17. Blog app : class based template

The template we used in previous chapter is not object oriented. In other words, it is based on procedural approach. So, in this chapter, we're going to introduce class based views.
A view is a callable taking a request and returning a response. This can be more than just a function, and Django provides an example of some classes which can be used as views (Class Based Views). These allow us to structure our views and reuse code by harnessing inheritance and mixins. There are also some generic views for simple tasks, but we may want to design our own structure of reusable views which suits our use case.
Django provides base view classes which will suit a wide range of applications. All views inherit from the View class, which handles linking the view in to the URLs, HTTP method dispatching and other simple features. RedirectView is for a simple HTTP redirect, and TemplateView extends the base class to make it also render a template.
I'll show the final result first:
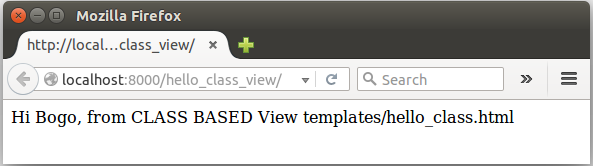
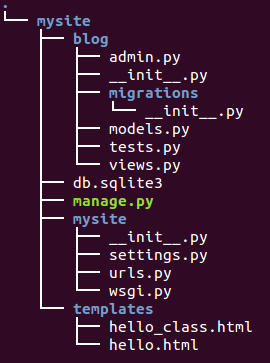
Basically the same as the previous hello.html except the string that indicates class based:
<html>
<body>
Hi {{name}}, from CLASS BASED templates/hello_class.html
</body>
</html>
mysite/settings.py:
...
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
...
TEMPLATE_LOADERS = ['django.template.loaders.filesystem.Loader',
'django.template.loaders.app_directories.Loader']
TEMPLATES = [
{
'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'templates')],
'APP_DIRS': True,
'OPTIONS': {
'context_processors': [
'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth',
'django.template.context_processors.debug',
'django.template.context_processors.i18n',
'django.template.context_processors.media',
'django.template.context_processors.static',
'django.template.context_processors.tz',
'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages',
],
},
},
]
We newly define a class called HelloTemplate(TemplateView):
from django.http import HttpResponse
from django.template.loader import get_template
from django.template import Context
from django.shortcuts import render_to_response
from django.views.generic.base import TemplateView
# Create your views here.
def hello(request):
name = "Bogo"
html = "<html><body>Hi %s from views.py. </body></html>" %name
return HttpResponse(html)
def hello_template(request):
name = "Bogo"
tp = get_template("hello.html")
html = tp.render(Context({'name': name}))
return HttpResponse(html)
def hello_template_simple(request):
name = 'Bogo'
return render_to_response('hello.html', {'name': name})
class HelloTemplate(TemplateView):
template_name = "hello_class.html"
def get_context_data(self, **kwargs):
context = super(HelloTemplate, self).get_context_data(**kwargs)
context['name'] = 'Bogo'
return context
Note that we have defined hello_template_simple(). This is not a class based approach, but included here to show it is simpler than the funtction hello_template(). It has fewer lines of code while it requires another import "from django.shortcuts import render_to_response".
The class
django.views.generic.base.TemplateView renders a given template, with the context containing parameters captured in the URL.
from django.conf.urls import patterns, include, url
from blog.views import HelloTemplate
#from django.contrib import admin
#admin.autodiscover()
urlpatterns = patterns('',
# Examples:
# url(r'^$', 'DjangoTestProject.views.home', name='home'),
# url(r'^blog/', include('blog.urls')),
#url(r'^admin/', include(admin.site.urls)),
url(r'^hello/$', 'blog.views.hello'),
url(r'^hello_template/$', 'blog.views.hello_template'),
url(r'^hello_template_simple/$', 'blog.views.hello_template_simple'),
url(r'^hello_class_view/$', HelloTemplate.as_view()),
Let's run server:
$ python manage.py runserver
We get the following results:
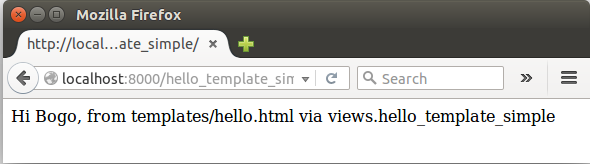

The simplest way to use generic views is to create them directly in your URLconf. If we're only changing a few simple attributes on a class-based view, we can simply pass them into the as_view() method call itself.
mysite/urls.py:
from django.conf.urls import patterns, include, url
from blog.views import HelloTemplate
from django.contrib import admin
admin.autodiscover()
from django.views.generic import TemplateView
urlpatterns = patterns('',
# Examples:
# url(r'^$', 'DjangoTestProject.views.home', name='home'),
# url(r'^blog/', include('blog.urls')),
url(r'^admin/', include(admin.site.urls)),
url(r'^hello/$', 'blog.views.hello'),
url(r'^hello_template/$', 'blog.views.hello_template'),
url(r'^hello_template_simple/$', 'blog.views.hello_template_simple'),
url(r'^hello_class_view/$', HelloTemplate.as_view()),
url(r'^about/', TemplateView.as_view(template_name="about.html")),
)
Any arguments passed to as_view() will override attributes set on the class. In our example, we set template_name on the TemplateView. A similar overriding pattern can be used for the url attribute on RedirectView.
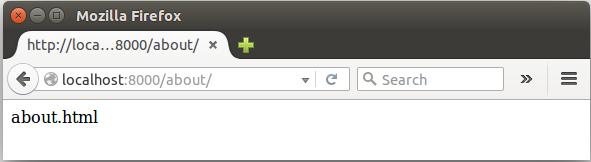
The second, more powerful way to use generic views is to inherit from an existing view and override attributes (such as the template_name) or methods (such as get_context_data) in our subclass to provide new values or methods. Consider, for example, a view that just displays one template, about.html. Django has a generic view to do this - TemplateView - so we can just subclass it, and override the template name.
blog/views:
from django.http import HttpResponse
from django.template.loader import get_template
from django.template import Context
from django.shortcuts import render_to_response
from django.views.generic.base import TemplateView
# Create your views here.
def hello(request):
name = "Bogo"
html = "Hi %s from views.py. " %name
return HttpResponse(html)
def hello_template(request):
name = "Bogo"
tp = get_template("hello.html")
html = tp.render(Context({'name': name}))
return HttpResponse(html)
def hello_template_simple(request):
name = 'Bogo'
return render_to_response('hello_simple.html', {'name': name})
class HelloTemplate(TemplateView):
template_name = "hello_class.html"
def get_context_data(self, **kwargs):
context = super(HelloTemplate, self).get_context_data(**kwargs)
context['name'] = 'Bogo'
return context
class AboutView(TemplateView):
template_name = "about.html"
Now we just need to add this new view into our URLconf. TemplateView is a class, not a function, so we point the URL to the as_view() class method instead, which provides a function-like entry to class-based views.
mysite/urls.py:
from django.conf.urls import patterns, include, url
from blog.views import HelloTemplate
from django.contrib import admin
admin.autodiscover()
from django.views.generic import TemplateView
from blog.views import AboutView
urlpatterns = patterns('',
# Examples:
# url(r'^$', 'DjangoTestProject.views.home', name='home'),
# url(r'^blog/', include('blog.urls')),
url(r'^admin/', include(admin.site.urls)),
url(r'^hello/$', 'blog.views.hello'),
url(r'^hello_template/$', 'blog.views.hello_template'),
url(r'^hello_template_simple/$', 'blog.views.hello_template_simple'),
url(r'^hello_class_view/$', HelloTemplate.as_view()),
#url(r'^about/', TemplateView.as_view(template_name="about.html")),
url(r'^about/', AboutView.as_view()),
)
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization