile/$', 'driver.views.Profile'),
url('', include('social.apps.django_app.urls', namespace='social')),
]
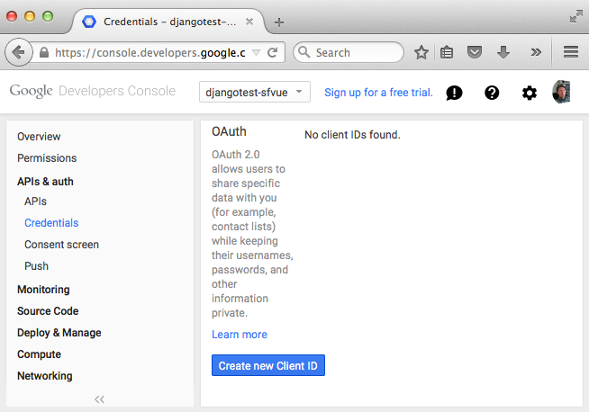
- Go to https://console.developers.google.com/project and click the Create button.
- Under APIs and auth > Credentials, Create new Client ID.
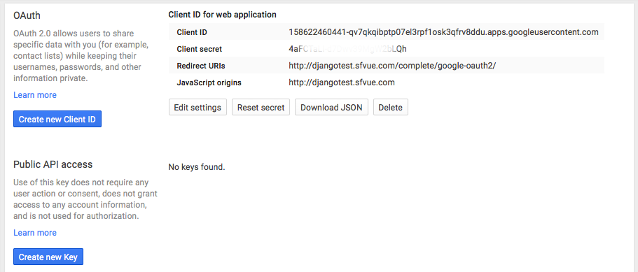
- Copy the App ID and App Secret, and place them into Django's settings.py file:
SOCIAL_AUTH_GOOGLE_OAUTH2_KEY = SOCIAL_AUTH_GOOGLE_OAUTH2_SECRET =
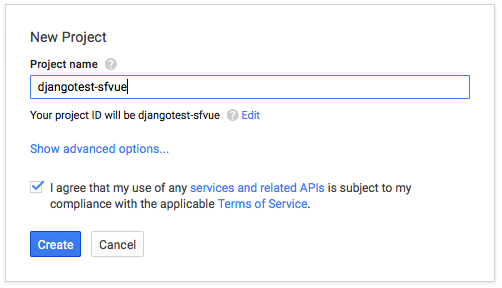
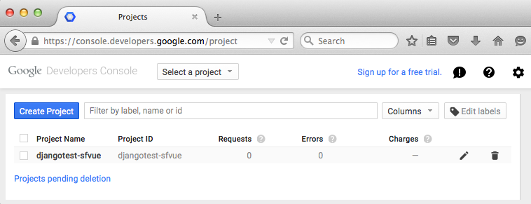
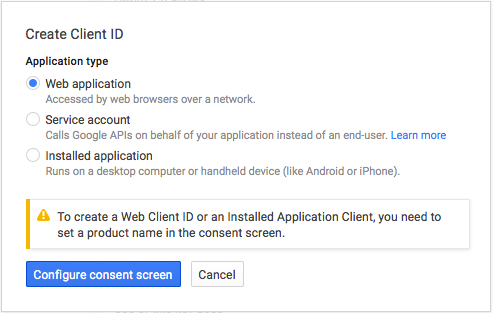
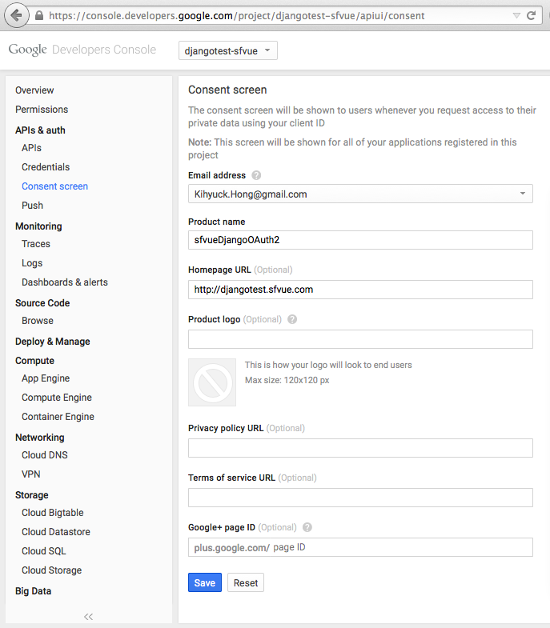
Our case is "Web application":
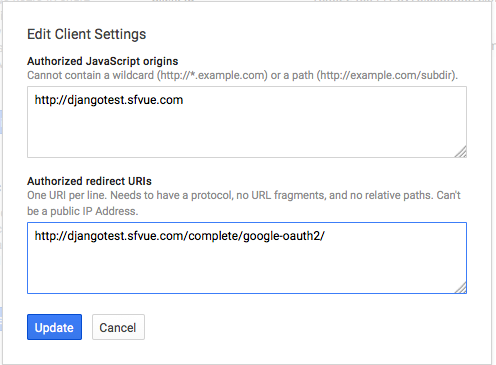
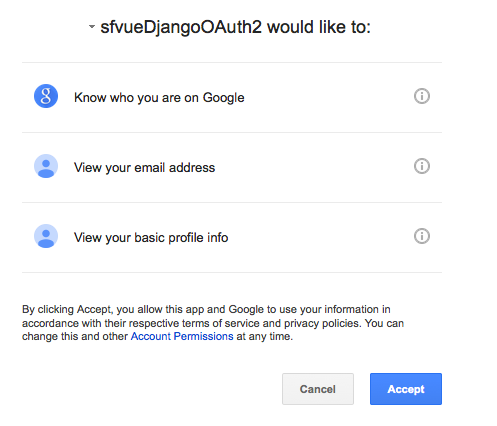
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="/static/css/car.css" />
{% block extrahead %}{% endblock %}
</head>
<body>
<div id="pageContainer">
<div id="nav_top_right">
{% if user.is_authenticated %}
<p><a href="/logout/">Logout</a></p>
{% else %}
<p><a href="/login/">Login</a></p>
<p><a href="{% url 'social:begin' 'facebook' %}?next={{ request.path }}">Login with Facebook</a></p>
<p><a href="{% url 'social:begin' 'google-oauth2' %}?next={{ request.path }}">Login with Google</a></p>
{% endif %}
</div>
{% block content %}
{% endblock %}
</div>
</body>
</html>
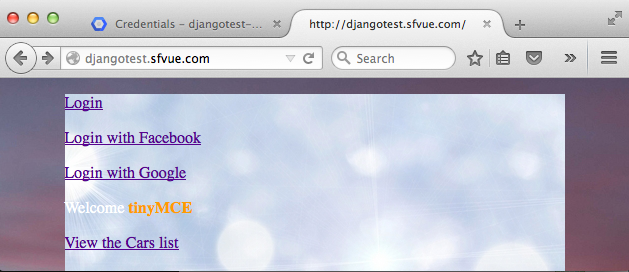
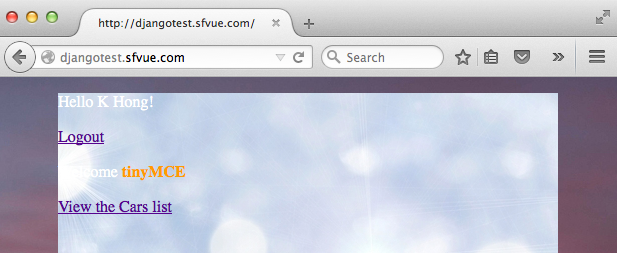
Now we are logged in with Google OAuth2:
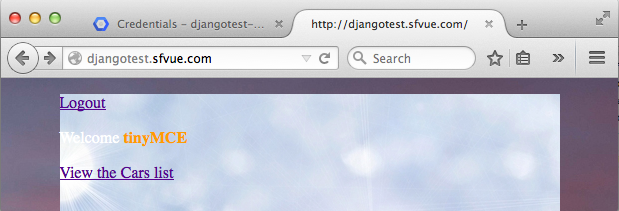
Let's add greetings after a user logged in.
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="/static/css/car.css" />
{% block extrahead %}{% endblock %}
</head>
<body>
<div id="pageContainer">
<div id="nav_top_right">
{% if user.is_authenticated %}
<p>Hello {{ user.get_full_name|default:user.username }}!</p>
<p><a href="/logout/">Logout</a></p>
{% else %}
<p><a href="/login/">Login</a></p>
<p><a href="{% url 'social:begin' 'facebook' %}?next={{ request.path }}">Login with Facebook</a></p>
<p><a href="{% url 'social:begin' 'google-oauth2' %}?next={{ request.path }}">Login with Google</a></p>
{% endif %}
</div>
{% block content %}
{% endblock %}
</div>
</body>
</html>
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization