Algorithms - Closest Pair of Points
bogotobogo.com site search:
bogotobogo.com site search:
Closest Pair of Points
Getting the minimum distance among the given set of points usually requires O(n^2). But by using divide/conquer algorithm with some tricks, we can achieve O(n log n) complexity.
We split the points, and get the minimum distances from left and right side of the split. If we are lucky, we can get the closest pair from one of the two sides. However, if we are unlucky, the closest pair of points are from both sides. In other words, one from left, and one from right side. In this case, we compare the points which are within the strip of width 2d.
We can get more on this algorithm from wiki.
.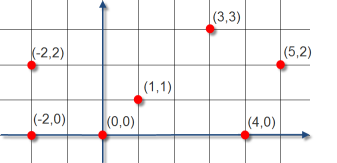
Input points
// The closest pair
#include <iostream>
#include <climits>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
struct Point {double x, y;};
// sort by x
inline int compareX(const void* a, const void* b)
{
Point *p1 = (Point *)a, *p2 = (Point *)b;
return (p1->x - p2->x);
}
// sort by y
inline int compareY(const void* a, const void* b)
{
Point *p1 = (Point *)a, *p2 = (Point *)b;
return (p1->y - p2->y);
}
// find the distance between two points
inline double dist(Point p1, Point p2)
{
return sqrt( (p1.x - p2.x)*(p1.x - p2.x) +
(p1.y - p2.y)*(p1.y - p2.y) );
}
double bruteForce(Point P[], int n, Point &p1;, Point &p2;)
{
double min = DBL_MAX;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
for (int j = i+1; j < n; ++j)
if (dist(P[i], P[j]) < min) {
min = dist(P[i], P[j]);
p1.x = P[i].x, p1.y = P[i].y;
p2.x = P[j].x, p2.y = P[j].y;
}
return min;
}
// returns minimum of two values
inline double min(double x, double y)
{
return (x < y)? x : y;
}
// find the distance beween the closest points of
// strip of given size. All points in strip[] are sorted by y.
double stripPoints(Point strip[], int size, double d, Point &p1;, Point &p2;)
{
double min = d; // Initialize the minimum distance as d
qsort(strip, size, sizeof(Point), compareY);
// Pick all points one by one and try the next points
// till the difference between y's is smaller than d.
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
for (int j = i+1; j < size && (strip[j].y - strip[i].y) < min; ++j)
if (dist(strip[i],strip[j]) < min) {
min = dist(strip[i], strip[j]);
p1.x = strip[i].x, p1.y = strip[i].y;
p2.x = strip[j].x, p2.y = strip[j].y;
}
return min;
}
// find the smallest distance recursively.
// All point in array P are sorted by x
double closest(Point P[], Point strip[], int n, Point &p1;, Point &p2;)
{
static Point ptemp1, ptemp2, ptemp3, ptemp4;
// use brute force when there are not enough points
if (n <= 3)
return bruteForce(P, n, ptemp1, ptemp2);
// mid point
int mid = n/2;
Point midPoint = P[mid];
// calculate the smallest distance
// dl: left of mid point
// dr: right side of the mid point
double dl = closest(P, strip, mid, ptemp1, ptemp2);
double dr = closest(P + mid, strip, n-mid, ptemp3, ptemp4);
// assign the pair that has smaller distance
if(dl < dr) {
p1.x = ptemp1.x; p1.y = ptemp1.y;
p2.x = ptemp2.x; p2.y = ptemp2.y;
}
else {
p1.x = ptemp3.x; p1.y = ptemp3.y;
p2.x = ptemp4.x; p2.y = ptemp4.y;
}
double dmin = min(dl, dr);
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (abs(P[i].x - midPoint.x) < dmin)
strip[j++] = P[i];
double dmin_strip = stripPoints(strip, j, dmin, ptemp1, ptemp2);
double final_min = dmin;
if(dmin_strip < dmin) {
p1.x = ptemp1.x; p1.y = ptemp1.y;
p2.x = ptemp2.x; p2.y = ptemp2.y;
final_min = dmin_strip;
}
return final_min;
}
int main()
{
// data points
Point P[] = {{0,0}, {-2,0}, {4,0}, {1,1},
{3,3}, {-2,2}, {5,2}};
// closest pair
Point p1 = {DBL_MAX, DBL_MAX}, p2 = {DBL_MAX, DBL_MAX};
int n = sizeof(P) / sizeof(P[0]);
qsort(P, n, sizeof(Point), compareX);
// array to store points in a strip
Point *strip = new Point[n];
// get the distance and pair of points
cout << "The closest distance is " << closest(P, strip, n, p1, p2) << endl;
cout << "between (" << p1.x << "," << p1.y << ") and ("
<< p2.x << "," << p2.y << ")" << endl;
delete[] strip;
return 0;
}
Output is:
The closest distance is 1.41421 between (0,0) and (1,1)
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization