AWS : VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) 3 - VPC Wizard with NAT
The picture below shows the NAT instance basics (Scenario 2: VPC with Public and Private Subnets (NAT)).
Here are the setup specifics of our VPC with NAT:
- The virtual private cloud (VPC) is of size /16 (example CIDR: 10.0.0.0/16) provides 65,536 private IP addresses.
- The public subnet is of size /24 (example CIDR: 10.0.0.0/24) provides 256 private IP addresses.
- The private subnet of size /24 (example CIDR: 10.0.1.0/24) provides 256 private IP addresses.
- The Internet gateway connects the VPC to the Internet and to other AWS products.
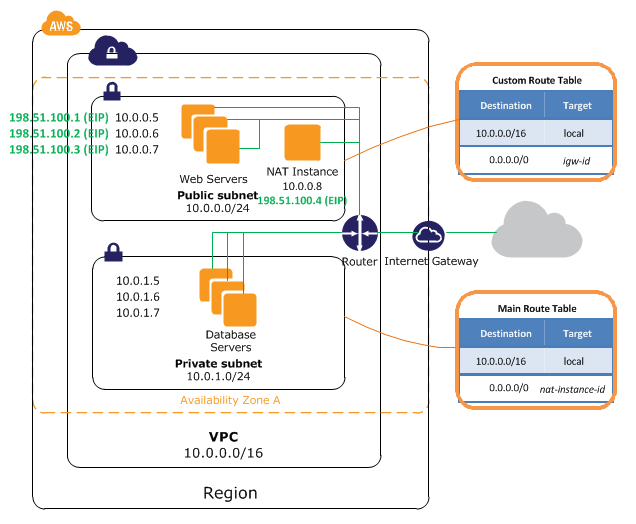
The main route table sends the traffic from the instances in the private subnet to the NAT instance in the public subnet.
The NAT instance sends the traffic to the Internet gateway for the VPC. The traffic is attributed to the Elastic IP address of the NAT instance. The NAT instance specifies a high port number for the response. If a response comes back, the NAT instance sends it to an instance in the private subnet based on the port number for the response.
The instances in the public subnet can receive inbound traffic directly from the Internet, whereas the instances in the private subnet can't.
The instances in the public subnet can send outbound traffic directly to the Internet, whereas the instances in the private subnet can't.
Instead, the instances in the private subnet can access the Internet by using a network address translation (NAT) instance that you launch into the public subnet.
Let's create a VPC using the VPC Wizard in the VPC Console with NAT in public subnet.
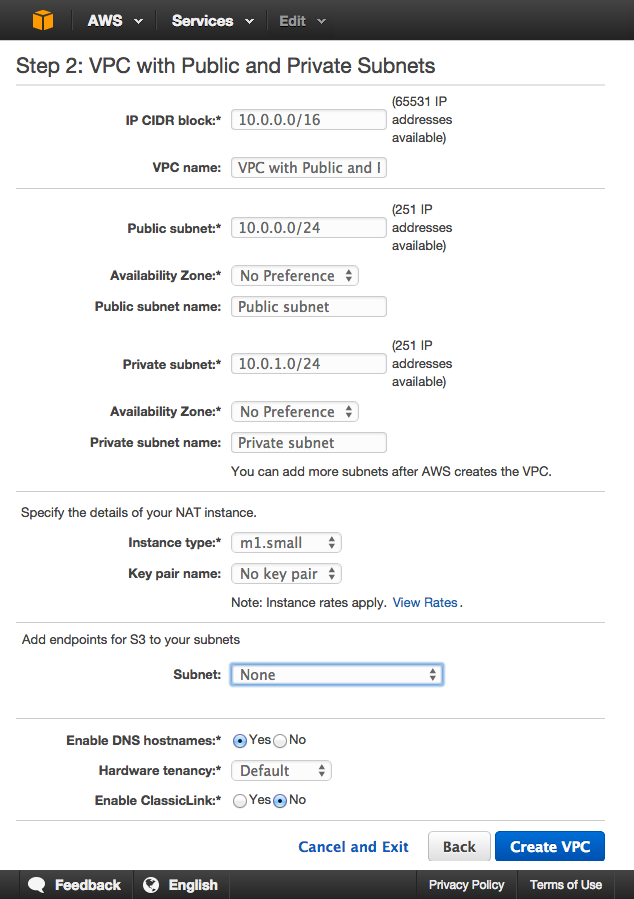
A network address translation (NAT) instance has its own Elastic IP address. This enables instances in the private subnet to send requests to the Internet. In other words, it will act as the gateway for all the instance(s) inside the private subnet (10.0.1.0/24).
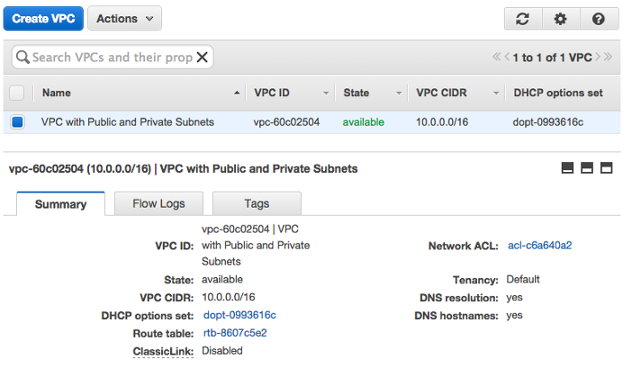
Here is the summary for the created VPC:
Private subnet and route table:
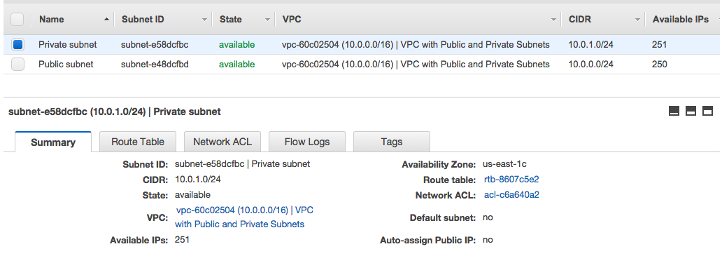
The picture below shows the main route table.
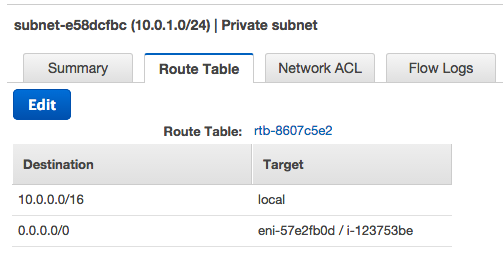
The main route table is associated with our private subnet. The route table contains an entry that enables instances in the subnet to communicate with other instances in the VPC, and an entry that enables instances in the subnet to communicate with the Internet through the NAT instance.
The first row describes the entry for local routing in the VPC. This entry enables the instances in the VPC to communicate with each other.
The second row describes the entry that sends all other subnet traffic to the NAT instance, which is specified using its AWS-assigned identifiers (for example, network interface eni-* and instance i-*).
Public subnet and route table:
The custom route table shown below is associated with our public subnet.
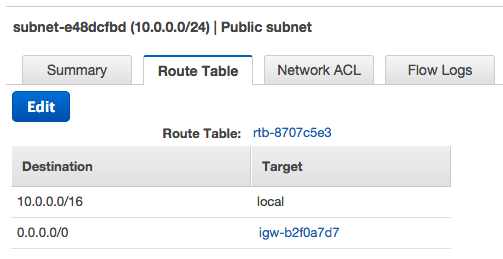
This route table contains an entry that enables instances in the subnet to communicate with other instances in the VPC, and an entry that enables instances in the subnet to communicate directly with the Internet.
The first row describes the entry for local routing in the VPC. This entry enables the instances in this VPC to communicate with each other.
The second row describes the entry for routing all other subnet traffic to the Internet over the Internet gateway, which is specified using its AWS-assigned identifier (for example, igw-*).
Setup rules to the NATSG security group:
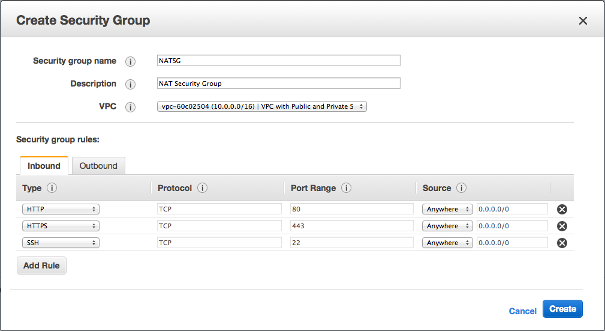
Let's change the security group of the NAT instance.
In the navigation pane, click Network Interfaces, then select the network interface for the NAT instance from the list, and then select Change Security Groups from the Actions list.
In the Change Security Groups dialog box, select the NATSG security group that we created from the Security groups list.
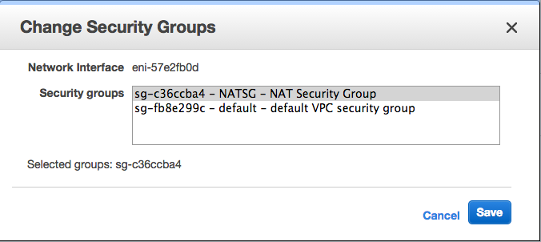
Click Save.
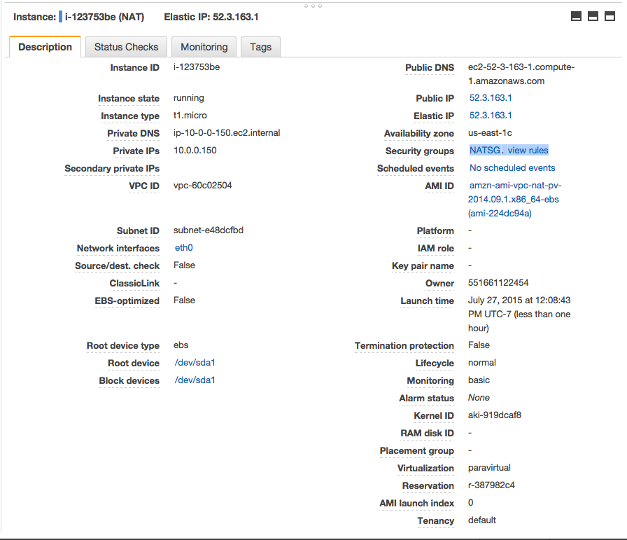
We can see the security group for NAT instance has been changed:
AWS (Amazon Web Services)
- AWS : EKS (Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes)
- AWS : Creating a snapshot (cloning an image)
- AWS : Attaching Amazon EBS volume to an instance
- AWS : Adding swap space to an attached volume via mkswap and swapon
- AWS : Creating an EC2 instance and attaching Amazon EBS volume to the instance using Python boto module with User data
- AWS : Creating an instance to a new region by copying an AMI
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 1
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 2 - Creating and Deleting a Bucket
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 3 - Bucket Versioning
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 4 - Uploading a large file
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 5 - Uploading folders/files recursively
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 6 - Bucket Policy for File/Folder View/Download
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 7 - How to Copy or Move Objects from one region to another
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 8 - Archiving S3 Data to Glacier
- AWS : Creating a CloudFront distribution with an Amazon S3 origin
- AWS : Creating VPC with CloudFormation
- AWS : WAF (Web Application Firewall) with preconfigured CloudFormation template and Web ACL for CloudFront distribution
- AWS : CloudWatch & Logs with Lambda Function / S3
- AWS : Lambda Serverless Computing with EC2, CloudWatch Alarm, SNS
- AWS : Lambda and SNS - cross account
- AWS : CLI (Command Line Interface)
- AWS : CLI (ECS with ALB & autoscaling)
- AWS : ECS with cloudformation and json task definition
- AWS Application Load Balancer (ALB) and ECS with Flask app
- AWS : Load Balancing with HAProxy (High Availability Proxy)
- AWS : VirtualBox on EC2
- AWS : NTP setup on EC2
- AWS: jq with AWS
- AWS & OpenSSL : Creating / Installing a Server SSL Certificate
- AWS : OpenVPN Access Server 2 Install
- AWS : VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) 1 - netmask, subnets, default gateway, and CIDR
- AWS : VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) 2 - VPC Wizard
- AWS : VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) 3 - VPC Wizard with NAT
- DevOps / Sys Admin Q & A (VI) - AWS VPC setup (public/private subnets with NAT)
- AWS - OpenVPN Protocols : PPTP, L2TP/IPsec, and OpenVPN
- AWS : Autoscaling group (ASG)
- AWS : Setting up Autoscaling Alarms and Notifications via CLI and Cloudformation
- AWS : Adding a SSH User Account on Linux Instance
- AWS : Windows Servers - Remote Desktop Connections using RDP
- AWS : Scheduled stopping and starting an instance - python & cron
- AWS : Detecting stopped instance and sending an alert email using Mandrill smtp
- AWS : Elastic Beanstalk with NodeJS
- AWS : Elastic Beanstalk Inplace/Rolling Blue/Green Deploy
- AWS : Identity and Access Management (IAM) Roles for Amazon EC2
- AWS : Identity and Access Management (IAM) Policies, sts AssumeRole, and delegate access across AWS accounts
- AWS : Identity and Access Management (IAM) sts assume role via aws cli2
- AWS : Creating IAM Roles and associating them with EC2 Instances in CloudFormation
- AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) Roles, SSO(Single Sign On), SAML(Security Assertion Markup Language), IdP(identity provider), STS(Security Token Service), and ADFS(Active Directory Federation Services)
- AWS : Amazon Route 53
- AWS : Amazon Route 53 - DNS (Domain Name Server) setup
- AWS : Amazon Route 53 - subdomain setup and virtual host on Nginx
- AWS Amazon Route 53 : Private Hosted Zone
- AWS : SNS (Simple Notification Service) example with ELB and CloudWatch
- AWS : Lambda with AWS CloudTrail
- AWS : SQS (Simple Queue Service) with NodeJS and AWS SDK
- AWS : Redshift data warehouse
- AWS : CloudFormation
- AWS : CloudFormation Bootstrap UserData/Metadata
- AWS : CloudFormation - Creating an ASG with rolling update
- AWS : Cloudformation Cross-stack reference
- AWS : OpsWorks
- AWS : Network Load Balancer (NLB) with Autoscaling group (ASG)
- AWS CodeDeploy : Deploy an Application from GitHub
- AWS EC2 Container Service (ECS)
- AWS EC2 Container Service (ECS) II
- AWS Hello World Lambda Function
- AWS Lambda Function Q & A
- AWS Node.js Lambda Function & API Gateway
- AWS API Gateway endpoint invoking Lambda function
- AWS API Gateway invoking Lambda function with Terraform
- AWS API Gateway invoking Lambda function with Terraform - Lambda Container
- Amazon Kinesis Streams
- AWS: Kinesis Data Firehose with Lambda and ElasticSearch
- Amazon DynamoDB
- Amazon DynamoDB with Lambda and CloudWatch
- Loading DynamoDB stream to AWS Elasticsearch service with Lambda
- Amazon ML (Machine Learning)
- Simple Systems Manager (SSM)
- AWS : RDS Connecting to a DB Instance Running the SQL Server Database Engine
- AWS : RDS Importing and Exporting SQL Server Data
- AWS : RDS PostgreSQL & pgAdmin III
- AWS : RDS PostgreSQL 2 - Creating/Deleting a Table
- AWS : MySQL Replication : Master-slave
- AWS : MySQL backup & restore
- AWS RDS : Cross-Region Read Replicas for MySQL and Snapshots for PostgreSQL
- AWS : Restoring Postgres on EC2 instance from S3 backup
- AWS : Q & A
- AWS : Security
- AWS : Security groups vs. network ACLs
- AWS : Scaling-Up
- AWS : Networking
- AWS : Single Sign-on (SSO) with Okta
- AWS : JIT (Just-in-Time) with Okta
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization