Docker & Kubernetes : Terraform and AWS EKS
The Amazon EKS service allows us to manage Kubernetes servers. We will see how to create/destroy a sample Kubernetes architecture in AWS using Terraform.
The sample architecture includes the following resources:
- EKS Cluster: AWS managed Kubernetes cluster of master servers
- AutoScaling Group containing 2 m4.large instances based on the latest EKS Amazon Linux 2 AMI: Operator managed Kubernetes worker nodes for running Kubernetes service deployments
- Associated VPC, Internet Gateway, Security Groups, and Subnets: Operator managed networking resources for the EKS Cluster and worker node instances
- Associated IAM Roles and Policies: Operator managed access resources for EKS and worker node instances
We can create Kubernetes cluster using Getting Started with AWS EKS, however, in this post, we'll use community created Terraform module to launch and configure our EKS cluster and nodes.
Let's clone the community terraform module for EKS, terraform-aws-eks:
$ git clone https://github.com/WesleyCharlesBlake/terraform-aws-eks.git $ cd terraform-aws-eks
Let's make sure we have a working Terraform binary:
$ terraform version Terraform v0.11.10 + provider.aws v1.48.0 + provider.http v1.0.1 Your version of Terraform is out of date! The latest version is 0.11.10. You can update by downloading from www.terraform.io/downloads.html
If not installed, we need to download the Terraform binary (Download Terraform). On Mac:
$ brew update && brew install terraform
The Heptio Authenticator is used to integrate our AWS IAM settings with our Kubernetes RBAC permissions.
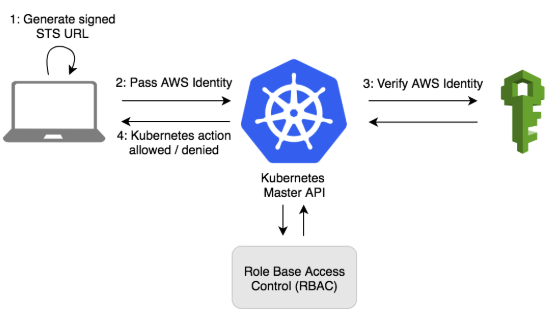
Picture from https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/opensource/deploying-heptio-authenticator-kops/
To install this, run the following from a terminal:
$ curl -o aws-iam-authenticator https://amazon-eks.s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/1.10.3/2018-07-26/bin/darwin/amd64/aws-iam-authenticator
Apply execute permissions to the binary:
$ chmod +x ./aws-iam-authenticator
Copy the binary to a folder in the $PATH. We recommend creating a $HOME/bin/aws-iam-authenticator and ensuring that $HOME/bin comes first in the $PATH:
$ cp ./aws-iam-authenticator $HOME/bin/aws-iam-authenticator && export PATH=$HOME/bin:$PATH
Add $HOME/bin to your PATH environment variable. For Bash shells on macOS:
$ echo 'export PATH=$HOME/bin:$PATH' >> ~/.bash_profile
Test that the aws-iam-authenticator binary works:
$ source ~/.bash_profile $ aws-iam-authenticator help A tool to authenticate to Kubernetes using AWS IAM credentials ...
In order to create an EKS cluster using Terraform, we need to configure the AWS provider by adding the provider to the Terraform configuration file (provider.tf):
provider "aws" {
region = "${var.aws_region}"
profile = "eks"
}
The region variable is stored in vars.tf:
variable "aws_region" {
description = "US EAST Virginia"
default = "us-east-1"
}
Actually, the provider needs AWS credentials via environment variables:
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID={AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID_HERE}
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY={AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY_HERE}
If the env vars are not provided, Terraform will get them from credentials file, $HOME/.aws/credentials:
[eks] aws_access_key_id = AK...5Q aws_secret_access_key = KL...jb
Let's start by initializing the Terraform state:
$ terraform init Initializing modules... - module.eks ... * provider.aws: version = "~> 1.48" * provider.http: version = "~> 1.0" Terraform has been successfully initialized! ...
Plan our deployment:
$ terraform plan -var 'cluster-name=eks-demo-cluster' -var 'desired-capacity=2' -out eks-demo-cluster-output
...
Terraform will perform the following actions:
+ module.eks.aws_autoscaling_group.eks
+ module.eks.aws_eks_cluster.eks
+ module.eks.aws_iam_instance_profile.node
+ module.eks.aws_iam_role.cluster
+ module.eks.aws_iam_role.node
+ module.eks.aws_iam_role_policy_attachment.cluster-AmazonEKSClusterPolicy
+ module.eks.aws_iam_role_policy_attachment.cluster-AmazonEKSServicePolicy
+ module.eks.aws_iam_role_policy_attachment.node-AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnly
+ module.eks.aws_iam_role_policy_attachment.node-AmazonEKSWorkerNodePolicy
+ module.eks.aws_iam_role_policy_attachment.node-AmazonEKS_CNI_Policy
+ module.eks.aws_internet_gateway.eks
+ module.eks.aws_launch_configuration.eks
+ module.eks.aws_route_table.eks
+ module.eks.aws_route_table_association.eks[0]
+ module.eks.aws_route_table_association.eks[1]
+ module.eks.aws_security_group.cluster
+ module.eks.aws_security_group.node
+ module.eks.aws_security_group_rule.cluster-ingress-node-https
+ module.eks.aws_security_group_rule.cluster-ingress-workstation-https
+ module.eks.aws_security_group_rule.node-ingress-cluster
+ module.eks.aws_security_group_rule.node-ingress-self
+ module.eks.aws_subnet.eks[0]
+ module.eks.aws_subnet.eks[1]
+ module.eks.aws_vpc.eks
...
Plan: 24 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
This plan was saved to: eks-demo-cluster-output
To perform exactly these actions, run the following command to apply:
terraform apply "eks-demo-cluster-output"
Apply that plan:
$ terraform apply "eks-demo-cluster-output"
Once the cluster running, we need to create the KubeConfig file that will be used to manage the cluster.
The terraform module stores the kubeconfig information in it's state store. We can view it with the following command:
$ terraform output kubeconfig
Actually, we saw the same output from the "terraform apply ..." command.
And we can save it for use with the following command:
$ terraform output kubeconfig > ${HOME}/.kube/config-eks-demo-cluster-tf
Then, we may want to add this new config to the kubectl config list:
$ export KUBECONFIG=${HOME}/.kube/config-eks-demo-cluster-tf:${HOME}/.kube/config
$ echo "export KUBECONFIG=${KUBECONFIG}" >> ${HOME}/.bash_profile
Update the Kube config:
$ aws eks update-kubeconfig --name eks-demo-cluster Added new context arn:aws:eks:us-east-1:***:cluster/eks-demo-cluster to /Users/kihyuckhong/.kube/config-eks-demo-cluster-tf
The terraform state also contains a config-map we can use for our EKS workers.
View the configmap:
$ terraform output config-map
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: aws-auth
namespace: kube-system
data:
mapRoles: |
- rolearn: arn:aws:iam::***:role/eks-demo-cluster-eks-node-role
username: system:node:{{EC2PrivateDNSName}}
groups:
- system:bootstrappers
- system:nodes
Save the config-map:
$ terraform output config-map > /tmp/config-map-aws-auth.yml
Apply the config-map:
$ kubectl apply -f /tmp/config-map-aws-auth.yml configmap/aws-auth created
Confirm our cluster Nodes:
$ kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION ip-10-0-0-173.ec2.internal Ready <none> 2m v1.10.3 ip-10-0-1-97.ec2.internal Ready <none> 2m v1.10.3
We now have a fully working Amazon EKS Cluster that is ready to use!
The official Kubernetes dashboard is not deployed by default. However, we can deploy the dashboard with the kubectl command:
$ kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/master/src/deploy/recommended/kubernetes-dashboard.yaml secret/kubernetes-dashboard-certs created serviceaccount/kubernetes-dashboard created role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard-minimal created rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard-minimal created deployment.apps/kubernetes-dashboard created service/kubernetes-dashboard created
Since this is deployed to our private cluster, we need to access it via a proxy. Kube-proxy is available to proxy our requests to the dashboard service. Let's run the following command:
$ kubectl proxy --port=8080 --address='0.0.0.0' --disable-filter=true W1126 16:14:15.144712 63279 proxy.go:140] Request filter disabled, your proxy is vulnerable to XSRF attacks, please be cautious Starting to serve on [::]:8080
This will start the proxy, listen on port 8080, listen on all interfaces, and will disable the filtering of non-localhost requests.
While leaving the proxy running in our current terminal tab, we may want to open a new terminal tab to continue.
Authentication is normally handled by reading the local kubectl file, but our kubectl authentication is plugin based. So, we are going to grant Admin privileges to the Dashboard Service Account while granting admin privileges to Dashboard's Service Account might be a security risk.
First we will deploy the deployment file, dashboard-admin.yaml:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: kubernetes-dashboard
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: kubernetes-dashboard
namespace: kube-system
We can now deploy it to our cluster:
$ kubectl create -f dashboard-admin.yaml clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created
The dashboard can now be accessed from:
http://localhost:8080/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/https:kubernetes-dashboard:/proxy/
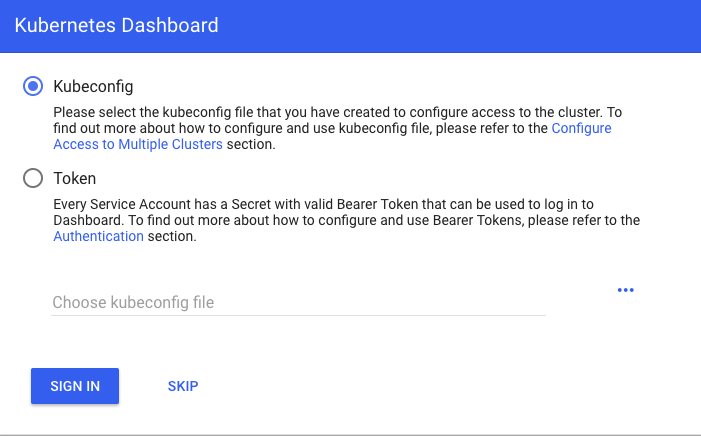
Select "Skip":
We need RDS Postgres since we're not containerizing it in this post.
See how we want to set it up : Docker & Kubernetes 4 : Django with RDS via AWS Kops
Our Django app can be deployed with "kubectl" command:
$ cd deploy $ kubectl apply -f rds/ secret/postgres-credentials created service/postgres-service created $ kubectl apply -f redis/ deployment.apps/redis created service/redis-service created $ kubectl apply -f django/ deployment.apps/django created job.batch/django-migrations created service/django-service created $ kubectl apply -f celery/ deployment.apps/celery-beat created deployment.apps/celery-worker created
Now we can see the container and pods from Kube dashboard.
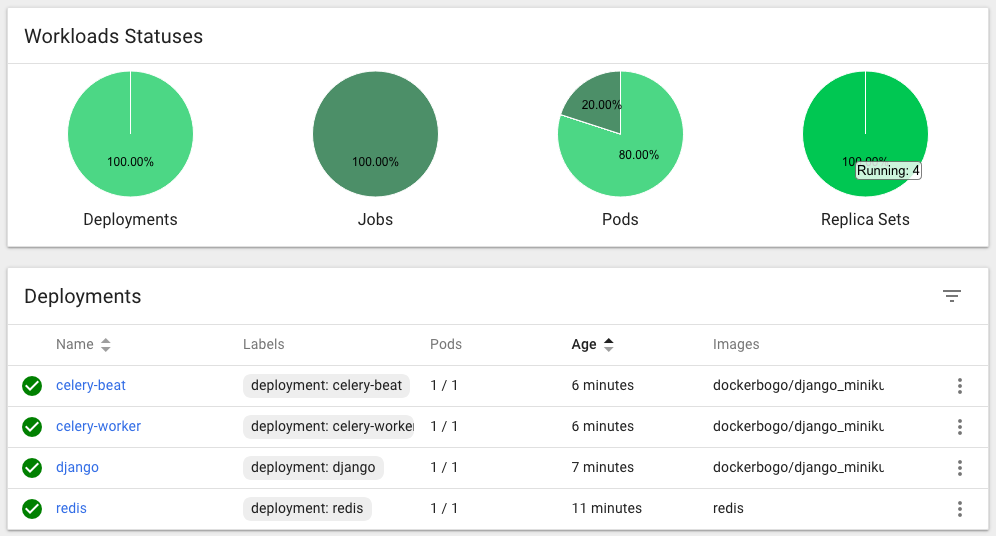
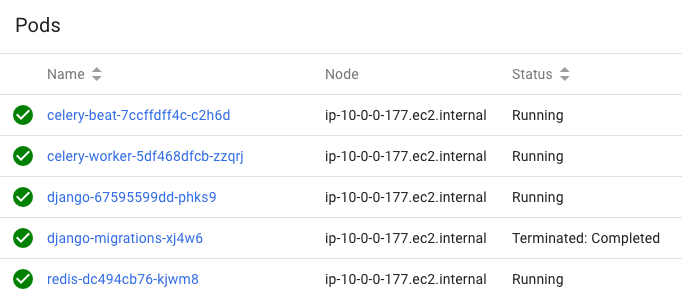
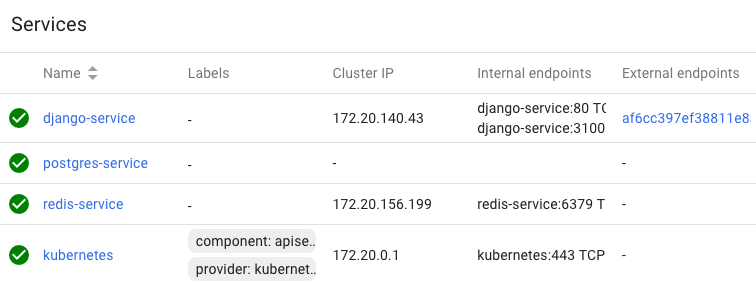
How can we access our Django App?
We need to retrieve the Load balancer endpoint which is in the row of the django-service. Just click it.
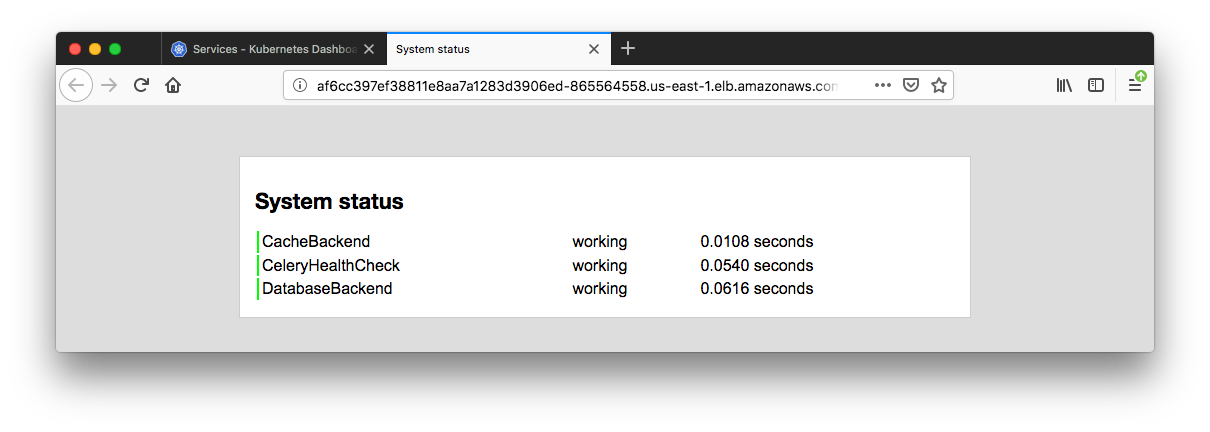
To delete the resources created for this EKS cluster, run the following commands.
View the plan:
$ terraform plan -destroy -out eks-demo-cluster-destroy-tf
Execute the plan:
$ terraform apply "eks-demo-cluster-destroy-tf"
terraform modules:
Amazon EKS Workshop > Launch using Terraform > Get Terraform Module
I used the module but got an error of getting ipv6 instead of ipv4 address:
* module.eks.aws_security_group_rule.cluster-ingress-workstation-https: "cidr_blocks.0" must contain a valid network CIDR, got "2600:1700:38d0:3e60:8c72:8bc4:ab29:80bc/32"
Fix (modules/eks/workstation-external-ip.tf):
# Workstation External IP
data "http" "workstation-external-ip" {
#url = "http://icanhazip.com" . =>
url = "http://ipv4.icanhazip.com"
}
locals {
workstation-external-cidr = "${chomp(data.http.workstation-external-ip.body)}/32"
}
The fixed module and Django app are available from terraform-aws-eks/
Note: got another error which appeared to be related to the instance type and cni. So, I switched the type to t2.medium from t2.micro:
Failed create pod sandbox: rpc error: code = Unknown desc = NetworkPlugin cni failed to set up pod "django-migrations-s6m64_default" network: add cmd: failed to assign an IP address to container
Docker & K8s
- Docker install on Amazon Linux AMI
- Docker install on EC2 Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker container vs Virtual Machine
- Docker install on Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker Hello World Application
- Nginx image - share/copy files, Dockerfile
- Working with Docker images : brief introduction
- Docker image and container via docker commands (search, pull, run, ps, restart, attach, and rm)
- More on docker run command (docker run -it, docker run --rm, etc.)
- Docker Networks - Bridge Driver Network
- Docker Persistent Storage
- File sharing between host and container (docker run -d -p -v)
- Linking containers and volume for datastore
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically I - FROM, MAINTAINER, and build context
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically II - revisiting FROM, MAINTAINER, build context, and caching
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically III - RUN
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically IV - CMD
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically V - WORKDIR, ENV, ADD, and ENTRYPOINT
- Docker - Apache Tomcat
- Docker - NodeJS
- Docker - NodeJS with hostname
- Docker Compose - NodeJS with MongoDB
- Docker - Prometheus and Grafana with Docker-compose
- Docker - StatsD/Graphite/Grafana
- Docker - Deploying a Java EE JBoss/WildFly Application on AWS Elastic Beanstalk Using Docker Containers
- Docker : NodeJS with GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker : Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline with Jenkinsfile and Github
- Docker : Jenkins Master and Slave
- Docker - ELK : ElasticSearch, Logstash, and Kibana
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elasticsearch on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Filebeat on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Logstash on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Kibana on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elastic Stack with Docker Compose
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK) via Elasticsearch operator on minikube
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Stack via Helm on minikube
- Docker Compose - A gentle introduction with WordPress
- Docker Compose - MySQL
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services via docker-compose
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part A (install vault, unsealing, static secrets, and policies)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part B (EaaS, dynamic secrets, leases, and revocation)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part C (Consul)
- Docker Compose with two containers - Flask REST API service container and an Apache server container
- Docker compose : Nginx reverse proxy with multiple containers
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Getting started
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Front Proxy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ambassador - Envoy API Gateway on Kubernetes
- Docker Packer
- Docker Cheat Sheet
- Docker Q & A #1
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part I
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part II
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker II (snapshot app with nginx)
- Docker - NodeJS and MySQL app with React in a docker
- Docker - Step by Step NodeJS and MySQL app with React - I
- Installing LAMP via puppet on Docker
- Docker install via Puppet
- Nginx Docker install via Ansible
- Apache Hadoop CDH 5.8 Install with QuickStarts Docker
- Docker - Deploying Flask app to ECS
- Docker Compose - Deploying WordPress to AWS
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI EC2 type)
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI Fargate type)
- Docker - ECS Fargate
- Docker - AWS ECS service discovery with Flask and Redis
- Docker & Kubernetes : minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes 2 : minikube Django with Postgres - persistent volume
- Docker & Kubernetes 3 : minikube Django with Redis and Celery
- Docker & Kubernetes 4 : Django with RDS via AWS Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kops on AWS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ingress controller on AWS with Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul - Auto-unseal using Transit Secrets Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes & Persistent Volumes Claims - hostPath and annotations
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes - Dynamic volume provisioning
- Docker & Kubernetes : DaemonSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Secrets
- Docker & Kubernetes : kubectl command
- Docker & Kubernetes : Assign a Kubernetes Pod to a particular node in a Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : Configure a Pod to Use a ConfigMap
- AWS : EKS (Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Run a React app in a minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Minikube install on AWS EC2
- Docker & Kubernetes : Cassandra with a StatefulSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Terraform and AWS EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Pods and Service definitions
- Docker & Kubernetes : Service IP and the Service Type
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes DNS with Pods and Services
- Docker & Kubernetes : Headless service and discovering pods
- Docker & Kubernetes : Scaling and Updating application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Horizontal pod autoscaler on minikubes
- Docker & Kubernetes : From a monolithic app to micro services on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Rolling updates
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deployments to GKE (Rolling update, Canary and Blue-green deployments)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Slack Chat Bot with NodeJS on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery with Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline for Dev, Canary, and Production Environments on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : NodePort vs LoadBalancer vs Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB / MongoExpress on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Load Testing with Locust on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB with StatefulSets on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up Ingress with NGINX Controller on Minikube (Mac)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller for Dashboard service on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Ingress with AWS ALB Ingress Controller in EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up a private cluster on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Namespaces (default, kube-public, kube-system) and switching namespaces (kubens)
- Docker & Kubernetes : StatefulSets on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : RBAC
- Docker & Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, and IAM
- Docker & Kubernetes - Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, IAM with EKS ALB, Part 1
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : My first Helm deploy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Readiness and Liveness Probes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm chart repository with Github pages
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB with Ingress to Minikube using Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 2 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 3 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart for Node/Express and MySQL with Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using Helm and Prometheus Operator - Monitoring Kubernetes node resources out of the box
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using kube-prometheus-stack Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio (service mesh) sidecar proxy on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on Minikube with AWS EC2 for Bookinfo Application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part I)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part II - Prometheus, Grafana, pin a service, split traffic, and inject faults)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Package Manager with MySQL on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying Memcached on Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : EKS Control Plane (API server) Metrics with Prometheus
- Docker & Kubernetes : Spinnaker on EKS with Halyard
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery Pipelines with Spinnaker and Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-dind (docker-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-kind (k8s-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : nodeSelector, nodeAffinity, taints/tolerations, pod affinity and anti-affinity - Assigning Pods to Nodes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Jenkins-X on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD App of Apps with Heml on Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD on Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : GitOps with ArgoCD for Continuous Delivery to Kubernetes clusters (minikube) - guestbook
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization