4. Hello World - Templates

Please allow me to digress here.
I've tried "Hello World" numerous times whenever I started learning something new. It's always good to have a feeling of "mission accomplished." But sometimes that was it, and I stopped there.
I'll show you here what can we do with Django if you stay firm.
The following pictures are from my forum site using Django (http://www.bogotobogo.com/dj/forums/).
As we can see from the pictures above, we'll be able to setup discussion pages with user registration. It may take couple of days or at most a week or two. If you have your domain, you can have forums/blogs under your full control.
Regarding the web services platform, I like Ruby On Rails mainly because it's MVC is crystal clear. Also, I've tried LaRavel 4 which is php based, it's good as well, and I think it has a potential to beat other php frameworks such as Symphony. With Ruby, I was able to deploy it using Heroku but not with my shared host service. LaRavel, I have yet to deploy it.
Anyway, I like Python, and I'm kind of biased toward to Django!
So far, we created a project and made an app (HelloWorldApp). By modifying the url.py and views.py, we were able to get a very humble page on a local machine where the development version of server was running.
Let's create something more dynamic which produces "Hello world! from Bogo" by modifying the HelloWorldApp/views.py:
from django.http import HttpResponse
def foo(request):
name = "Bogo"
html = "<html><body>Hello World! from %s</body></html>" % name
return HttpResponse(html)
The third line of code within the view constructs an HTML response using Python's "format-string" capability. The %s within the string is a placeholder, and the percent sign after the string means "Replace the %s in the preceding string with the value of the variable now."
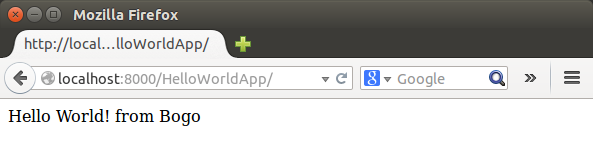
As we can guess from the code above, any change to the design of the page (html) requires a change to the Python code and it's not a good idea to hard-code HTML directly in our views. It will be much cleaner and more maintainable to separate the design of the page from the Python code itself. We can do this with Django's template system, which we discuss in next section.
A template is simply a text file. It can generate any text-based format (HTML, XML, CSV, etc.).
A Django template is intended to separate the presentation of a document from its data. A template defines placeholders and various bits of basic logic (template tags) that regulate how the document should be displayed. Usually, templates are used for producing HTML.
Here is a sample from djangobook:
<html>
<head><title>Ordering notice</title></head>
<body>
<h1>Ordering notice</h1>
<p>Dear {{ person_name }},</p>
<p>Thanks for placing an order from {{ company }}. It's scheduled to
ship on {{ ship_date|date:"F j, Y" }}.</p>
<p>Here are the items you've ordered:</p>
<ul>
{% for item in item_list %}
<li>{{ item }}</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
{% if ordered_warranty %}
<p>Your warranty information will be included in the packaging.</p>
{% else %}
<p>You didn't order a warranty, so you're on your own when
the products inevitably stop working.</p>
{% endif %}
<p>Sincerely,<br />{{ company }}</p>
</body>
</html>
- Any text surrounded by a pair of braces, {{ person_name }}, is a variable. This means "insert the value of the variable with the given name."
- Any text that's surrounded by curly braces and percent signs, {% if ordered_warranty %}, is a template tag. The definition of a tag is quite broad: a tag just tells the template system to "do something." This example template contains a for tag ({% for item in item_list %}) and an if tag ({% if ordered_warranty %}).
- A for tag works very much like a for statement in Python, letting us loop over each item in a sequence. An if tag acts as a logical "if" statement. In this particular case, the tag checks whether the value of the ordered_warranty variable evaluates to True. If it does, the template system will display everything between the {% if ordered_warranty %} and {% else %}. If not, the template system will display everything between {% else %} and {% endif %}. Note that the {% else %} is optional.
- The second paragraph of this template contains an example of a filter, which is the most convenient way to alter the formatting of a variable. In this example, {{ ship_date|date:"F j, Y" }}, we're passing the ship_date variable to the date filter, giving the date filter the argument "F j, Y". The date filter formats dates in a given format, as specified by that argument. Filters are attached using a pipe character (|), as a reference to Unix pipes.
So far, we created a project and made an app (HelloWorldApp). By modifying the url.py and views.py, we were able to get a very humble page on a local machine where the development version of server was running.
As we already know, the html page has several invariants such as header or footer etc. So, we may want to have a template with our site design in it.
Let's go to the app directory (HelloWorldApp) and make templates directory:
$ cd HelloWorldApp $ mkdir -p templates/helloDJ $ touch templates/helloDJ/base.html
Let's make the base.html as below:
<html>
<head>
<title>This is Hello World app!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to Django at bogotobogo.com</h1>
{% block content %}
{% endblock %}
</body>
</html>
Everything is a normal html except for the {% block %} part. Djangle template language provides us dynamic contents and something will happen in the block portion. Actually, Django equips us for tags, filters, and output.
Django first looks into settings for TEMPLATE_DIRS, and into app folders. This can be customized by setting TEMPLATE_LOADERS which default to :
('django.template.loaders.filesystem.Loader',
'django.template.loaders.app_directories.Loader')
We may also want to create another template called home.html:
{% extends "helloDJ/base.html" %}
{% block content %}
{{ Testing }}
{{ HelloHello }}
{% endblock %}
This is an inheritance of the template. The extends block tag means home.html will be shown inside base.html. The two braces "{{" and "}}" are basically a print statement.
Our base.html will stay with little change throughout several html pages. But the extension will take any specifics of a certain page within the frame of the base.html. In other words, any block in home.html will show up in the same named block in base.html.
The {{ HelloHello }} will output the variable HelloHello passed by the views. So, we need to go back and fix our views.py:
from django.shortcuts import render_to_response
def foo(request,):
return render_to_response("helloDJ/home.html",
{"Testing" : "Django Template Inheritance ",
"HelloHello" : "Hello World - Django"})
Here, the HelloHello is a variable and it's a key for dictionary feed for the template. Django will take over and properly render a page for us:
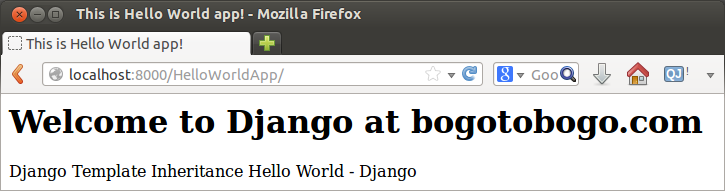
Let's run the server:
python manage.py runserver
Now, we can run our first web application using template and template inheritance:
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization