Algorithms - Bellman Ford Shortest Path Algorithm - 2020
bogotobogo.com site search:
Bellman Ford Shortest Path Algorithm
Like Dijkstra's Shortest Path, this Bellman-Ford is based on the relaxation technique, in which an approximation to the correct distance is gradually replaced by more accurate values until eventually reaching the optimum solution.
/*
procedure BellmanFord(list vertices, list edges, vertex source)
// This implementation takes a vetext source
// and fills distance array with shortest-path information
// Step 1: initialize graph
for each vertex v in vertices:
if v is source
distance[v] := 0
else
distance[v] := infinity
// Step 2: relax edges repeatedly
for i from 1 to size(vertices)-1:
for each edge (u, v) with weight w in edges:
if distance[u] + w < distance[v]:
distance[v] := distance[u] + w
// Step 3: check for negative-weight cycles
for each edge (u, v) with weight w in edges:
if distance[u] + w < distance[v]:
error "Graph contains a negative-weight cycle"
*/
#include <iostream>
typedef struct {
int u, v, w;
} Edge;
const int NODES = 5 ; /* the number of nodes */
int EDGES; /* the number of edges */
Edge edges[32]; /* large enough for n <= 2^NODES=32 */
int d[32]; /* d[i] is the minimum distance from source node s to node i */
#define INFINITY INT_MAX
void BellmanFord(int src)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < NODES; ++i) d[i] = INFINITY;
d[src] = 0;
for (i = 0; i < NODES - 1; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < EDGES; ++j) {
if (d[edges[j].u] + edges[j].w < d[edges[j].v]) {
d[edges[j].v] = d[edges[j].u] + edges[j].w;
}
}
}
for (i = 0; i < NODES - 1; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < EDGES; ++j) {
if (d[edges[j].u] + edges[j].w < d[edges[j].v]) {
printf("Graph contains a negative-weight cycle\n");
exit(1);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int i, j, w;
int k = 0;
FILE *fin = fopen("path/BellmanFord.txt", "r");
for (i = 0; i < NODES; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < NODES; ++j) {
fscanf(fin, "%d", &w;);
if (w != 0) {
edges[k].u = i;
edges[k].v = j;
edges[k].w = w;
k++;
}
}
}
fclose(fin);
EDGES = k;
for (i = 0; i < NODES; ++i) printf("Node %d\t", i );
printf("\n--------------------------------------\n");
int source_vertex = 0;
BellmanFord(source_vertex);
for (i = 0; i < NODES; ++i) printf("%d\t", d[i] );
return 0;
}
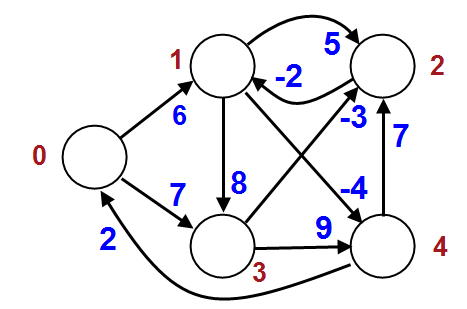
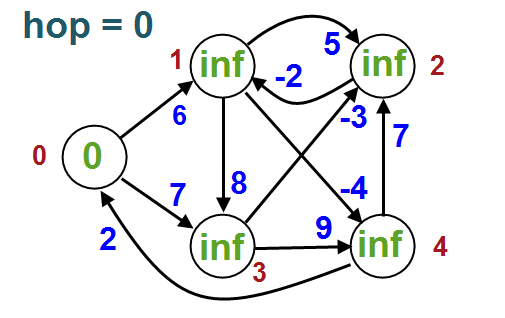
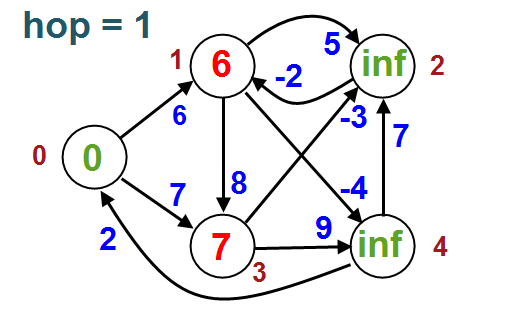
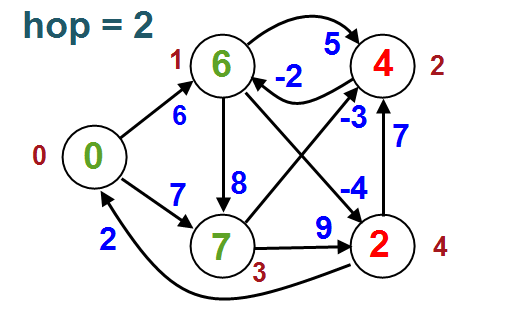
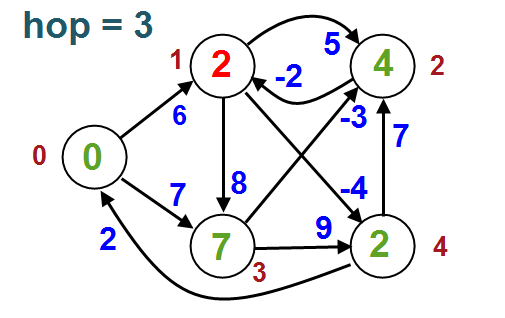
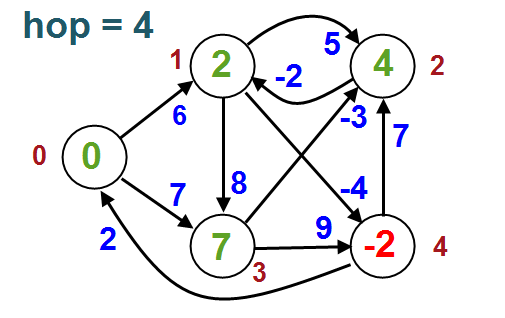
Input file:
0 6 0 7 0 0 0 5 8 -4 0 -2 0 0 0 0 0 -3 0 9 2 0 7 0 0
Output:
Node 0 Node 1 Node 2 Node 3 Node 4 -------------------------------------- 0 2 4 7 -2
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization