Docker : Ambassador - Envoy API Gateway on Kubernetes
Ambassador is an open source Kubernetes-Native API Gateway built on the Envoy Proxy.
API Gateway is an entry point for all client requests. The requests are proxied/routed to the appropriate services. Usually, traffic management, authentication, and monitoring are implemented in the API Gateway hiding the details from our services.
Ambassador operates as a specialized control plane to expose Envoy's functionality as Kubernetes annotations.
Here's what Ambassador does:
- Makes it easy to change and add to your Envoy configuration via Kubernetes annotations
- Adds the out-of-the-box configuration necessary for production Envoy, e.g., monitoring, health/liveness checks, and more
- Extends Envoy with traditional API Gateway functionality such as authentication
- Integrates with Istio, for organizations who need a full-blown service mesh
In this post, we will see how we can deploy Envoy on Kubernetes via Ambassador.
Ambassador only deploys in Kubernetes. This means that Ambassador delegates all the hard parts of scaling and availability to Kubernetes.
Fore more about API gateway, please check Microservices API Gateways vs. Traditional Enterprise API Gateways and Envoy vs NGINX vs HAProxy: Why the open source Ambassador API Gateway chose Envoy.
We'll use minikube:
$ minikube start There is a newer version of minikube available (v0.32.0). Download it here: https://github.com/kubernetes/minikube/releases/tag/v0.32.0 To disable this notification, run the following: minikube config set WantUpdateNotification false Starting local Kubernetes v1.10.0 cluster... Starting VM... Getting VM IP address... Moving files into cluster... Setting up certs... Connecting to cluster... Setting up kubeconfig... Starting cluster components... Kubectl is now configured to use the cluster. Loading cached images from config file. $
To check if we're using a cluster with RBAC enabled. We should see the API version .rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 if RBAC is enabled:
$ kubectl api-versions ... rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 ...
Current status of the cluster looks like this:
$ kubectl get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 8h $ kubectl get pods No resources found.
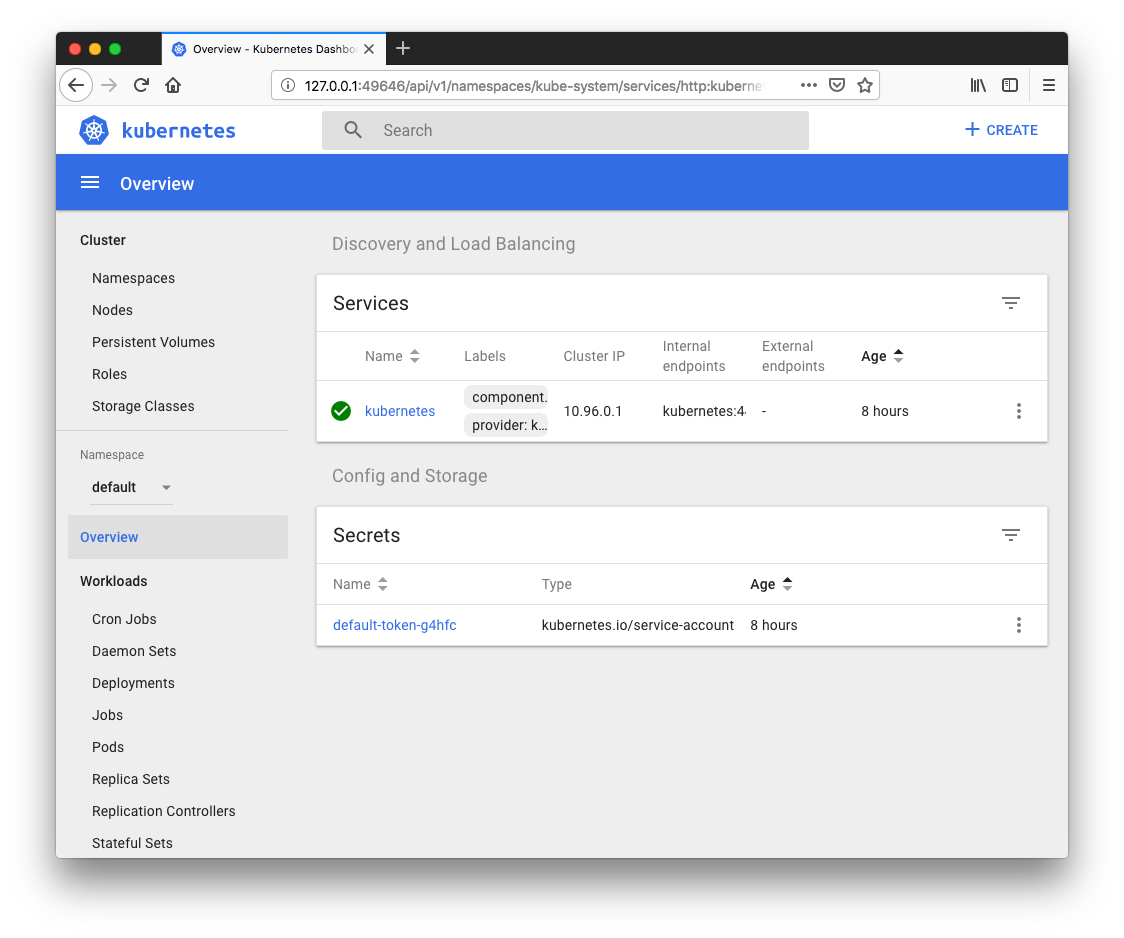
To install Ambassador/Envoy on Kubernetes, run the following:
$ kubectl apply -f https://www.getambassador.io/yaml/ambassador/ambassador-rbac.yaml service/ambassador-admin created clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/ambassador created serviceaccount/ambassador created clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/ambassador created deployment.extensions/ambassador created
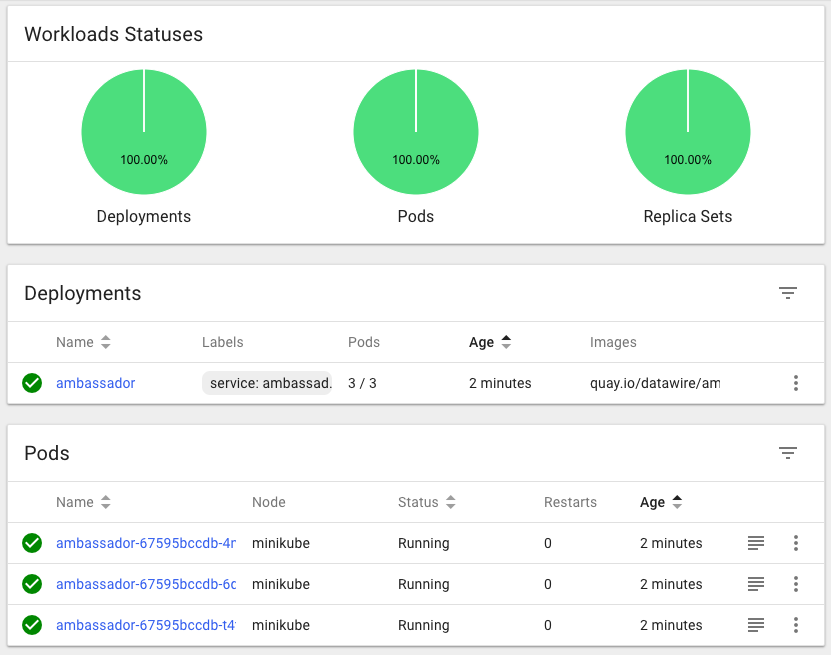
Now we have a Kubernetes deployment for Ambassador that includes readiness and liveness checks. By default, it will also create 3 instances of Ambassador. Each Ambassador instance consists of an Envoy proxy along with the Ambassador control plane.
$ kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE ambassador-67595bccdb-4nkn2 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 24s ambassador-67595bccdb-6ddbj 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 24s ambassador-67595bccdb-t4tzz 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 24s $ kubectl get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE ambassador-admin NodePort 10.99.19.183 <none> 8877:30384/TCP 32s kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 9h
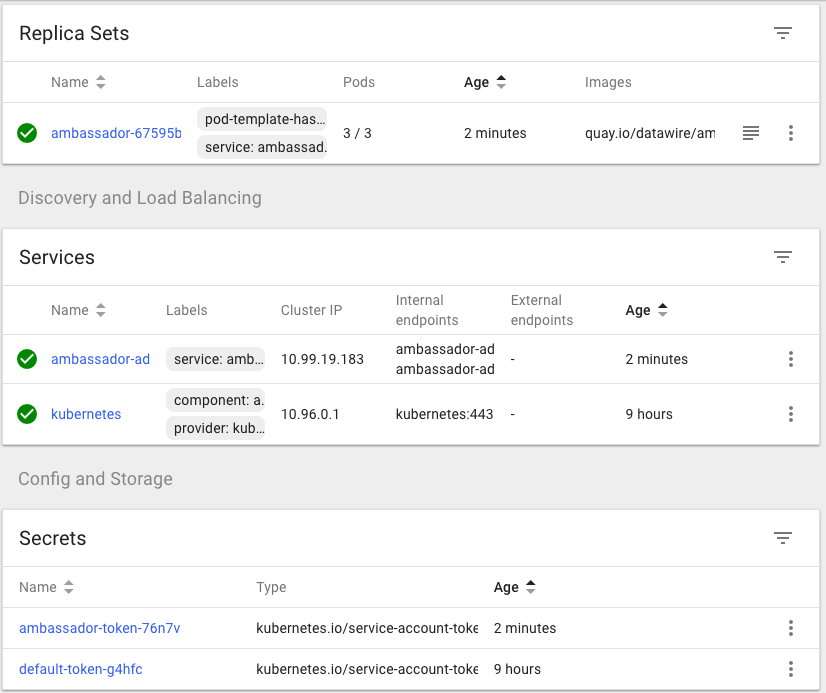
In order to deploy this service, we must create a Kubernetes manifest that specifies the desired end state of the service. For example, the my-service service could be defined as below:
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: my-service
spec:
selector:
app: MyApp
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 9376
Because a Kubernetes service is the fundamental abstraction by which new services are exposed to other services and end users, Ambassador extends the service with custom annotations. For example:
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: my-service
annotations:
getambassador.io/config: |
---
apiVersion: ambassador/v0
kind: Mapping
name: my_service_mapping
prefix: /my-service/
service: my-service
spec:
selector:
app: MyApp
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 9376
Now, we need to create a Kubernetes service to point to the Ambassador deployment. We'll use a LoadBalancer service. If our cluster doesn't support LoadBalancer services, we may want to change to a NodePort or ClusterIP.
As we can see, the routing configuration for Ambassador is associated with each individual service. In other words, with this approach, there is no centralized Ambassador configuration file.
An a practical example, we'll use http://httpbin.org as shown in following ambassador-svc.yaml configuration:
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
service: ambassador
name: ambassador
annotations:
getambassador.io/config: |
---
apiVersion: ambassador/v0
kind: Mapping
name: httpbin_mapping
prefix: /httpbin/
service: httpbin.org:80
host_rewrite: httpbin.org
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
ports:
- name: ambassador
port: 80
targetPort: 80
selector:
service: ambassador
Let's deploy this service to Kubernetes:
$ kubectl apply -f ambassador-svc.yaml service/ambassador created
Envoy is now running on our cluster, along with the Ambassador control plane.
$ kubectl get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE ambassador LoadBalancer 10.100.2.208 <pending> 80:32649/TCP 46s ambassador-admin NodePort 10.99.19.183 <none> 8877:30384/TCP 18h kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 1d
By using Kubernetes annotations, Ambassador integrates transparently into our existing Kubernetes deployment workflow.
Ambassador will detect the change to our Kubernetes annotation and add the route to Envoy. Note that we used a dummy service in this example; typically, we would associate the annotation with our real Kubernetes service.
In order to get access to our microservices through Ambassador, we need an external URL to Ambassador's service interface. Let's start by getting the external IP address of Ambassador. You can get the IP address by running kubectl describe service ambassador and looking at the LoadBalancer Ingress line:
$ kubectl describe service ambassador
Name: ambassador
Namespace: default
Labels: service=ambassador
Annotations: getambassador.io/config:
---
apiVersion: ambassador/v0
kind: Mapping
name: httpbin_mapping
prefix: /httpbin/
service: httpbin.org:80
host_rewrite: httpbin.org
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
{"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Service","metadata":{"annotations":{"getambassador.io/config":"---\napiVersion: ambassador/v0\nkind: Mapping\n...
Selector: service=ambassador
Type: LoadBalancer
IP: 10.100.2.208
Port: ambassador 80/TCP
TargetPort: 80/TCP
NodePort: ambassador 32649/TCP
Endpoints: 172.17.0.7:80,172.17.0.8:80,172.17.0.9:80
Session Affinity: None
External Traffic Policy: Cluster
Events: <none>
On Minikube, we'll need to use minikube service --url ambassador:
minikube service --url ambassador http://192.168.99.100:32649
We can now speak to the httpbin service using Ambassador. Let's send a request via curl, then Ambassador routes the request to the httpbin service:
$ curl $(minikube service --url ambassador)/httpbin/ip
{
"origin": "108.239.135.40"
}
$ curl $(minikube service --url ambassador)/httpbin/user-agent
{
"user-agent": "curl/7.54.0"
}
$ curl $(minikube service --url ambassador)/httpbin/headers
{
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Connection": "close",
"Host": "httpbin.org",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.54.0",
"X-Envoy-Expected-Rq-Timeout-Ms": "3000",
"X-Envoy-Original-Path": "/httpbin/headers"
}
}
Here is the list of URIs of the http://httpbin.org:
- http://httpbin.org/ip Returns Origin IP.
- http://httpbin.org/user-agent Returns user-agent.
- http://httpbin.org/headers Returns header dict.
- http://httpbin.org/get Returns GET data.
- http://httpbin.org/post Returns POST data.
- http://httpbin.org/put Returns PUT data.
- http://httpbin.org/delete Returns DELETE data
- http://httpbin.org/gzip Returns gzip-encoded data.
- http://httpbin.org/status/:code Returns given HTTP Status code.
- http://httpbin.org/response-headers?key=val Returns given response headers.
- http://httpbin.org/redirect/:n 302 Redirects n times.
- http://httpbin.org/relative-redirect/:n 302 Relative redirects n times.
- http://httpbin.org/cookies Returns cookie data.
- http://httpbin.org/cookies/set/:name/:value Sets a simple cookie.
- http://httpbin.org/basic-auth/:user/:passwd Challenges HTTPBasic Auth.
- http://httpbin.org/hidden-basic-auth/:user/:passwd 404'd BasicAuth.
- http://httpbin.org/digest-auth/:qop/:user/:passwd Challenges HTTP Digest Auth.
- http://httpbin.org/stream/:n Streams n–100 lines.
- http://httpbin.org/delay/:n Delays responding for n–10 seconds.
Docker & K8s
- Docker install on Amazon Linux AMI
- Docker install on EC2 Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker container vs Virtual Machine
- Docker install on Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker Hello World Application
- Nginx image - share/copy files, Dockerfile
- Working with Docker images : brief introduction
- Docker image and container via docker commands (search, pull, run, ps, restart, attach, and rm)
- More on docker run command (docker run -it, docker run --rm, etc.)
- Docker Networks - Bridge Driver Network
- Docker Persistent Storage
- File sharing between host and container (docker run -d -p -v)
- Linking containers and volume for datastore
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically I - FROM, MAINTAINER, and build context
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically II - revisiting FROM, MAINTAINER, build context, and caching
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically III - RUN
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically IV - CMD
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically V - WORKDIR, ENV, ADD, and ENTRYPOINT
- Docker - Apache Tomcat
- Docker - NodeJS
- Docker - NodeJS with hostname
- Docker Compose - NodeJS with MongoDB
- Docker - Prometheus and Grafana with Docker-compose
- Docker - StatsD/Graphite/Grafana
- Docker - Deploying a Java EE JBoss/WildFly Application on AWS Elastic Beanstalk Using Docker Containers
- Docker : NodeJS with GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker : Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline with Jenkinsfile and Github
- Docker : Jenkins Master and Slave
- Docker - ELK : ElasticSearch, Logstash, and Kibana
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elasticsearch on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Filebeat on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Logstash on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Kibana on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elastic Stack with Docker Compose
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK) via Elasticsearch operator on minikube
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Stack via Helm on minikube
- Docker Compose - A gentle introduction with WordPress
- Docker Compose - MySQL
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services via docker-compose
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part A (install vault, unsealing, static secrets, and policies)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part B (EaaS, dynamic secrets, leases, and revocation)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part C (Consul)
- Docker Compose with two containers - Flask REST API service container and an Apache server container
- Docker compose : Nginx reverse proxy with multiple containers
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Getting started
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Front Proxy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ambassador - Envoy API Gateway on Kubernetes
- Docker Packer
- Docker Cheat Sheet
- Docker Q & A #1
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part I
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part II
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker II (snapshot app with nginx)
- Docker - NodeJS and MySQL app with React in a docker
- Docker - Step by Step NodeJS and MySQL app with React - I
- Installing LAMP via puppet on Docker
- Docker install via Puppet
- Nginx Docker install via Ansible
- Apache Hadoop CDH 5.8 Install with QuickStarts Docker
- Docker - Deploying Flask app to ECS
- Docker Compose - Deploying WordPress to AWS
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI EC2 type)
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI Fargate type)
- Docker - ECS Fargate
- Docker - AWS ECS service discovery with Flask and Redis
- Docker & Kubernetes : minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes 2 : minikube Django with Postgres - persistent volume
- Docker & Kubernetes 3 : minikube Django with Redis and Celery
- Docker & Kubernetes 4 : Django with RDS via AWS Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kops on AWS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ingress controller on AWS with Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul - Auto-unseal using Transit Secrets Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes & Persistent Volumes Claims - hostPath and annotations
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes - Dynamic volume provisioning
- Docker & Kubernetes : DaemonSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Secrets
- Docker & Kubernetes : kubectl command
- Docker & Kubernetes : Assign a Kubernetes Pod to a particular node in a Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : Configure a Pod to Use a ConfigMap
- AWS : EKS (Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Run a React app in a minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Minikube install on AWS EC2
- Docker & Kubernetes : Cassandra with a StatefulSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Terraform and AWS EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Pods and Service definitions
- Docker & Kubernetes : Service IP and the Service Type
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes DNS with Pods and Services
- Docker & Kubernetes : Headless service and discovering pods
- Docker & Kubernetes : Scaling and Updating application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Horizontal pod autoscaler on minikubes
- Docker & Kubernetes : From a monolithic app to micro services on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Rolling updates
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deployments to GKE (Rolling update, Canary and Blue-green deployments)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Slack Chat Bot with NodeJS on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery with Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline for Dev, Canary, and Production Environments on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : NodePort vs LoadBalancer vs Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB / MongoExpress on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Load Testing with Locust on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB with StatefulSets on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up Ingress with NGINX Controller on Minikube (Mac)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller for Dashboard service on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Ingress with AWS ALB Ingress Controller in EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up a private cluster on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Namespaces (default, kube-public, kube-system) and switching namespaces (kubens)
- Docker & Kubernetes : StatefulSets on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : RBAC
- Docker & Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, and IAM
- Docker & Kubernetes - Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, IAM with EKS ALB, Part 1
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : My first Helm deploy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Readiness and Liveness Probes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm chart repository with Github pages
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB with Ingress to Minikube using Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 2 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 3 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart for Node/Express and MySQL with Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using Helm and Prometheus Operator - Monitoring Kubernetes node resources out of the box
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using kube-prometheus-stack Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio (service mesh) sidecar proxy on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on Minikube with AWS EC2 for Bookinfo Application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part I)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part II - Prometheus, Grafana, pin a service, split traffic, and inject faults)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Package Manager with MySQL on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying Memcached on Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : EKS Control Plane (API server) Metrics with Prometheus
- Docker & Kubernetes : Spinnaker on EKS with Halyard
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery Pipelines with Spinnaker and Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-dind (docker-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-kind (k8s-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : nodeSelector, nodeAffinity, taints/tolerations, pod affinity and anti-affinity - Assigning Pods to Nodes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Jenkins-X on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD App of Apps with Heml on Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD on Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : GitOps with ArgoCD for Continuous Delivery to Kubernetes clusters (minikube) - guestbook
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization