Working with Docker images
Docker images are used to create Docker containers.
Docker images are the build component of Docker.
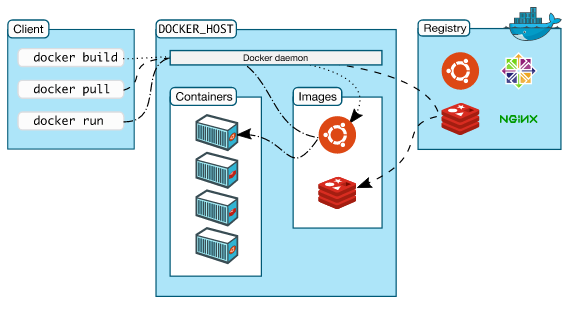
Picture credit : Understand the architecture
We create Docker containers using [base] images. An image can be basic, with nothing but the operating-system fundamentals, or it can consist of a sophisticated pre-built application stack ready for launch.
When we build images with docker, each action taken (i.e. a command executed such as apt-get install) forms a new layer on top of the previous one. These base images then can be used to create new containers.
Docker registries hold images.
These are public or private stores from which we can upload or download images.
The public Docker registry is provided with the Docker Hub.
We use "docker run" command from client to tell the Docker daemon to run a container, for example:
$ docker run -it ubuntu:latest /bin/bash
Basically, it's a container "launch" command.
At docker, a Docker client is launched and at run subcommand, a new container will be launched.
The new container will be built from ubuntu base image with "latest" tag.
Here i: interactive, : terminal.
As described in the official document, here are the things happening under the hood:
- Pulls the ubuntu image:
Docker checks for the presence of the ubuntu image and, if it doesn't exist locally on the host, then Docker downloads it from Docker Hub.
If the image already exists, then Docker uses it for the new container.
- Creates a new container:
Once Docker has the image, it uses it to create a container.
- Allocates a filesystem and mounts a read-write layer:
The container is created in the file system and a read-write layer is added to the image.
- Allocates a network and sets up an IP address:
Creates a network interface that allows the Docker container to talk to the local host.
- Executes a process that we specify:
Runs our application.
$ docker search ubuntu NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL AUTOMATED ubuntu Ubuntu is a Debian-based Linux operating s... 4416 [OK] ubuntu-upstart Upstart is an event-based replacement for ... 65 [OK] ...
docker pull pulls an image from registry to local machine.
$ docker pull ubuntu latest: Pulling from ubuntu 20ee58809289: Pull complete f905badeb558: Pull complete 119df6bf2a3a: Pull complete 94d6eea646bc: Pull complete bb4eabee84bf: Pull complete Digest: sha256:85af8b61adffea165e84e47e0034923ec237754a208501fce5dbeecbb197062c Status: Downloaded newer image for ubuntu:latest
Docker images can consist of multiple layers.
In the example above, the image consists of five layers (20ee58809289,...,bb4eabee84bf).
We can use a tag to specify what to download. For example, 'latest' for tag:
$ docker pull ubuntu:latest
To list the images on the host:
docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED VIRTUAL SIZE ubuntu latest bb4eabee84bf 2 weeks ago 124.8 MB ubuntu 16.04 bb4eabee84bf 2 weeks ago 124.8 MB centos 7 2a332da70fd1 9 weeks ago 196.8 MB ubuntu trusty 9bc953763843 10 weeks ago 188 MB debian latest cea663c8c811 10 weeks ago 125.1 MB centos latest ce20c473cd8a 9 months ago 172.3 MB
Now we want to launch a container:
$ docker run -it ubuntu:latest /bin/bash
We're logged in as a root:
root@859d4a27d4c8:/# whoami root
Check the OS:
root@859d4a27d4c8:/# cat /etc/*release DISTRIB_ID=Ubuntu DISTRIB_RELEASE=16.04 ...
Let's check what processes are currently running:
root@859d4a27d4c8:/# top
...
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
1 root 20 0 18232 2032 1556 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.09 bash
14 root 20 0 36628 1704 1272 R 0.0 0.0 0:00.02 top
As we can see there are only two processes, and they are isolated ones from the host processes.
"Ctrl + P + Q" will do the trick:
root@859d4a27d4c8:/# k@laptop:~$
From the PID, we can check the "top" on the host is using different space from the "top" on the docker container:
k@laptop:~$ pa aux | grep top root 14512 0.0 0.0 36628 1704 pts/17 S+ 22:01 0:00 top
Now, we may want to get back to our container again via "attach". To do that, we need to know the "CONTAINER ID":
k@laptop:~$ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 859d4a27d4c8 ubuntu:latest "/bin/bash" 5 minutes ago Up 5 minutes cranky_swartz
Let's do attach:
k@laptop:~$ docker attach 859d4a27d4c8 root@859d4a27d4c8:/#
We can stop the container and get out of it via "Ctrl + D":
root@859d4a27d4c8:/# exit k@laptop:~$
If we issue "docker ps" command again, we see the container is not running anymore:
k@laptop:~$ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES k@laptop:~$
We can list all containers including old ones that stopped running using "docker ps -a":
k@laptop:~$ docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 859d4a27d4c8 ubuntu:latest "/bin/bash" 31 minutes ago Exited (0) 4 minutes ago cranky_swartz ...
To run a container in background, we use "docker start" command:
k@laptop:~$ docker start cranky_swartz cranky_swartz k@laptop:~$ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 859d4a27d4c8 ubuntu:latest "/bin/bash" 36 minutes ago Up 4 seconds cranky_swartz
We can check what processes are running inside a container using "docker top":
k@laptop:~$ docker top cranky_swartz UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD root 15680 1559 0 22:33 pts/17 00:00:00 /bin/bash
To stop a container running in background, we use "docker stop" command:
k@laptop:~$ docker stop cranky_swartz
What's in our system related to the Docker containers?
root@laptop:/# tree /var/lib/docker/containers |-- 859d4a27d4c883db39e68590f1d1d2c340f8775a94fe721eba85111d3b79c1fe │ |-- 859d4a27d4c883db39e68590f1d1d2c340f8775a94fe721eba85111d3b79c1fe-json.log │ |-- config.json │ |-- hostconfig.json │ |-- hostname │ |-- hosts │ |-- resolv.conf │ |-- resolv.conf.hash
Note that there are no binary images for the container which makes docker consumes much less space compare to the other virtual tools.
We can run a container in a "detach" mode, and later we can attach to it:
Note we need to use "-it" so that we can do something with the container after attaching. Also, we used "--name" to give our own name to the container.
k@laptop:~$ docker run -d -it --name=yaong ubuntu:16.04 /bin/bash 6bbba8e00d68a9b9c38bd7fdbd807dae01b9329d3b5ecd7ad2918305743bf5ea
Ok, it's started, and we can check it:
k@laptop:~$ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 6bbba8e00d68 ubuntu:16.04 "/bin/bash" About a minute ago Up About a minute yaong
To stop it:
k@laptop:~$ docker stop 6bbba8e00d68 6bbba8e00d68 k@laptop:~$ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES k@laptop:~$
Docker & K8s
- Docker install on Amazon Linux AMI
- Docker install on EC2 Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker container vs Virtual Machine
- Docker install on Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker Hello World Application
- Nginx image - share/copy files, Dockerfile
- Working with Docker images : brief introduction
- Docker image and container via docker commands (search, pull, run, ps, restart, attach, and rm)
- More on docker run command (docker run -it, docker run --rm, etc.)
- Docker Networks - Bridge Driver Network
- Docker Persistent Storage
- File sharing between host and container (docker run -d -p -v)
- Linking containers and volume for datastore
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically I - FROM, MAINTAINER, and build context
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically II - revisiting FROM, MAINTAINER, build context, and caching
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically III - RUN
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically IV - CMD
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically V - WORKDIR, ENV, ADD, and ENTRYPOINT
- Docker - Apache Tomcat
- Docker - NodeJS
- Docker - NodeJS with hostname
- Docker Compose - NodeJS with MongoDB
- Docker - Prometheus and Grafana with Docker-compose
- Docker - StatsD/Graphite/Grafana
- Docker - Deploying a Java EE JBoss/WildFly Application on AWS Elastic Beanstalk Using Docker Containers
- Docker : NodeJS with GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker : Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline with Jenkinsfile and Github
- Docker : Jenkins Master and Slave
- Docker - ELK : ElasticSearch, Logstash, and Kibana
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elasticsearch on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Filebeat on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Logstash on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Kibana on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elastic Stack with Docker Compose
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK) via Elasticsearch operator on minikube
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Stack via Helm on minikube
- Docker Compose - A gentle introduction with WordPress
- Docker Compose - MySQL
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services via docker-compose
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part A (install vault, unsealing, static secrets, and policies)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part B (EaaS, dynamic secrets, leases, and revocation)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part C (Consul)
- Docker Compose with two containers - Flask REST API service container and an Apache server container
- Docker compose : Nginx reverse proxy with multiple containers
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Getting started
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Front Proxy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ambassador - Envoy API Gateway on Kubernetes
- Docker Packer
- Docker Cheat Sheet
- Docker Q & A #1
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part I
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part II
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker II (snapshot app with nginx)
- Docker - NodeJS and MySQL app with React in a docker
- Docker - Step by Step NodeJS and MySQL app with React - I
- Installing LAMP via puppet on Docker
- Docker install via Puppet
- Nginx Docker install via Ansible
- Apache Hadoop CDH 5.8 Install with QuickStarts Docker
- Docker - Deploying Flask app to ECS
- Docker Compose - Deploying WordPress to AWS
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI EC2 type)
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI Fargate type)
- Docker - ECS Fargate
- Docker - AWS ECS service discovery with Flask and Redis
- Docker & Kubernetes : minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes 2 : minikube Django with Postgres - persistent volume
- Docker & Kubernetes 3 : minikube Django with Redis and Celery
- Docker & Kubernetes 4 : Django with RDS via AWS Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kops on AWS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ingress controller on AWS with Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul - Auto-unseal using Transit Secrets Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes & Persistent Volumes Claims - hostPath and annotations
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes - Dynamic volume provisioning
- Docker & Kubernetes : DaemonSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Secrets
- Docker & Kubernetes : kubectl command
- Docker & Kubernetes : Assign a Kubernetes Pod to a particular node in a Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : Configure a Pod to Use a ConfigMap
- AWS : EKS (Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Run a React app in a minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Minikube install on AWS EC2
- Docker & Kubernetes : Cassandra with a StatefulSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Terraform and AWS EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Pods and Service definitions
- Docker & Kubernetes : Service IP and the Service Type
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes DNS with Pods and Services
- Docker & Kubernetes : Headless service and discovering pods
- Docker & Kubernetes : Scaling and Updating application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Horizontal pod autoscaler on minikubes
- Docker & Kubernetes : From a monolithic app to micro services on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Rolling updates
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deployments to GKE (Rolling update, Canary and Blue-green deployments)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Slack Chat Bot with NodeJS on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery with Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline for Dev, Canary, and Production Environments on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : NodePort vs LoadBalancer vs Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB / MongoExpress on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Load Testing with Locust on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB with StatefulSets on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up Ingress with NGINX Controller on Minikube (Mac)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller for Dashboard service on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Ingress with AWS ALB Ingress Controller in EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up a private cluster on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Namespaces (default, kube-public, kube-system) and switching namespaces (kubens)
- Docker & Kubernetes : StatefulSets on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : RBAC
- Docker & Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, and IAM
- Docker & Kubernetes - Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, IAM with EKS ALB, Part 1
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : My first Helm deploy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Readiness and Liveness Probes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm chart repository with Github pages
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB with Ingress to Minikube using Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 2 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 3 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart for Node/Express and MySQL with Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using Helm and Prometheus Operator - Monitoring Kubernetes node resources out of the box
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using kube-prometheus-stack Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio (service mesh) sidecar proxy on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on Minikube with AWS EC2 for Bookinfo Application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part I)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part II - Prometheus, Grafana, pin a service, split traffic, and inject faults)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Package Manager with MySQL on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying Memcached on Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : EKS Control Plane (API server) Metrics with Prometheus
- Docker & Kubernetes : Spinnaker on EKS with Halyard
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery Pipelines with Spinnaker and Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-dind (docker-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-kind (k8s-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : nodeSelector, nodeAffinity, taints/tolerations, pod affinity and anti-affinity - Assigning Pods to Nodes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Jenkins-X on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD App of Apps with Heml on Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD on Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : GitOps with ArgoCD for Continuous Delivery to Kubernetes clusters (minikube) - guestbook
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization