Dockerfiles : building Docker images automatically II - revisiting FROM, MAINTAINER, build context, and caching
COntinued from Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically I - FROM, MAINTAINER, and build context.
This chapter is similar to the previous one, Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically I - FROM, MAINTAINER, and build context, that's because we want to make sure how docker build works with context.
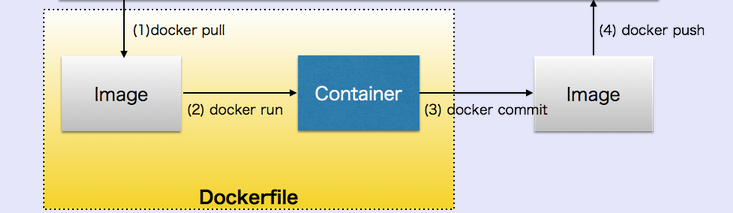
Image source: Docker
In this chapter, we're going to learn more on how to automate this process via instructions in Dockerfiles.
Let's download our base image:
$ docker pull debian:latest debian:latest: The image you are pulling has been verified 511136ea3c5a: Pull complete f10807909bc5: Pull complete f6fab3b798be: Pull complete Status: Downloaded newer image for debian:latest $ docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED VIRTUAL SIZE debian latest f6fab3b798be 2 weeks ago 85.1 MB
In our local working directory, we have only one file, Dockerfile:
$ ls Dockerfile
Each Dockerfile is a script, composed of various commands (instructions) and arguments listed successively to automatically perform actions on a base image in order to create (or form) a new one. They are used for organizing things and greatly help with deployments by simplifying the process start-to-finish.
Let's look at the syntax of docker build command:
$ docker build --help Usage: docker build [OPTIONS] PATH | URL | - Build a new image from the source code at PATH -t, --tag="" Repository name (and optionally a tag) to be applied to the resulting image in case of success
Dockerfiles begin with defining an image FROM which the build process starts. Followed by various other methods, commands and arguments (or conditions), in return, provide a new image which is to be used for creating docker containers.
FROM debian:latest MAINTAINER devops@bogotobogo.com
Let's run docker build command with the two-line Dockerfile:
$ docker image build -t bogodevops/demo:v1 . Sending build context to Docker daemon 2.56 kB Sending build context to Docker daemon Step 0 : FROM debian:latest ---> f6fab3b798be Step 1 : MAINTAINER k@bogotobogo.com ---> Running in 4181b54ab22e ---> 511bcbdd59ba Removing intermediate container 4181b54ab22e Successfully built 511bcbdd59ba
Now if we list the images:
$ docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED VIRTUAL SIZE bogodevops/demo v1 511bcbdd59ba About a minute ago 85.1 MB debian latest f6fab3b798be 2 weeks ago 85.1 MB
Note that the path to the source repository defines where to find the context of the build. The build is run by the Docker daemon, not by the CLI, so the whole context must be transferred to the daemon. The Docker CLI reports "Sending build context to Docker daemon" when the context (2.56kB) is sent to the daemon as shown in the output:
Sending build context to Docker daemon 2.56 kB
If we send big chuck to the daemon, it will take longer to copy things. For example, if we send duplicate device files(/de/zero) with dd:
$ dd if=/dev/zero of=testimage bs=4096 count=8192 8192+0 records in 8192+0 records out 33554432 bytes (34 MB) copied, 0.118561 s, 283 MB/s $ ls Dockerfile testimage $ docker image build -t bogodevops/demo:v1 . Sending build context to Docker daemon 33.56 MB Sending build context to Docker daemon Step 0 : FROM debian:latest ---> f6fab3b798be Step 1 : MAINTAINER k@bogotobogo.com ---> Using cache ---> 511bcbdd59ba Successfully built 511bcbdd59ba
Note that the size has been increased from 2.56kb to 33.56MB. That's why the Docker document gives us a Warning like this:
"Warning Avoid using your root directory, /, as the root of the source repository. The docker build command will use whatever dicrectory contains the Dockerfile as the build context (including all of its subdirectories). The build context will be sent to the Docker daemon before building the image, which means if you use / as the source repository, the entire contents of your hard drive will get sent to the daemon (and thus to the machine running the daemon). You probably don't want that."
Or like this:
"Warning: Do not use your root directory, /, as the PATH as it causes the build to transfer the entire contents of your hard drive to the Docker daemon.
So, we should be aware of the context of our build directory!
Again:
"The build is run by the Docker daemon, not by the CLI. The first thing a build process does is send the entire context (recursively) to the daemon. In most cases, it's best to start with an empty directory as context and keep your Dockerfile in that directory. Add only the files needed for building the Dockerfile"
Also note the the difference in the Step 1 of the two cases:
In the first instance of docker build:
Step 1 : MAINTAINER k@bogotobogo.com ---> Running in 4181b54ab22e ---> 511bcbdd59ba
But in the second run, Docker used cache:
Step 1 : MAINTAINER k@bogotobogo.com ---> Using cache ---> 511bcbdd59ba
When we build a Docker image, it's using a Dockerfile, and every instruction in the Dockerfile is run inside of a container. If that returns successfully, then that container is stored as a new image.
In our case, in Step 0, we created 'f6fab3b798be' which is a hash identifier, and Step 1, we created '511bcbdd59ba' hash.
Note that in our 2nd run (the 'docker run' with 'dd'), the hash is the same. What does this mean? If the instructions in our Dockerfile are the same, Docker uses the cache:
$ docker images -a REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED VIRTUAL SIZE bogodevops/demo v1 511bcbdd59ba 57 minutes ago 85.1 MB debian latest f6fab3b798be 2 weeks ago 85.1 MB <none> <none> f10807909bc5 2 weeks ago 85.1 MB <none> <none> 511136ea3c5a 17 months ago 0 B
So, every step along the way, we create a new image. As it succeeds, we'll build a new layer on top of the previous one as we read in an instruction. As this caching allows us to build other environment similar to the previous image without rebuilding from every steps involved.
Docker & K8s
- Docker install on Amazon Linux AMI
- Docker install on EC2 Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker container vs Virtual Machine
- Docker install on Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker Hello World Application
- Nginx image - share/copy files, Dockerfile
- Working with Docker images : brief introduction
- Docker image and container via docker commands (search, pull, run, ps, restart, attach, and rm)
- More on docker run command (docker run -it, docker run --rm, etc.)
- Docker Networks - Bridge Driver Network
- Docker Persistent Storage
- File sharing between host and container (docker run -d -p -v)
- Linking containers and volume for datastore
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically I - FROM, MAINTAINER, and build context
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically II - revisiting FROM, MAINTAINER, build context, and caching
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically III - RUN
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically IV - CMD
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically V - WORKDIR, ENV, ADD, and ENTRYPOINT
- Docker - Apache Tomcat
- Docker - NodeJS
- Docker - NodeJS with hostname
- Docker Compose - NodeJS with MongoDB
- Docker - Prometheus and Grafana with Docker-compose
- Docker - StatsD/Graphite/Grafana
- Docker - Deploying a Java EE JBoss/WildFly Application on AWS Elastic Beanstalk Using Docker Containers
- Docker : NodeJS with GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker : Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline with Jenkinsfile and Github
- Docker : Jenkins Master and Slave
- Docker - ELK : ElasticSearch, Logstash, and Kibana
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elasticsearch on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Filebeat on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Logstash on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Kibana on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elastic Stack with Docker Compose
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK) via Elasticsearch operator on minikube
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Stack via Helm on minikube
- Docker Compose - A gentle introduction with WordPress
- Docker Compose - MySQL
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services via docker-compose
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part A (install vault, unsealing, static secrets, and policies)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part B (EaaS, dynamic secrets, leases, and revocation)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part C (Consul)
- Docker Compose with two containers - Flask REST API service container and an Apache server container
- Docker compose : Nginx reverse proxy with multiple containers
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Getting started
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Front Proxy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ambassador - Envoy API Gateway on Kubernetes
- Docker Packer
- Docker Cheat Sheet
- Docker Q & A #1
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part I
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part II
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker II (snapshot app with nginx)
- Docker - NodeJS and MySQL app with React in a docker
- Docker - Step by Step NodeJS and MySQL app with React - I
- Installing LAMP via puppet on Docker
- Docker install via Puppet
- Nginx Docker install via Ansible
- Apache Hadoop CDH 5.8 Install with QuickStarts Docker
- Docker - Deploying Flask app to ECS
- Docker Compose - Deploying WordPress to AWS
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI EC2 type)
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI Fargate type)
- Docker - ECS Fargate
- Docker - AWS ECS service discovery with Flask and Redis
- Docker & Kubernetes : minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes 2 : minikube Django with Postgres - persistent volume
- Docker & Kubernetes 3 : minikube Django with Redis and Celery
- Docker & Kubernetes 4 : Django with RDS via AWS Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kops on AWS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ingress controller on AWS with Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul - Auto-unseal using Transit Secrets Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes & Persistent Volumes Claims - hostPath and annotations
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes - Dynamic volume provisioning
- Docker & Kubernetes : DaemonSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Secrets
- Docker & Kubernetes : kubectl command
- Docker & Kubernetes : Assign a Kubernetes Pod to a particular node in a Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : Configure a Pod to Use a ConfigMap
- AWS : EKS (Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Run a React app in a minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Minikube install on AWS EC2
- Docker & Kubernetes : Cassandra with a StatefulSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Terraform and AWS EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Pods and Service definitions
- Docker & Kubernetes : Service IP and the Service Type
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes DNS with Pods and Services
- Docker & Kubernetes : Headless service and discovering pods
- Docker & Kubernetes : Scaling and Updating application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Horizontal pod autoscaler on minikubes
- Docker & Kubernetes : From a monolithic app to micro services on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Rolling updates
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deployments to GKE (Rolling update, Canary and Blue-green deployments)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Slack Chat Bot with NodeJS on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery with Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline for Dev, Canary, and Production Environments on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : NodePort vs LoadBalancer vs Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB / MongoExpress on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Load Testing with Locust on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB with StatefulSets on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up Ingress with NGINX Controller on Minikube (Mac)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller for Dashboard service on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Ingress with AWS ALB Ingress Controller in EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up a private cluster on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Namespaces (default, kube-public, kube-system) and switching namespaces (kubens)
- Docker & Kubernetes : StatefulSets on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : RBAC
- Docker & Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, and IAM
- Docker & Kubernetes - Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, IAM with EKS ALB, Part 1
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : My first Helm deploy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Readiness and Liveness Probes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm chart repository with Github pages
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB with Ingress to Minikube using Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 2 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 3 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart for Node/Express and MySQL with Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using Helm and Prometheus Operator - Monitoring Kubernetes node resources out of the box
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using kube-prometheus-stack Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio (service mesh) sidecar proxy on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on Minikube with AWS EC2 for Bookinfo Application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part I)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part II - Prometheus, Grafana, pin a service, split traffic, and inject faults)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Package Manager with MySQL on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying Memcached on Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : EKS Control Plane (API server) Metrics with Prometheus
- Docker & Kubernetes : Spinnaker on EKS with Halyard
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery Pipelines with Spinnaker and Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-dind (docker-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-kind (k8s-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : nodeSelector, nodeAffinity, taints/tolerations, pod affinity and anti-affinity - Assigning Pods to Nodes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Jenkins-X on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD App of Apps with Heml on Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD on Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : GitOps with ArgoCD for Continuous Delivery to Kubernetes clusters (minikube) - guestbook
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization