Creating a CloudFront distribution with an Amazon S3 origin
CloudFront is a service launched by Amazon, powered by cloud computing technology. It is a content delivery web service. It integrates with other Amazon Web Services products to give developers and businesses an easy way to distribute content to end users with low latency, high data transfer speeds, and no minimum usage commitments.
In this chapter, we'll see how we can use Amazon S3 as a storage, and make CloudFront to deliver contents at a much higher speed with lower latency.
Using a network of edge locations around the world, Amazon CloudFront caches copies of our static content close to viewers, lowering latency when they download our objects and giving us the high, sustained data transfer rates needed to deliver large popular objects to end users at scale. Requests for our dynamic content are carried back to our origin servers running in Amazon Web Services (e.g., Amazon EC2, Elastic Load Balancing) over optimized network paths for a more reliable and consistent experience.
CloudFront makes our website's files (such as HTML, images, and video) available from data centers around the world (called edge locations). In other words, these network paths are constantly monitored by Amazon and connections from CloudFront edge locations to the origin are reused to serve our dynamic content from our content delivery network (CDN) with the best possible performance.
Here are the features of CloudFront:
- Cache content for faster delivery.
- Lower load on origin.
- Dynamic and static content.
- Streaming video.
- Custom SSL certificate.
- Low TTLs (as short as 0 seconds).
- Free origin fetches?
- Optimized for AWS.
We created a bucket (c.cloudfront.test) and uploaded a file (index.html). To get the link, let's select "properties" under "Action":
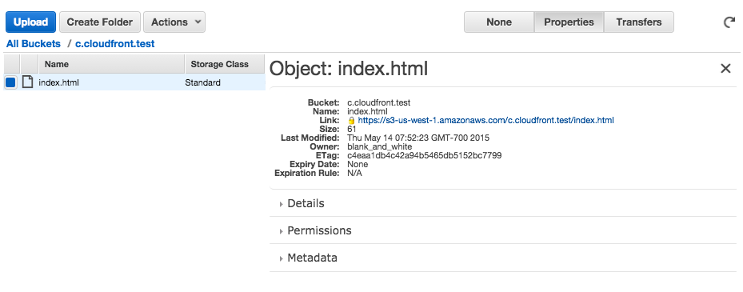
Then, open a browser, and put the link:
We got "This XML file does not appear to have any style information associated with it. The document tree is shown below." error.
We need to make it public:
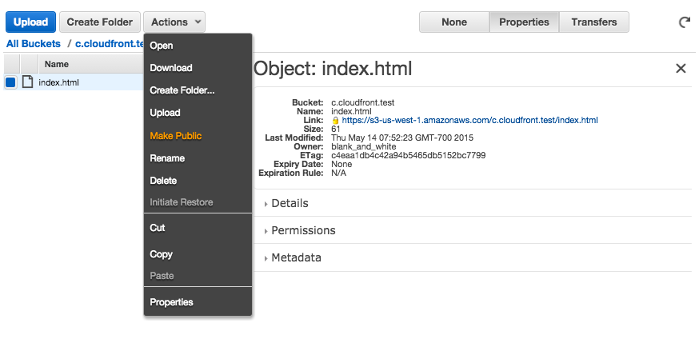
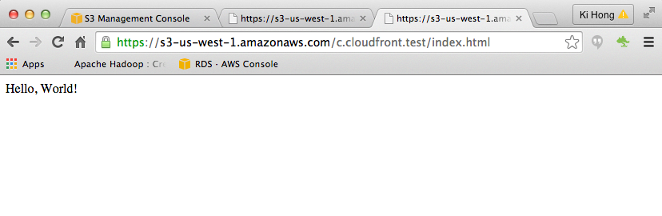
Now, our index.html works!
 When we compare the properties, in front of the link, we now have an icon indicating public instead of a lock icon:
When we compare the properties, in front of the link, we now have an icon indicating public instead of a lock icon:
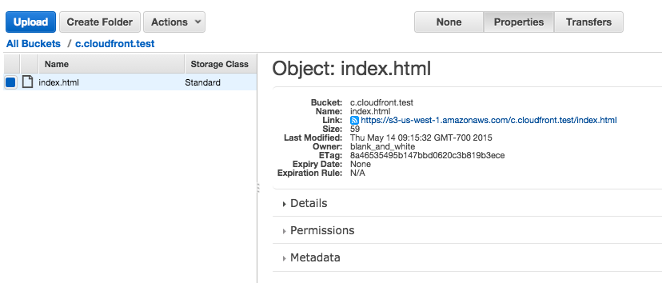
Now let's move on to CloudFront!
We'll create a CloudFront distribution with an Amazon S3 origin, which makes our website available from data centers around the world.
Here are the steps to create a distribution:
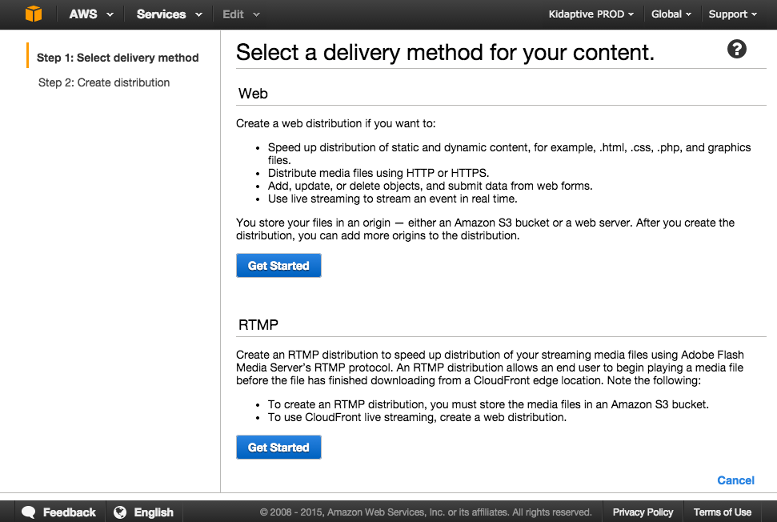
- Open the CloudFront console.
- Click Create Distribution.
- On the Select a delivery method for our content page, under Web, click Get Started.
- On the Create Distribution page, under Origin Settings, enter the Amazon S3 static website hosting endpoint for our bucket in the Origin Domain Name box.
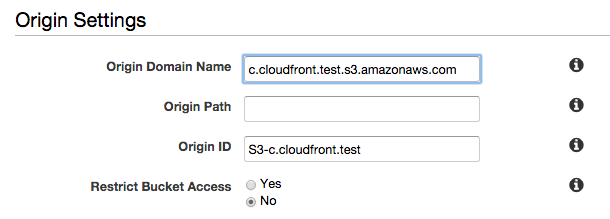
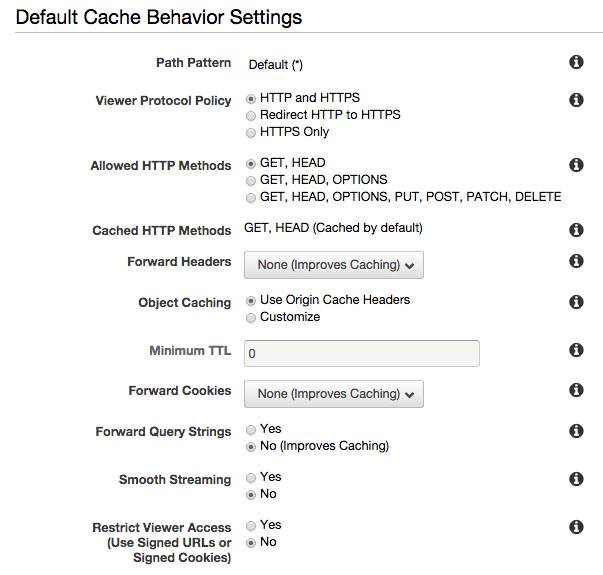
- Leave the values under Default Cache Behavior Settings at their default settings.
- Under Distribution Settings,
do the following:
Leave Price Class set to Use All Edge Locations (Best Performance).
Set Default Root Object to index.html. This is the default page that the CloudFront distribution returns if the URL used to access the distribution does not contain a file name.
Set Logging to On.
In Bucket for Logs, select the logging bucket that we created.
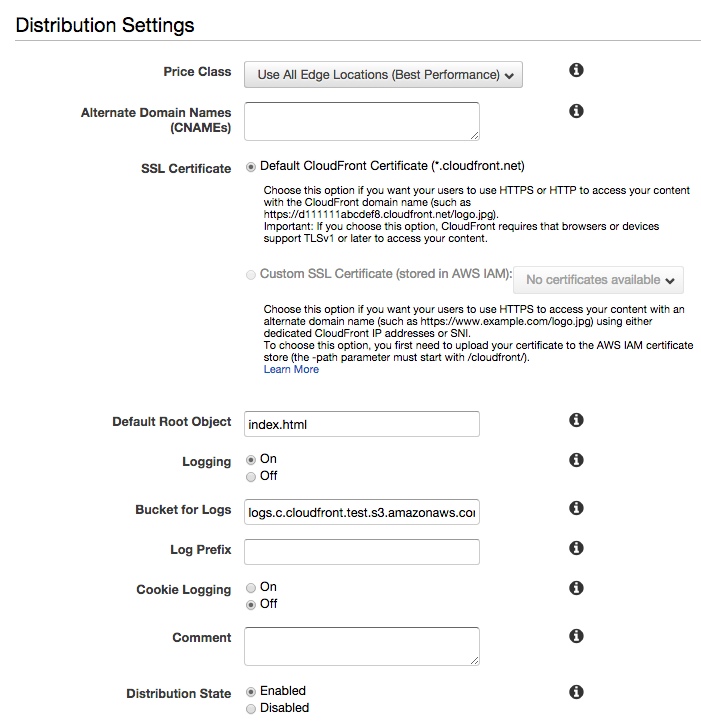
Leave the other settings at their default values. - Click Create Distribution:
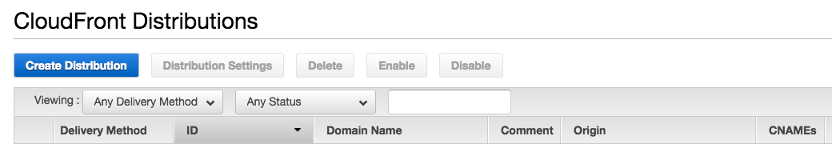
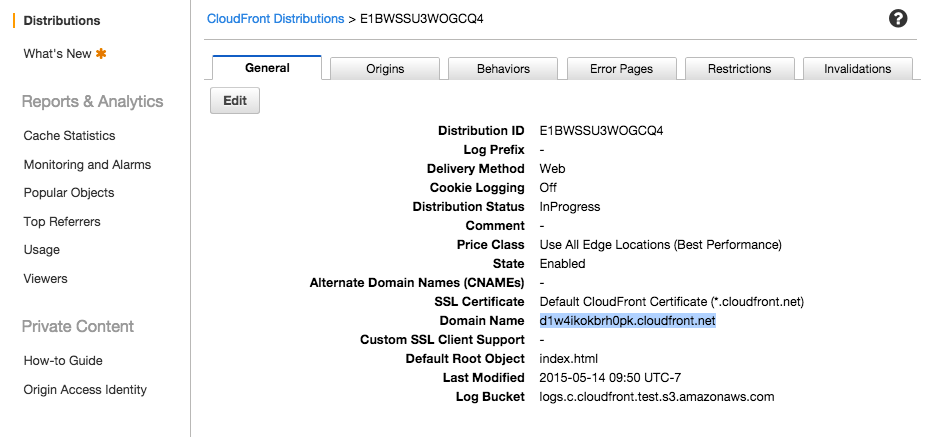
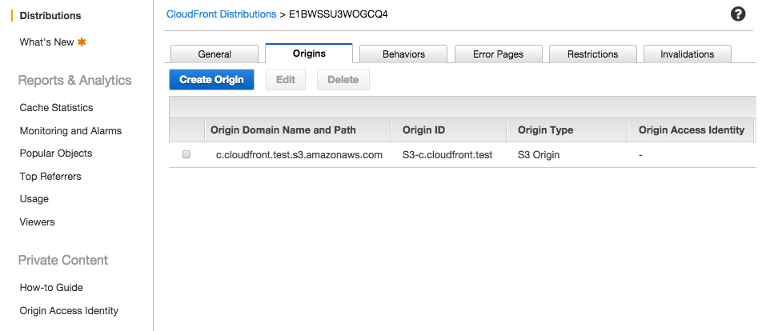
After creating the Distribution, we can check several information about it:
Using the domain name, we can see our distributed contents in the browser:
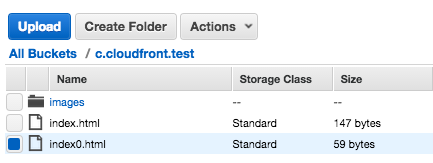
To make it more practical, we added an image file to S3:
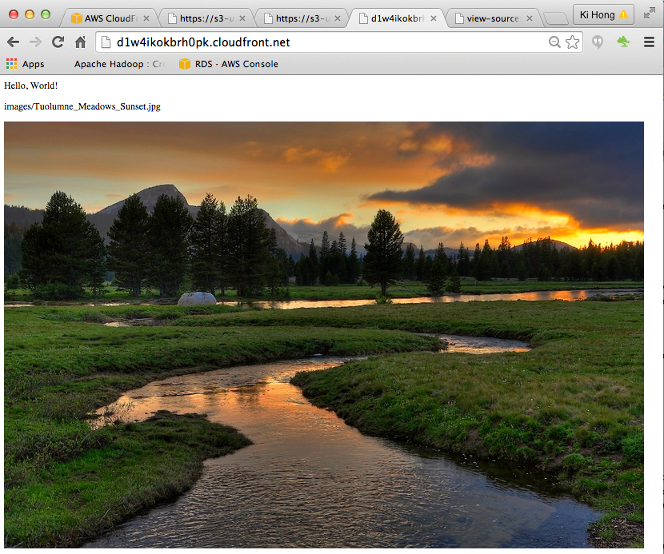
The index.html should be changed accordingly:
<html>
<body>
<p>Hello, World!</p>
<p>images/Tuolumne_Meadows_Sunset.jpg</p>
<img src="images/Tuolumne_Meadows_Sunset.jpg">
</body>
</html>
Here is our new page:
This section is from Updating Existing Objects Using the Same Object Names.
Although we can update existing objects in a CloudFront distribution and use the same object names, AWS does not recommend it. CloudFront distributes objects to edge locations only when the objects are requested, not when we put new or updated objects in our origin. If we update an existing object in our origin with a newer version that has the same name, an edge location won't get that new version from your origin until both of the following occur:
- The old version of the object in the cache expires. For more information, see Specifying How Long Objects Stay in a CloudFront Edge Cache (Expiration).
- There's an end user request for the object at that edge location.
If we use the same names when we replace objects, we can't control when CloudFront starts to serve the new files. By default, CloudFront caches objects in edge locations for 24 hours. (For more information, see Specifying How Long Objects Stay in a CloudFront Edge Cache (Expiration).) For example, if we're replacing all of the objects on an entire website:
- Objects for the less popular pages may not be in any edge locations. The new versions of these objects will start being served on the next request.
- Objects for some pages may be in some edge locations and not in others, so our end users will see different versions depending on which edge location they're served from.
New versions of the objects for the most popular pages might not be served for up to 24 hours because CloudFront might have retrieved the objects for those pages just before we replaced the objects with new versions.
AWS (Amazon Web Services)
- AWS : EKS (Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes)
- AWS : Creating a snapshot (cloning an image)
- AWS : Attaching Amazon EBS volume to an instance
- AWS : Adding swap space to an attached volume via mkswap and swapon
- AWS : Creating an EC2 instance and attaching Amazon EBS volume to the instance using Python boto module with User data
- AWS : Creating an instance to a new region by copying an AMI
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 1
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 2 - Creating and Deleting a Bucket
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 3 - Bucket Versioning
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 4 - Uploading a large file
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 5 - Uploading folders/files recursively
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 6 - Bucket Policy for File/Folder View/Download
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 7 - How to Copy or Move Objects from one region to another
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 8 - Archiving S3 Data to Glacier
- AWS : Creating a CloudFront distribution with an Amazon S3 origin
- AWS : Creating VPC with CloudFormation
- AWS : WAF (Web Application Firewall) with preconfigured CloudFormation template and Web ACL for CloudFront distribution
- AWS : CloudWatch & Logs with Lambda Function / S3
- AWS : Lambda Serverless Computing with EC2, CloudWatch Alarm, SNS
- AWS : Lambda and SNS - cross account
- AWS : CLI (Command Line Interface)
- AWS : CLI (ECS with ALB & autoscaling)
- AWS : ECS with cloudformation and json task definition
- AWS Application Load Balancer (ALB) and ECS with Flask app
- AWS : Load Balancing with HAProxy (High Availability Proxy)
- AWS : VirtualBox on EC2
- AWS : NTP setup on EC2
- AWS: jq with AWS
- AWS & OpenSSL : Creating / Installing a Server SSL Certificate
- AWS : OpenVPN Access Server 2 Install
- AWS : VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) 1 - netmask, subnets, default gateway, and CIDR
- AWS : VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) 2 - VPC Wizard
- AWS : VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) 3 - VPC Wizard with NAT
- DevOps / Sys Admin Q & A (VI) - AWS VPC setup (public/private subnets with NAT)
- AWS - OpenVPN Protocols : PPTP, L2TP/IPsec, and OpenVPN
- AWS : Autoscaling group (ASG)
- AWS : Setting up Autoscaling Alarms and Notifications via CLI and Cloudformation
- AWS : Adding a SSH User Account on Linux Instance
- AWS : Windows Servers - Remote Desktop Connections using RDP
- AWS : Scheduled stopping and starting an instance - python & cron
- AWS : Detecting stopped instance and sending an alert email using Mandrill smtp
- AWS : Elastic Beanstalk with NodeJS
- AWS : Elastic Beanstalk Inplace/Rolling Blue/Green Deploy
- AWS : Identity and Access Management (IAM) Roles for Amazon EC2
- AWS : Identity and Access Management (IAM) Policies, sts AssumeRole, and delegate access across AWS accounts
- AWS : Identity and Access Management (IAM) sts assume role via aws cli2
- AWS : Creating IAM Roles and associating them with EC2 Instances in CloudFormation
- AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) Roles, SSO(Single Sign On), SAML(Security Assertion Markup Language), IdP(identity provider), STS(Security Token Service), and ADFS(Active Directory Federation Services)
- AWS : Amazon Route 53
- AWS : Amazon Route 53 - DNS (Domain Name Server) setup
- AWS : Amazon Route 53 - subdomain setup and virtual host on Nginx
- AWS Amazon Route 53 : Private Hosted Zone
- AWS : SNS (Simple Notification Service) example with ELB and CloudWatch
- AWS : Lambda with AWS CloudTrail
- AWS : SQS (Simple Queue Service) with NodeJS and AWS SDK
- AWS : Redshift data warehouse
- AWS : CloudFormation
- AWS : CloudFormation Bootstrap UserData/Metadata
- AWS : CloudFormation - Creating an ASG with rolling update
- AWS : Cloudformation Cross-stack reference
- AWS : OpsWorks
- AWS : Network Load Balancer (NLB) with Autoscaling group (ASG)
- AWS CodeDeploy : Deploy an Application from GitHub
- AWS EC2 Container Service (ECS)
- AWS EC2 Container Service (ECS) II
- AWS Hello World Lambda Function
- AWS Lambda Function Q & A
- AWS Node.js Lambda Function & API Gateway
- AWS API Gateway endpoint invoking Lambda function
- AWS API Gateway invoking Lambda function with Terraform
- AWS API Gateway invoking Lambda function with Terraform - Lambda Container
- Amazon Kinesis Streams
- AWS: Kinesis Data Firehose with Lambda and ElasticSearch
- Amazon DynamoDB
- Amazon DynamoDB with Lambda and CloudWatch
- Loading DynamoDB stream to AWS Elasticsearch service with Lambda
- Amazon ML (Machine Learning)
- Simple Systems Manager (SSM)
- AWS : RDS Connecting to a DB Instance Running the SQL Server Database Engine
- AWS : RDS Importing and Exporting SQL Server Data
- AWS : RDS PostgreSQL & pgAdmin III
- AWS : RDS PostgreSQL 2 - Creating/Deleting a Table
- AWS : MySQL Replication : Master-slave
- AWS : MySQL backup & restore
- AWS RDS : Cross-Region Read Replicas for MySQL and Snapshots for PostgreSQL
- AWS : Restoring Postgres on EC2 instance from S3 backup
- AWS : Q & A
- AWS : Security
- AWS : Security groups vs. network ACLs
- AWS : Scaling-Up
- AWS : Networking
- AWS : Single Sign-on (SSO) with Okta
- AWS : JIT (Just-in-Time) with Okta
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization