Docker - ELK 7.6 : Filebeat

Elastic Stack docker/kubernetes series:
Filebeat is a lightweight shipper for forwarding and centralizing log data. Installed as an agent on our servers, Filebeat monitors the log files or locations that we specify, collects log events, and forwards them either to Elasticsearch or Logstash for indexing.
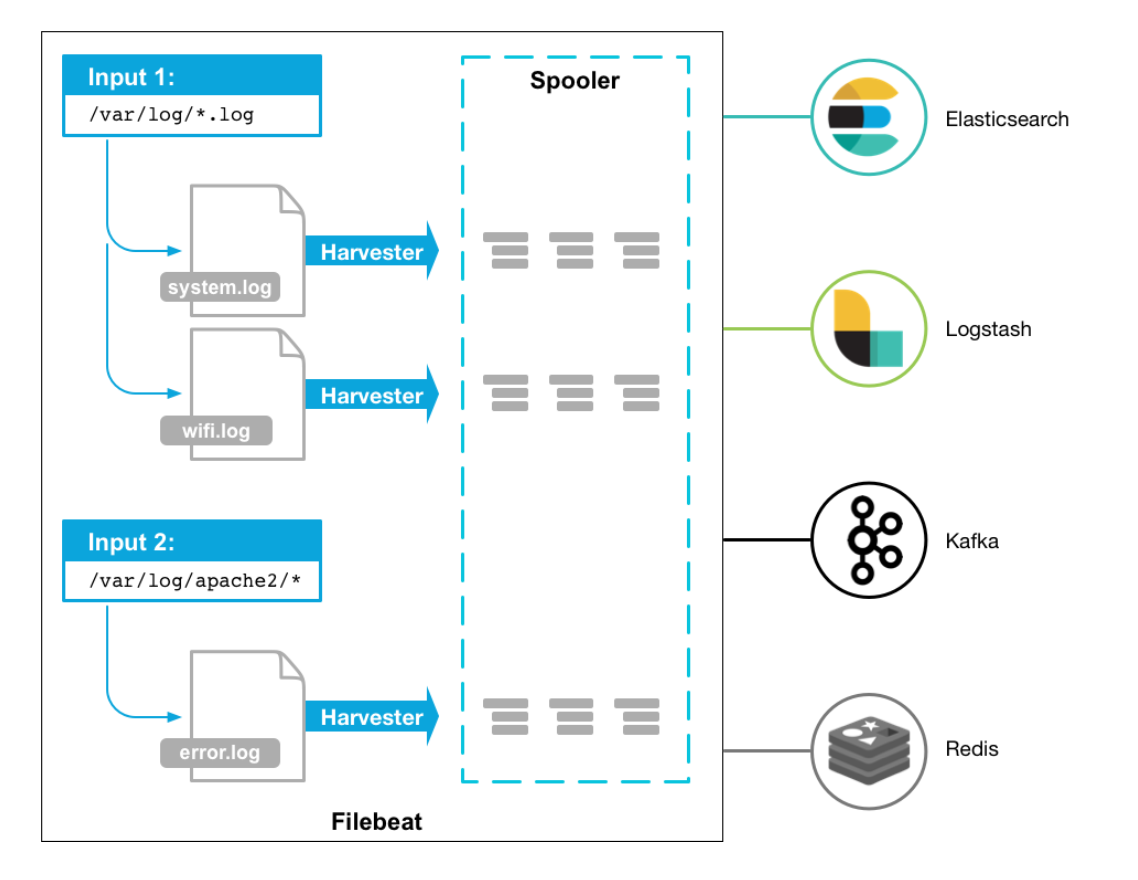
source: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/current/how-filebeat-works.html
Filebeat is one of the best log file shippers out there today — it’s lightweight, supports SSL and TLS encryption, supports back pressure with a good built-in recovery mechanism (it records the last successful line indexed in the registry, so in case of network issues or interruptions in transmissions, remembers where it left off when re-establishing a connection). However, it cannot, in most cases, turn our logs into easy-to-analyze structured log messages using filters for log enhancements. That's the role played by Logstash. That's why we will almost always need to use Filebeat and Logstashin tandem. Filebeat (log files), and the other members of the Beats family (Packetbeat: network metrics), Metricbeat: server metrics), acts as a lightweight agent deployed on the edge host, pumping data into Logstash for aggregation, filtering and enrichment.
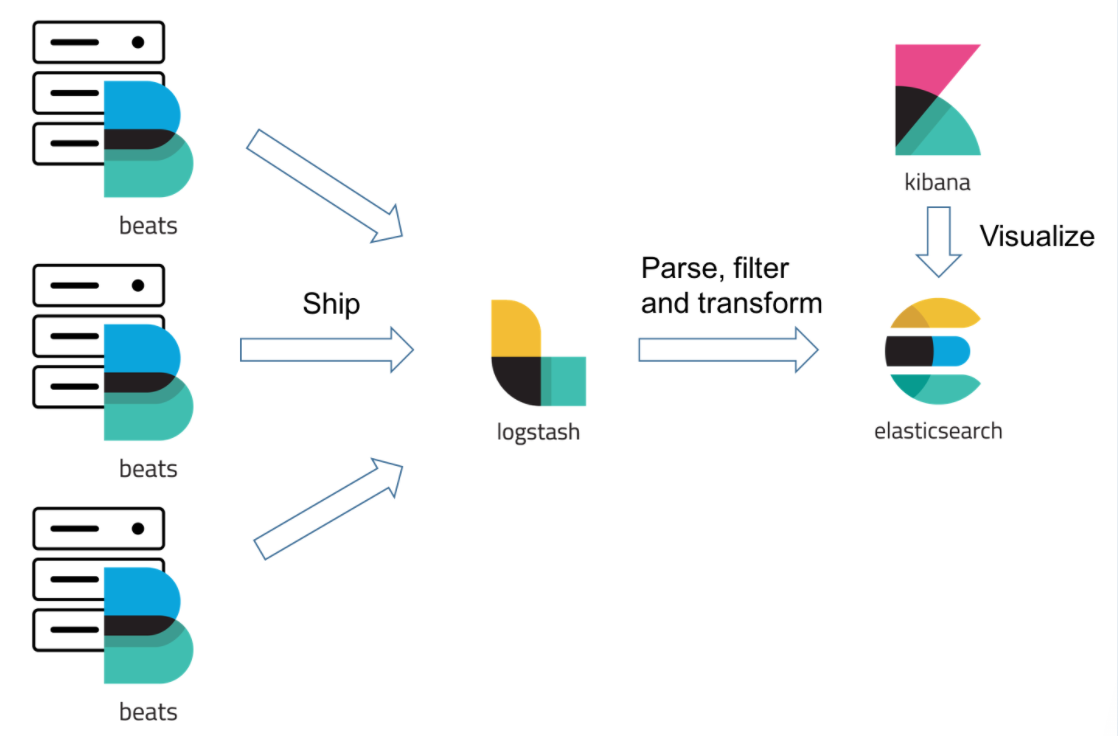
We can ship logs on hosts via Filebeat directly into Elasticsearch. Since Filebeat ships data in JSON format, Elasticsearch should be able to parse the timestamp and message fields without too much hassle. However, adding context to the log messages by parsing them up into separate fields, filtering out unwanted bits of data and enriching others — cannot be handled without Logstash.
When we start Filebeat, it starts one or more inputs that look in the locations we've specified for log data. For each log that Filebeat locates, Filebeat starts a harvester. Each harvester reads a single log for new content and sends the new log data to libbeat, which aggregates the events and sends the aggregated data to the output that we've configured for Filebeat.
Filebeat is available as Docker images. The images use centos:7 as the base image.
A list of all published Docker images and tags is available at www.docker.elastic.co.
Issue a docker pull command against the Elastic Docker registry:
$ docker pull docker.elastic.co/beats/filebeat:7.6.2
For the latest updates on working with Elastic stack and Filebeat, skip this and please check Docker - ELK 7.6 : Logstash on Centos 7.
As discussed earlier, the filebeat can directly ship logs to elasticsearch bypassing optional Logstash. So, we need to make sure that the "elasticsearch" and "kibana" containers are running with dokcer network (here, "mynetwork"):
$ docker network create mynetwork --driver bridge $ docker run -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 --net=mynetwork --name elasticsearch -e "discovery.type=single-node" docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.6.2 $ docker run --name kibana --net=mynetwork -p 5601:5601 kibana:7.6.2 $ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 07d4880601e6 kibana:7.6.2 "/usr/local/bin/dumb…" 2 hours ago Up 2 hours 0.0.0.0:5601->5601/tcp kibana 3602c16cd3b1 docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.6.2 "/usr/local/bin/dock…" 3 hours ago Up 3 hours 0.0.0.0:9200->9200/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9300->9300/tcp elasticsearch
Running Filebeat with the setup command will create the index pattern and load visualizations , dashboards, and machine learning jobs. Run this command:
$ docker run --net=mynetwork --name filebeat docker.elastic.co/beats/filebeat:7.6.2 setup -E setup.kibana.host=kibana:5601 -E output.elasticsearch.hosts=["elasticsearch:9200"] Overwriting ILM policy is disabled. Set `setup.ilm.overwrite:true` for enabling. Index setup finished. Loading dashboards (Kibana must be running and reachable) Loaded dashboards Setting up ML using setup --machine-learning is going to be removed in 8.0.0. Please use the ML app instead. See more: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elastic-stack-overview/current/xpack-ml.html Loaded machine learning job configurations Loaded Ingest pipelines
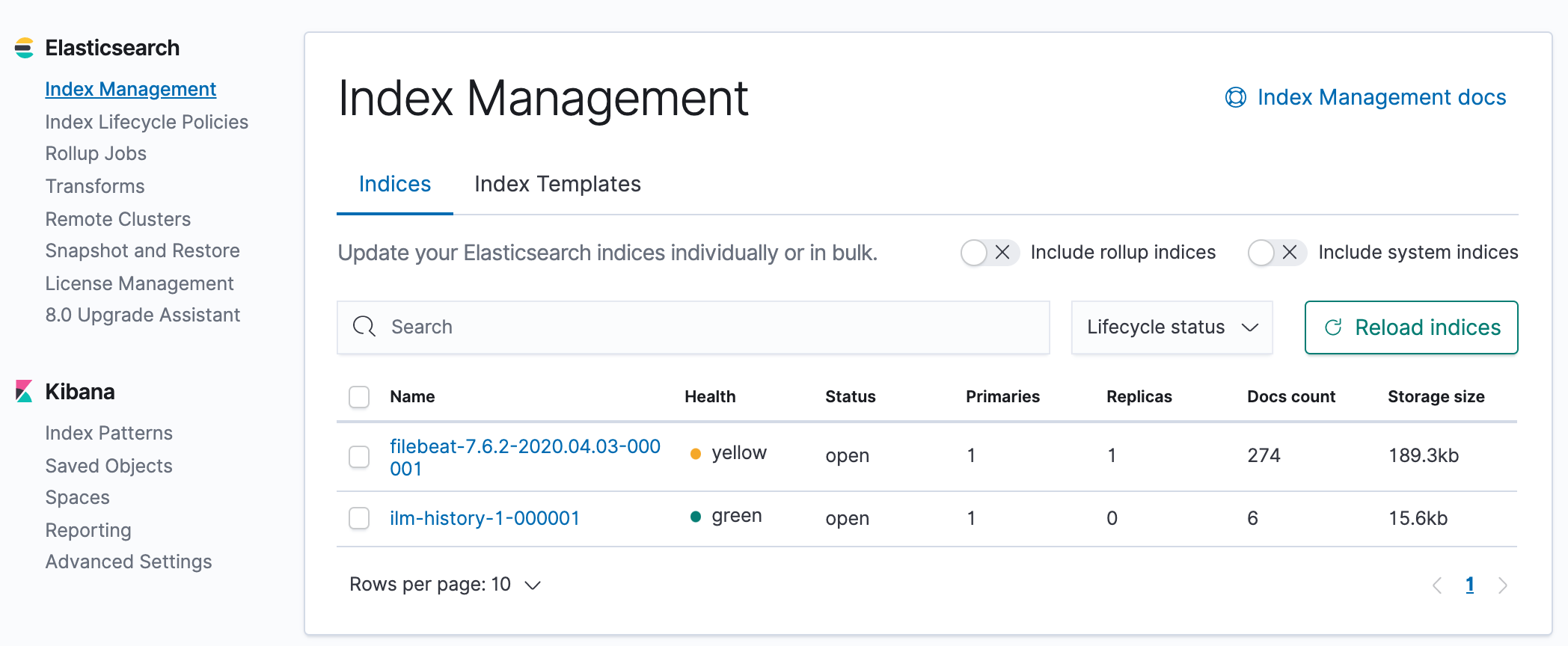
Now, we can check the beat is in Kibana:
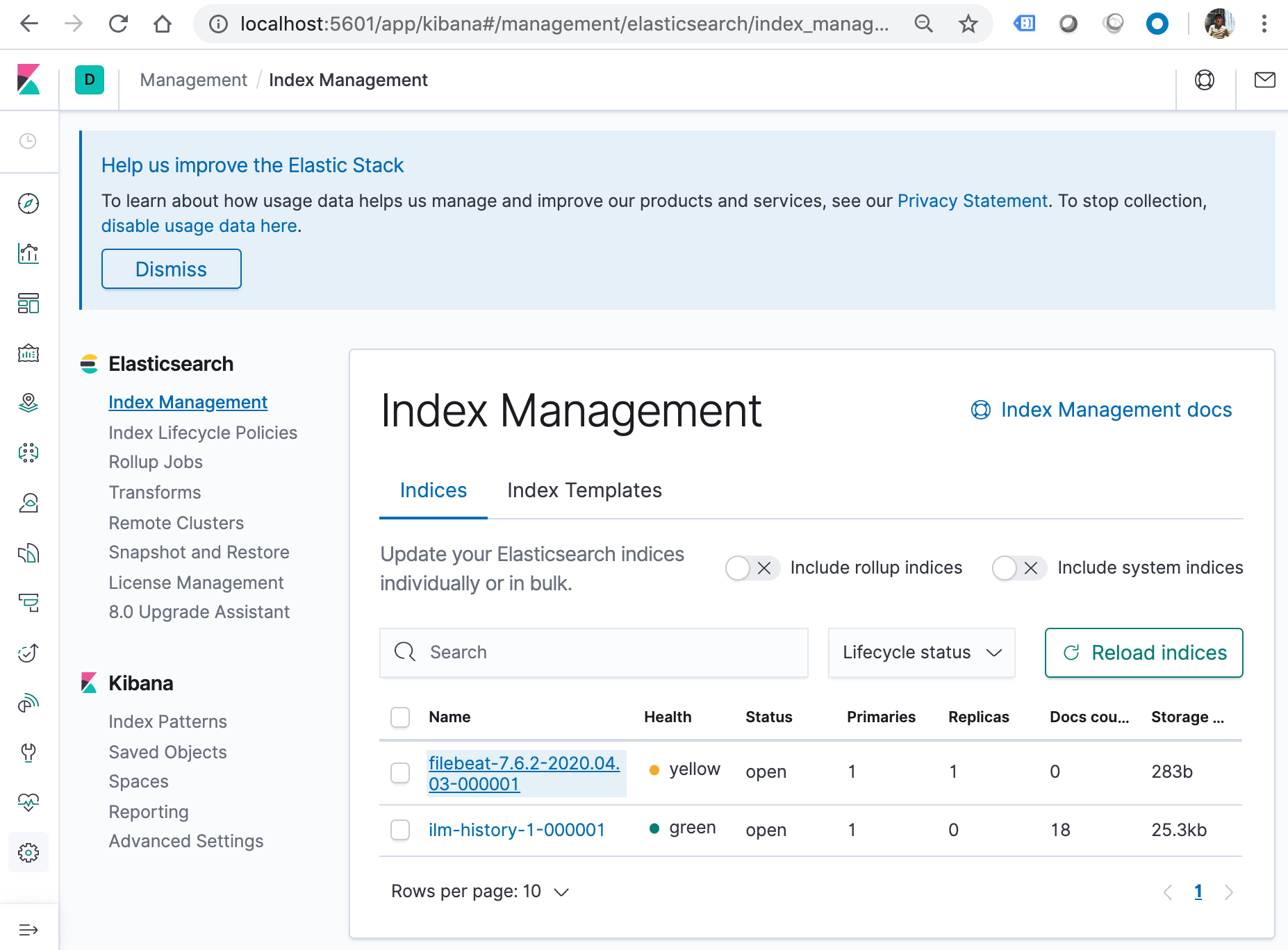
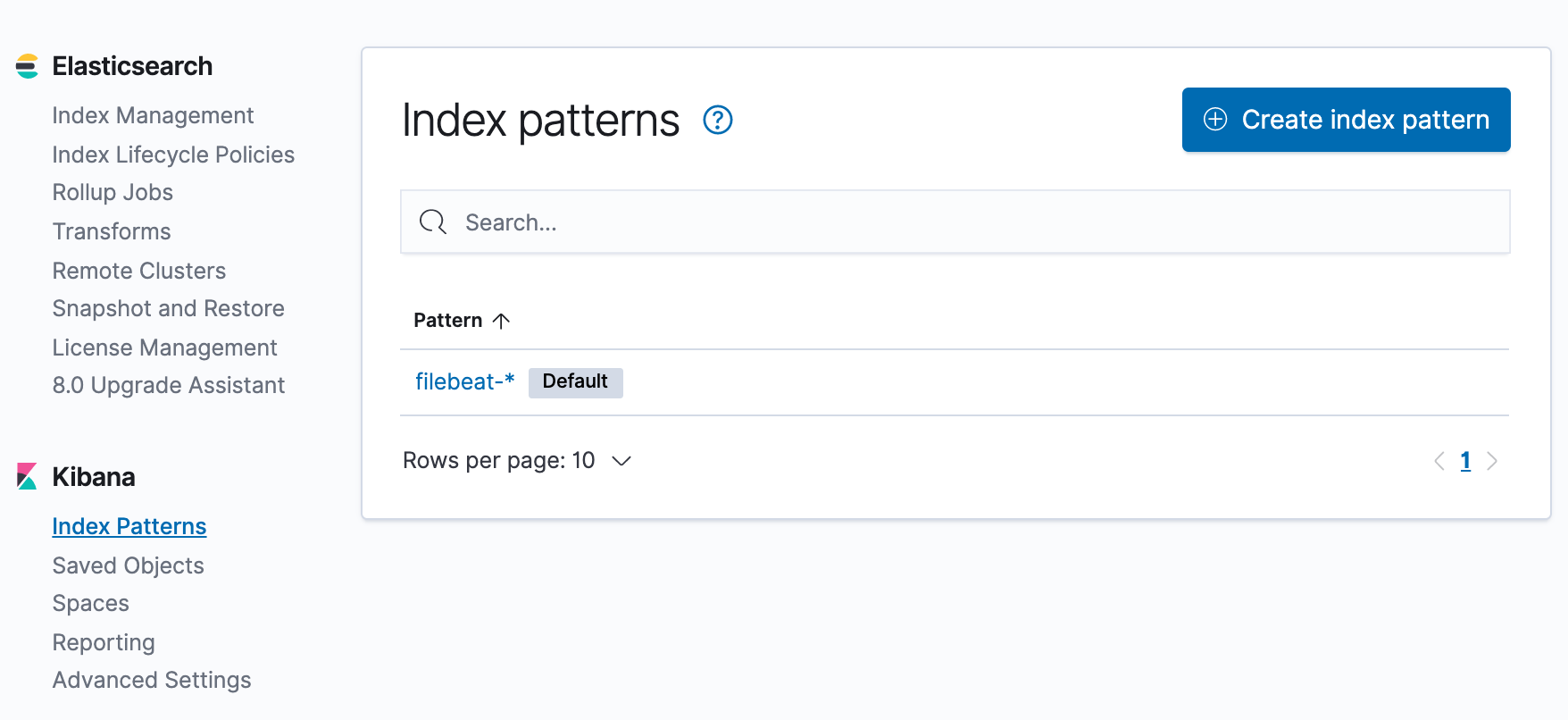
The Docker image provides several methods for configuring Filebeat. The conventional approach is to provide a configuration file via a volume mount, but it's also possible to create a custom image with our configuration included.
Download an example configuration file as a starting point:
$ curl -L -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/elastic/beats/7.6/deploy/docker/filebeat.docker.yml
$ cat filebeat.docker.yml
filebeat.config:
modules:
path: ${path.config}/modules.d/*.yml
reload.enabled: false
filebeat.autodiscover:
providers:
- type: docker
hints.enabled: true
processors:
- add_cloud_metadata: ~
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: '${ELASTICSEARCH_HOSTS:localhost:9200}'
username: '${ELASTICSEARCH_USERNAME:}'
password: '${ELASTICSEARCH_PASSWORD:}'
To test this works, we may want to restart the other containers ("elasticsearch" and "kibana"):
We'll configure Filebeat on Docker by providing the filebeat.docker.yml via a volume mount. With docker run, the volume mount can be specified like this:
$ docker run -d \ --name=filebeat \ --user=root \ --network=mynetwork \ --volume="$(pwd)/filebeat.docker.yml:/usr/share/filebeat/filebeat.yml:ro" \ --volume="/var/lib/docker/containers:/var/lib/docker/containers:ro" \ --volume="/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro" \ docker.elastic.co/beats/filebeat:7.6.2 filebeat -e -strict.perms=false \ -E output.elasticsearch.hosts=["elasticsearch:9200"] 944f1aa052cf109332a31f8ab1685d8455299ba8fdd260ba14e3990fb6e995b9 $ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 944f1aa052cf docker.elastic.co/beats/filebeat:7.6.2 "/usr/local/bin/dock…" 6 minutes ago Up 6 minutes filebeat 49673f99c7d1 kibana:7.6.2 "/usr/local/bin/dumb…" 13 minutes ago Up 13 minutes 0.0.0.0:5601->5601/tcp kibana 8fc7a98f6fc9 docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.6.2 "/usr/local/bin/dock…" 13 minutes ago Up 13 minutes 0.0.0.0:9200->9200/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9300->9300/tcp elasticsearch
Docker & K8s
- Docker install on Amazon Linux AMI
- Docker install on EC2 Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker container vs Virtual Machine
- Docker install on Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker Hello World Application
- Nginx image - share/copy files, Dockerfile
- Working with Docker images : brief introduction
- Docker image and container via docker commands (search, pull, run, ps, restart, attach, and rm)
- More on docker run command (docker run -it, docker run --rm, etc.)
- Docker Networks - Bridge Driver Network
- Docker Persistent Storage
- File sharing between host and container (docker run -d -p -v)
- Linking containers and volume for datastore
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically I - FROM, MAINTAINER, and build context
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically II - revisiting FROM, MAINTAINER, build context, and caching
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically III - RUN
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically IV - CMD
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically V - WORKDIR, ENV, ADD, and ENTRYPOINT
- Docker - Apache Tomcat
- Docker - NodeJS
- Docker - NodeJS with hostname
- Docker Compose - NodeJS with MongoDB
- Docker - Prometheus and Grafana with Docker-compose
- Docker - StatsD/Graphite/Grafana
- Docker - Deploying a Java EE JBoss/WildFly Application on AWS Elastic Beanstalk Using Docker Containers
- Docker : NodeJS with GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker : Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline with Jenkinsfile and Github
- Docker : Jenkins Master and Slave
- Docker - ELK : ElasticSearch, Logstash, and Kibana
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elasticsearch on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Filebeat on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Logstash on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Kibana on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elastic Stack with Docker Compose
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK) via Elasticsearch operator on minikube
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Stack via Helm on minikube
- Docker Compose - A gentle introduction with WordPress
- Docker Compose - MySQL
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services via docker-compose
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part A (install vault, unsealing, static secrets, and policies)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part B (EaaS, dynamic secrets, leases, and revocation)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part C (Consul)
- Docker Compose with two containers - Flask REST API service container and an Apache server container
- Docker compose : Nginx reverse proxy with multiple containers
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Getting started
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Front Proxy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ambassador - Envoy API Gateway on Kubernetes
- Docker Packer
- Docker Cheat Sheet
- Docker Q & A #1
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part I
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part II
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker II (snapshot app with nginx)
- Docker - NodeJS and MySQL app with React in a docker
- Docker - Step by Step NodeJS and MySQL app with React - I
- Installing LAMP via puppet on Docker
- Docker install via Puppet
- Nginx Docker install via Ansible
- Apache Hadoop CDH 5.8 Install with QuickStarts Docker
- Docker - Deploying Flask app to ECS
- Docker Compose - Deploying WordPress to AWS
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI EC2 type)
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI Fargate type)
- Docker - ECS Fargate
- Docker - AWS ECS service discovery with Flask and Redis
- Docker & Kubernetes : minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes 2 : minikube Django with Postgres - persistent volume
- Docker & Kubernetes 3 : minikube Django with Redis and Celery
- Docker & Kubernetes 4 : Django with RDS via AWS Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kops on AWS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ingress controller on AWS with Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul - Auto-unseal using Transit Secrets Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes & Persistent Volumes Claims - hostPath and annotations
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes - Dynamic volume provisioning
- Docker & Kubernetes : DaemonSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Secrets
- Docker & Kubernetes : kubectl command
- Docker & Kubernetes : Assign a Kubernetes Pod to a particular node in a Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : Configure a Pod to Use a ConfigMap
- AWS : EKS (Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Run a React app in a minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Minikube install on AWS EC2
- Docker & Kubernetes : Cassandra with a StatefulSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Terraform and AWS EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Pods and Service definitions
- Docker & Kubernetes : Service IP and the Service Type
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes DNS with Pods and Services
- Docker & Kubernetes : Headless service and discovering pods
- Docker & Kubernetes : Scaling and Updating application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Horizontal pod autoscaler on minikubes
- Docker & Kubernetes : From a monolithic app to micro services on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Rolling updates
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deployments to GKE (Rolling update, Canary and Blue-green deployments)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Slack Chat Bot with NodeJS on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery with Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline for Dev, Canary, and Production Environments on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : NodePort vs LoadBalancer vs Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB / MongoExpress on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Load Testing with Locust on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB with StatefulSets on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up Ingress with NGINX Controller on Minikube (Mac)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller for Dashboard service on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Ingress with AWS ALB Ingress Controller in EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up a private cluster on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Namespaces (default, kube-public, kube-system) and switching namespaces (kubens)
- Docker & Kubernetes : StatefulSets on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : RBAC
- Docker & Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, and IAM
- Docker & Kubernetes - Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, IAM with EKS ALB, Part 1
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : My first Helm deploy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Readiness and Liveness Probes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm chart repository with Github pages
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB with Ingress to Minikube using Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 2 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 3 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart for Node/Express and MySQL with Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using Helm and Prometheus Operator - Monitoring Kubernetes node resources out of the box
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using kube-prometheus-stack Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio (service mesh) sidecar proxy on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on Minikube with AWS EC2 for Bookinfo Application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part I)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part II - Prometheus, Grafana, pin a service, split traffic, and inject faults)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Package Manager with MySQL on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying Memcached on Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : EKS Control Plane (API server) Metrics with Prometheus
- Docker & Kubernetes : Spinnaker on EKS with Halyard
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery Pipelines with Spinnaker and Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-dind (docker-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-kind (k8s-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : nodeSelector, nodeAffinity, taints/tolerations, pod affinity and anti-affinity - Assigning Pods to Nodes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Jenkins-X on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD App of Apps with Heml on Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD on Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : GitOps with ArgoCD for Continuous Delivery to Kubernetes clusters (minikube) - guestbook
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization