Linking containers and volume for datastore
How to create one container that can access a service on another?
In this article, we'll show how Docker does it. We'll launch WordPress site using Docker. In this article, we'll create 3 different Docker images:
- One image for WordPress itself.
- It's going to be linked to MySQL container.
- Then, it will be storing data. We call it "Data Container". Unlike the WordPress and MySQL containers, Data container can be run only once, and does not have to be running. It's enough to just define the volume and share the volume with MySQL. Then, the WordPress will be linked to the volume so that it can have an access to MySQL database's port, locally instead of remotely.

Image source : Riding The Next Wave: Docker Containers
Let's look inside /var/lib/docker folder in Ubuntu:
$ sudo ls /var/lib/docker aufs execdriver init repositories-aufs trust volumes containers graph linkgraph.db tmp vfs
When Docker starts an image and create a container that has a volume defined, it will store those in a UUID named directory inside two directories (volumes and vsf). Now the two directories are empty since we haven't defined any volume:
$ sudo ls /var/lib/docker/volumes $ sudo ls /var/lib/docker/vfs/dir
We're going to create a volume using tiny linux distro called busybox.
Docker system should maintain the consistency of the data store we're creating now in /var/lib/mysql directory.
For reference, here are the docker run args we're going to use to create a volume:
-
-v
Bind mount a volume (e.g., from the host: -v /host:/container, from Docker: -v /container) -
--name
Assign a name to the container - -d
Detached mode: run the container in the background and print the new container ID.
Then, run docker. The following command just runs a container and exits as we can see from the output of docker ps -a:.
$ docker run -v /var/lib/mysql --name=my_datastore -d busybox echo "My Datastore" $ docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 6a7e05a1e120 busybox "echo 'My Datastore' 3 minutes ago Exited (0) 3 minutes ago my_datastore
However, by running once, it has created a volume and this is the key: data container does not have to be running. If we inspect my_datastore:
$ docker inspect my_datastore
[
{
...
"Volumes": {
"/var/lib/mysql": "/var/lib/docker/volumes/7ec328ed9c22b7190c9998d13d3dc49d8d8249e336fd84667c5bf7fc724b70bc/_data"
},
"VolumesRW": {
"/var/lib/mysql": true
},
...
}
}
]
$
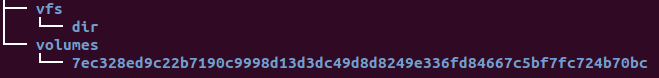
So, from now on, whenever anything write to will be stored in this area of local host system!
Now, we need to start MySQL container (OFFICIAL REPOSITORY mysql).
$ docker run --name my_mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=my-secret-pw --volumes-from my_datastore -d mysql ... Status: Downloaded newer image for mysql:latest 9173d3457bc8ec440fbf5df30d30db8102ede04d4e344c9593a1421057f99786
Note that we added my_mysql for the container name, passed environment variable MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD, and most importantly, added our datastore for --volumes-from, and running it in detached mode.
$ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 9173d3457bc8 mysql "/entrypoint.sh mysq 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes 3306/tcp my_mysql
Now, we have MySQL up and running.
If we inspect my_mysql container, we can see it's using the volume we specified:
$ docker inspect my_mysql
...
"Volumes": {
"/var/lib/mysql": "/var/lib/docker/volumes/7ec328ed9c22b7190c9998d13d3dc49d8d8249e336fd84667c5bf7fc724b70bc/_data"
},
"VolumesRW": {
"/var/lib/mysql": true
},
...
Note our WordPress container should have a link to our MySQL container!
Let's look into the inspection in the previous section, and we can locate the "ExposedPorts":
$ docker inspect my_mysql
...
"ExposedPorts": {
"3306/tcp": {}
},
...
We'll link to this port to WordPress so that it's available for WordPress internally:
$ docker run --link=my_mysql:mysql -p 8888:80 -d wordpress
Here, we used --link to add link to WordPress container in the form of container-name:alias, specified the ports: hostPort:containerPort, and run it in detached mode as before.
Now, we have two containers running:
$ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 9b149061e09b wordpress "/entrypoint.sh apac 6 seconds ago Up 5 seconds 0.0.0.0:8888->80/tcp jovial_noyce 9173d3457bc8 mysql "/entrypoint.sh mysq 30 minutes ago Up 30 minutes 3306/tcp my_mysql
Actually, we have three containers: two are running, and another holds the volume for datastore:
$ docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 9b149061e09b wordpress "/entrypoint.sh apac 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes 0.0.0.0:8888->80/tcp jovial_noyce 9173d3457bc8 mysql "/entrypoint.sh mysq 32 minutes ago Up 32 minutes 3306/tcp my_mysql 6a7e05a1e120 busybox "echo 'My Datastore' About an hour ago Exited (0) About an hour ago my_datastore
Now, we're able to access the instance from the host without the container's IP, since we used standard port mappings.
Then, access it via http://localhost:8888 or http://host-ip:8888 in a browser:
Docker & K8s
- Docker install on Amazon Linux AMI
- Docker install on EC2 Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker container vs Virtual Machine
- Docker install on Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker Hello World Application
- Nginx image - share/copy files, Dockerfile
- Working with Docker images : brief introduction
- Docker image and container via docker commands (search, pull, run, ps, restart, attach, and rm)
- More on docker run command (docker run -it, docker run --rm, etc.)
- Docker Networks - Bridge Driver Network
- Docker Persistent Storage
- File sharing between host and container (docker run -d -p -v)
- Linking containers and volume for datastore
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically I - FROM, MAINTAINER, and build context
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically II - revisiting FROM, MAINTAINER, build context, and caching
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically III - RUN
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically IV - CMD
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically V - WORKDIR, ENV, ADD, and ENTRYPOINT
- Docker - Apache Tomcat
- Docker - NodeJS
- Docker - NodeJS with hostname
- Docker Compose - NodeJS with MongoDB
- Docker - Prometheus and Grafana with Docker-compose
- Docker - StatsD/Graphite/Grafana
- Docker - Deploying a Java EE JBoss/WildFly Application on AWS Elastic Beanstalk Using Docker Containers
- Docker : NodeJS with GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker : Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline with Jenkinsfile and Github
- Docker : Jenkins Master and Slave
- Docker - ELK : ElasticSearch, Logstash, and Kibana
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elasticsearch on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Filebeat on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Logstash on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Kibana on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elastic Stack with Docker Compose
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK) via Elasticsearch operator on minikube
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Stack via Helm on minikube
- Docker Compose - A gentle introduction with WordPress
- Docker Compose - MySQL
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services via docker-compose
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part A (install vault, unsealing, static secrets, and policies)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part B (EaaS, dynamic secrets, leases, and revocation)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part C (Consul)
- Docker Compose with two containers - Flask REST API service container and an Apache server container
- Docker compose : Nginx reverse proxy with multiple containers
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Getting started
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Front Proxy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ambassador - Envoy API Gateway on Kubernetes
- Docker Packer
- Docker Cheat Sheet
- Docker Q & A #1
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part I
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part II
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker II (snapshot app with nginx)
- Docker - NodeJS and MySQL app with React in a docker
- Docker - Step by Step NodeJS and MySQL app with React - I
- Installing LAMP via puppet on Docker
- Docker install via Puppet
- Nginx Docker install via Ansible
- Apache Hadoop CDH 5.8 Install with QuickStarts Docker
- Docker - Deploying Flask app to ECS
- Docker Compose - Deploying WordPress to AWS
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI EC2 type)
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI Fargate type)
- Docker - ECS Fargate
- Docker - AWS ECS service discovery with Flask and Redis
- Docker & Kubernetes : minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes 2 : minikube Django with Postgres - persistent volume
- Docker & Kubernetes 3 : minikube Django with Redis and Celery
- Docker & Kubernetes 4 : Django with RDS via AWS Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kops on AWS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ingress controller on AWS with Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul - Auto-unseal using Transit Secrets Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes & Persistent Volumes Claims - hostPath and annotations
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes - Dynamic volume provisioning
- Docker & Kubernetes : DaemonSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Secrets
- Docker & Kubernetes : kubectl command
- Docker & Kubernetes : Assign a Kubernetes Pod to a particular node in a Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : Configure a Pod to Use a ConfigMap
- AWS : EKS (Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Run a React app in a minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Minikube install on AWS EC2
- Docker & Kubernetes : Cassandra with a StatefulSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Terraform and AWS EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Pods and Service definitions
- Docker & Kubernetes : Service IP and the Service Type
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes DNS with Pods and Services
- Docker & Kubernetes : Headless service and discovering pods
- Docker & Kubernetes : Scaling and Updating application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Horizontal pod autoscaler on minikubes
- Docker & Kubernetes : From a monolithic app to micro services on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Rolling updates
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deployments to GKE (Rolling update, Canary and Blue-green deployments)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Slack Chat Bot with NodeJS on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery with Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline for Dev, Canary, and Production Environments on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : NodePort vs LoadBalancer vs Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB / MongoExpress on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Load Testing with Locust on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB with StatefulSets on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up Ingress with NGINX Controller on Minikube (Mac)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller for Dashboard service on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Ingress with AWS ALB Ingress Controller in EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up a private cluster on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Namespaces (default, kube-public, kube-system) and switching namespaces (kubens)
- Docker & Kubernetes : StatefulSets on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : RBAC
- Docker & Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, and IAM
- Docker & Kubernetes - Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, IAM with EKS ALB, Part 1
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : My first Helm deploy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Readiness and Liveness Probes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm chart repository with Github pages
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB with Ingress to Minikube using Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 2 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 3 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart for Node/Express and MySQL with Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using Helm and Prometheus Operator - Monitoring Kubernetes node resources out of the box
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using kube-prometheus-stack Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio (service mesh) sidecar proxy on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on Minikube with AWS EC2 for Bookinfo Application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part I)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part II - Prometheus, Grafana, pin a service, split traffic, and inject faults)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Package Manager with MySQL on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying Memcached on Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : EKS Control Plane (API server) Metrics with Prometheus
- Docker & Kubernetes : Spinnaker on EKS with Halyard
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery Pipelines with Spinnaker and Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-dind (docker-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-kind (k8s-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : nodeSelector, nodeAffinity, taints/tolerations, pod affinity and anti-affinity - Assigning Pods to Nodes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Jenkins-X on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD App of Apps with Heml on Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD on Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : GitOps with ArgoCD for Continuous Delivery to Kubernetes clusters (minikube) - guestbook
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization