AngularJS Framework : Routing I

AngularJS routes enable us to create different URLs for different content in our application. A route is specified in the URL after the # sign. Thus, all the following URLs point to the same AngularJS application, but each points to a different route:
http://bogotobogo.com/index.html#View1 http://bogotobogo.com/index.html#View2 http://bogotobogo.com/index.html#View3 http://bogotobogo.com/index.html#View4
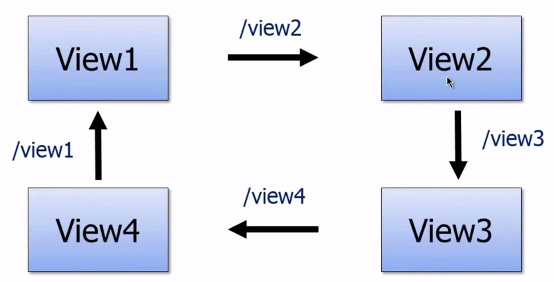
Picture from AngularJS Fundamentals In 60-ish Minutes
When the browser loads the links above, the same AngularJS application will be loaded (located at http://bogotobogo.com/index.html). However, AngularJS will look at the route (the part of the URL after the #) and decide what HTML template to show.
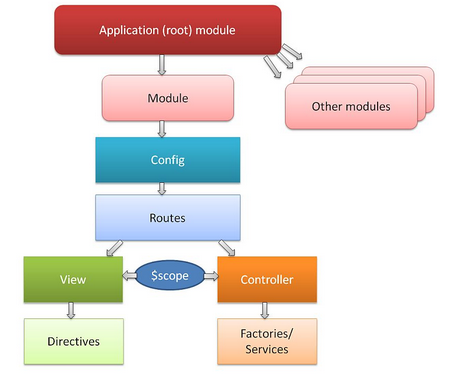
Picture from How to structure large angularJS applications
The following sections are largely based on Introduction to Angular.js in 50 Examples.
We'll start with the following simple code (angular_route0.html) that just listing the countries after reading in data from a json file (countries.json):
<html ng-app="countryApp">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Angular.js Example</title>
<script src="//ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.3.15/angular.min.js"></script>
<script>
var countryApp = angular.module('countryApp', []);
countryApp.controller('CountryController', function ($scope, $http){
$http.get('http://www.bogotobogo.com/AngularJS/files/Route/countries.json').success(function(data) {
$scope.countries = data;
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body ng-controller="CountryController">
<ul>
<li ng-repeat="country in countries">{{country.name}}</li>
<ul>
</body>
</html>
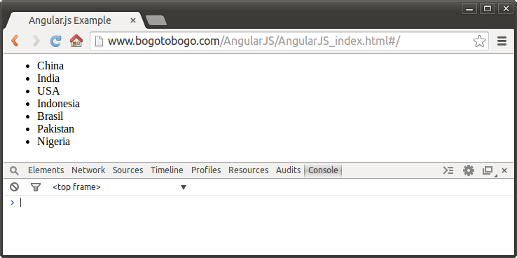
It is rendered like this:
Note that we used the injected $http to get the data from a remote resource (see Dependency Injection).
We started from the simple code in the previous section and modified to get the route to work (angular_route.html):
<html ng-app="countryApp">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Angular.js Example</title>
<script src="//ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.3.15/angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="//ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.3.15/angular-route.min.js"></script>
<script>
var countryApp = angular.module('countryApp', ['ngRoute']);
countryApp.config(function($routeProvider) {
$routeProvider.
when('/', {
template: '<ul><li ng-repeat="country in countries">{{country.name}}</li><ul>',
controller: 'CountryListController'
}).
when('/:countryName', {
template: '<h1>TODO create country detail view</h1>',
controller: 'CountryDetailController'
}).
otherwise({
redirectTo: '/'
});
});
countryApp.controller('CountryListController', function ($scope, $http){
$http.get('http://www.bogotobogo.com/AngularJS/files/Route/countries.json').success(function(data) {
$scope.countries = data;
});
});
countryApp.controller('CountryDetailController', function ($scope, $routeParams){
console.log($routeParams);
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div ng-view></div>
</body>
</html>
We see the dependency injection at work here. The ngRoute module provides routing and deeplinking services and directives for angular apps:
var countryApp = angular.module('countryApp', ['ngRoute']);
So, we need to add additional script tag, angular-route.js:
<script src="//ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.3.15/angular-route.min.js"></script>
The ngRoute module was added as a dependency to countryApp, and it provides the $routeProvider API:
countryApp.config(function($routeProvider) {
$routeProvider.
The config() call sets up the route using inline strings as templates:
template: '<ul><li ng-repeat="country in countries">{{country.name}}</li><ul>',
Also, we added a placeholder CountryDetailController:
countryApp.controller('CountryDetailController', function ($scope, $routeParams){
console.log($routeParams);
});
We added a div with the ng-view directive to the body, and this this where the route provider injects content rendered from the template associated with the current route:
<body> <div ng-view></div> </body>
The $routeParams in
countryApp.controller('CountryDetailController', function ($scope, $routeParams){
allow Angular to evaluate whatever in :countryName as a variable:
when('/:countryName', {
template: '<h1>TODO create country detail view</h1>',
controller: 'CountryDetailController'
}).
The following pictures show the pages when the URL is root (note that the root url ends with "#/"):
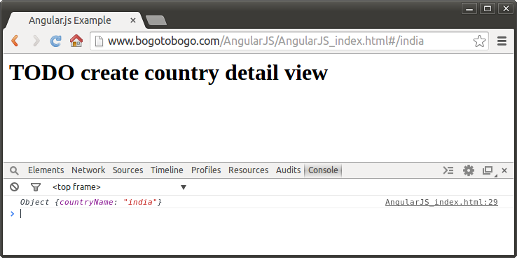
When we type a country name in the URL after the '#":
Continued at Routes II - separate url template files.
AngularJS
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization