Kubernetes II - kops (kubernetes-ops) on AWS
In this post, using kops installed on my Mac, we'll make Kubernetes cluster consists of 1 master
(t3.medium instance will be used in this post but the smaller instances such as t3.micro or t3.small will work as well) and 2 worker nodes (t2.nano). Note that the t3 is more suitable for the master
because it is better tuned for the burst nature of the master node.
Then, we are going to deploy two types of services: NodePort and LoadBalancer.
kops (kubernetes-ops) helps us create, destroy, upgrade and maintain production-grade, highly available, Kubernetes clusters from the command line. AWS (Amazon Web Services) is currently officially supported, with GCE and OpenStack in beta support, and VMware vSphere in alpha, and other platforms planned.
Kubernetes provides us with highly resilient infrastructure, automatic scaling (rollback), and self-healing of containers. It provides us REST APIs, thus hiding the complicated management of containers from us.
In short, we can think of it as kubectl for clusters.
One of the ways kops integrates with the existing Kubernetes community and software is that the main interaction with kops is via a relatively easy to use, declarative syntax command line utility, that's a lot like kubectl.
At a basic level, the difference between kops and kubectl is that kubectl interacts with applications or services deployed in your cluster, while kops interacts with entire clusters at a time. Instead of scaling an application deployment to 30 replicas like before, you might scale the number of nodes to 30 with a few quick declarative commands. As the administrator, that means you're not responsible for individually provisioning all the extra compute instances, and you don't have to rely on traditional DevOps tools like Chef or Ansible to configure them.
If you give kops a job within its scope, it gets it done and helps direct your choices to industry best practices. In addition, creating and managing Kubernetes clusters with kops is much faster than the first generation, more generalized DevOps tools. We're talking about under 20 minutes for a highly available multiple master cluster of essentially any size in private network topology. All it takes is a few choices, and kops works out the details of how to get it done.
In this tutorial, we'll be Installing Kubernetes on AWS with kops.
- Nodes:
Hosts that run Kubernetes applications - Maser:
The Master is responsible for managing the cluster. The master coordinates all activities in our cluster (scheduling applications, maintaining applications' desired state, scaling applications, and rolling out new updates). - Containers:
Units of packaging - kubelets:
Each node has a Kubelet. It is an agent for managing the node and communicating with the Kubernetes master - Pods:
Units of deployment which is collection of containers - Replication Controller:
Ensures availability and scalability - Labels:
Key-value pairs for identification - Services:
Collection of pods exposed as an endpoint
We must have kubectl installed in order to control Kubernetes clusters. As described earlier, kubectl is a command line tool that interacts with kube-apiserver and send commands to the master node and each kubectl command is converted into an API call.
On Linux, we can install it as binary using native Ubamtu/Debian package management:
$ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https
$ curl -s https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | sudo apt-key add -
$ sudo touch /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
$ echo "deb http://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install -y kubectl
$ kubectl version
Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"6", GitVersion:"v1.6.1", GitCommit:"b0b7a323cc5a4a2019b2e9520c21c7830b7f708e", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2017-04-03T20:44:38Z", GoVersion:"go1.7.5", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
...
We must have kubectl installed in order for kops to work with AWS. As described earlier, kubectl is a command line tool that interacts with kube-apiserver and send commands to the master node and each kubectl command is converted into an API call.
On Linux, we can install it as follows:
$ sudo pip install awscli
Download kops from the releases page :
$ curl -LO https://github.com/kubernetes/kops/releases/download/v1.18.0/kops-darwin-amd64 $ chmod +x ./kops-darwin-amd64 $ sudo mv ./kops-darwin-amd64 /usr/local/bin/kops
kops is an opinionated provisioning system:
- Fully automated installation
- Uses DNS to identify clusters
- Self-healing: everything runs in Auto-Scaling Groups
- Multiple OS support (Debian, Ubuntu 16.04 supported, CentOS & RHEL, Amazon Linux and CoreOS)
- High-Availability support
- Can directly provision, or generate terraform manifests
kops uses DNS for discovery, both inside the cluster and so that we can reach the kubernetes API server from clients. We will use one of my already existing domains in Route53, pykey.com.
kops has a strong opinion on the cluster name: it should be a valid DNS name. By doing so we will no longer get our clusters confused, we can share clusters with our colleagues unambiguously, and we can reach them without relying on remembering an IP address.
A Route53 hosted zone can serve subdomains. We can use subdomains to divide our clusters. As for our example, we will use useast1.dev.pykey.com. The API server endpoint will then be api.useast1.dev.pykey.com.
We can double-check that our cluster is configured correctly if we have the dig tool by running:
$ dig ns dev.pykey.com ... ;; ANSWER SECTION: dev.pykey.com. 300 IN CNAME pykey.com. pykey.com. 172800 IN NS ns-569.awsdns-07.net. pykey.com. 172800 IN NS ns-105.awsdns-13.com. pykey.com. 172800 IN NS ns-1158.awsdns-16.org. pykey.com. 172800 IN NS ns-1785.awsdns-31.co.uk. ...
We should see the 4 NS records that Route53 assigned our hosted zone. This is a critical component when setting up clusters. If we are experiencing problems with the Kubernetes API not coming up, chances are something is wrong with the cluster's DNS.
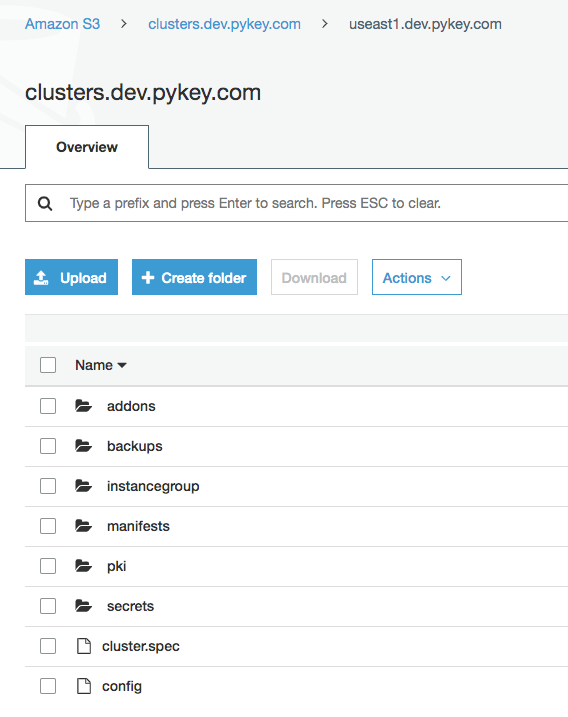
kops lets us manage our clusters even after installation. To do this, it must keep track of the clusters that we have created, along with their configuration, the keys they are using etc. This information is stored in an S3 bucket. S3 permissions are used to control access to the bucket.
In our example, we chose dev.pykey.com as our hosted zone, so let's pick clusters.dev.pykey.com as the S3 bucket name.
Let's create the S3 bucket using:
$ aws s3 mb s3://clusters.dev.pykey.com make_bucket: clusters.dev.pykey.com
We can export KOPS_STATE_STORE=s3://clusters.dev.pykey.com and then kops will use this location by default:
$ export KOPS_STATE_STORE=s3://clusters.dev.pykey.com
We may want to put this in our bash profile.
The following commands are used in this section:
kops create cluster: creates a cluster configuration. It does NOT actually create the cloud resources. This give us an opportunity to review the configuration or change it.kops update cluster: it does actually create the cloud resources.
Run kops create cluster to create our cluster configuration:
$ kops create cluster --zones=us-east-1a,us-east-1b,us-east-1c useast1.dev.pykey.com
I0903 14:24:04.227661 49380 create_cluster.go:557] Inferred --cloud=aws from zone "us-east-1a"
I0903 14:24:04.649711 49380 subnets.go:184] Assigned CIDR 172.20.32.0/19 to subnet us-east-1a
I0903 14:24:04.649756 49380 subnets.go:184] Assigned CIDR 172.20.64.0/19 to subnet us-east-1b
I0903 14:24:04.649778 49380 subnets.go:184] Assigned CIDR 172.20.96.0/19 to subnet us-east-1c
I0903 14:24:07.083525 49380 create_cluster.go:1547] Using SSH public key: /Users/kihyuckhong/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
Previewing changes that will be made:
I0903 14:24:09.588591 49380 executor.go:103] Tasks: 0 done / 91 total; 43 can run
I0903 14:24:10.950585 49380 executor.go:103] Tasks: 43 done / 91 total; 28 can run
I0903 14:24:11.651943 49380 executor.go:103] Tasks: 71 done / 91 total; 18 can run
I0903 14:24:12.270655 49380 executor.go:103] Tasks: 89 done / 91 total; 2 can run
I0903 14:24:12.420486 49380 executor.go:103] Tasks: 91 done / 91 total; 0 can run
Will create resources:
AutoscalingGroup/master-us-east-1a.masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
Granularity 1Minute
LaunchConfiguration name:master-us-east-1a.masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
MaxSize 1
Metrics [GroupDesiredCapacity, GroupInServiceInstances, GroupMaxSize, GroupMinSize, GroupPendingInstances, GroupStandbyInstances, GroupTerminatingInstances, GroupTotalInstances]
MinSize 1
Subnets [name:us-east-1a.useast1.dev.pykey.com]
SuspendProcesses []
Tags {Name: master-us-east-1a.masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com, KubernetesCluster: useast1.dev.pykey.com, kubernetes.io/cluster/useast1.dev.pykey.com: owned, k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/node-template/label/kops.k8s.io/instancegroup: master-us-east-1a, k8s.io/role/master: 1, kops.k8s.io/instancegroup: master-us-east-1a}
AutoscalingGroup/nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
Granularity 1Minute
LaunchConfiguration name:nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
MaxSize 2
Metrics [GroupDesiredCapacity, GroupInServiceInstances, GroupMaxSize, GroupMinSize, GroupPendingInstances, GroupStandbyInstances, GroupTerminatingInstances, GroupTotalInstances]
MinSize 2
Subnets [name:us-east-1a.useast1.dev.pykey.com, name:us-east-1b.useast1.dev.pykey.com, name:us-east-1c.useast1.dev.pykey.com]
SuspendProcesses []
Tags {Name: nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com, KubernetesCluster: useast1.dev.pykey.com, kubernetes.io/cluster/useast1.dev.pykey.com: owned, k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/node-template/label/kops.k8s.io/instancegroup: nodes, k8s.io/role/node: 1, kops.k8s.io/instancegroup: nodes}
DHCPOptions/useast1.dev.pykey.com
DomainName ec2.internal
DomainNameServers AmazonProvidedDNS
Shared false
Tags {Name: useast1.dev.pykey.com, KubernetesCluster: useast1.dev.pykey.com, kubernetes.io/cluster/useast1.dev.pykey.com: owned}
EBSVolume/a.etcd-events.useast1.dev.pykey.com
AvailabilityZone us-east-1a
Encrypted false
SizeGB 20
Tags {kubernetes.io/cluster/useast1.dev.pykey.com: owned, Name: a.etcd-events.useast1.dev.pykey.com, KubernetesCluster: useast1.dev.pykey.com, k8s.io/etcd/events: a/a, k8s.io/role/master: 1}
VolumeType gp2
EBSVolume/a.etcd-main.useast1.dev.pykey.com
AvailabilityZone us-east-1a
Encrypted false
SizeGB 20
Tags {k8s.io/etcd/main: a/a, k8s.io/role/master: 1, kubernetes.io/cluster/useast1.dev.pykey.com: owned, Name: a.etcd-main.useast1.dev.pykey.com, KubernetesCluster: useast1.dev.pykey.com}
VolumeType gp2
IAMInstanceProfile/masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
Shared false
IAMInstanceProfile/nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
Shared false
IAMInstanceProfileRole/masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
InstanceProfile name:masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com id:masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
Role name:masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
IAMInstanceProfileRole/nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
InstanceProfile name:nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com id:nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
Role name:nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
IAMRole/masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
ExportWithID masters
IAMRole/nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
ExportWithID nodes
IAMRolePolicy/master-policyoverride
Role name:masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
Managed true
IAMRolePolicy/masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
Role name:masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
Managed false
IAMRolePolicy/node-policyoverride
Role name:nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
Managed true
IAMRolePolicy/nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
Role name:nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
Managed false
InternetGateway/useast1.dev.pykey.com
VPC name:useast1.dev.pykey.com
Shared false
Tags {Name: useast1.dev.pykey.com, KubernetesCluster: useast1.dev.pykey.com, kubernetes.io/cluster/useast1.dev.pykey.com: owned}
Keypair/apiserver-aggregator
Signer name:apiserver-aggregator-ca id:cn=apiserver-aggregator-ca
Subject cn=aggregator
Type client
LegacyFormat false
Keypair/apiserver-aggregator-ca
Subject cn=apiserver-aggregator-ca
Type ca
LegacyFormat false
Keypair/apiserver-proxy-client
Signer name:ca id:cn=kubernetes
Subject cn=apiserver-proxy-client
Type client
LegacyFormat false
Keypair/ca
Subject cn=kubernetes
Type ca
LegacyFormat false
Keypair/etcd-clients-ca
Subject cn=etcd-clients-ca
Type ca
LegacyFormat false
Keypair/etcd-manager-ca-events
Subject cn=etcd-manager-ca-events
Type ca
LegacyFormat false
Keypair/etcd-manager-ca-main
Subject cn=etcd-manager-ca-main
Type ca
LegacyFormat false
Keypair/etcd-peers-ca-events
Subject cn=etcd-peers-ca-events
Type ca
LegacyFormat false
Keypair/etcd-peers-ca-main
Subject cn=etcd-peers-ca-main
Type ca
LegacyFormat false
Keypair/kops
Signer name:ca id:cn=kubernetes
Subject o=system:masters,cn=kops
Type client
LegacyFormat false
Keypair/kube-controller-manager
Signer name:ca id:cn=kubernetes
Subject cn=system:kube-controller-manager
Type client
LegacyFormat false
Keypair/kube-proxy
Signer name:ca id:cn=kubernetes
Subject cn=system:kube-proxy
Type client
LegacyFormat false
Keypair/kube-scheduler
Signer name:ca id:cn=kubernetes
Subject cn=system:kube-scheduler
Type client
LegacyFormat false
Keypair/kubecfg
Signer name:ca id:cn=kubernetes
Subject o=system:masters,cn=kubecfg
Type client
LegacyFormat false
Keypair/kubelet
Signer name:ca id:cn=kubernetes
Subject o=system:nodes,cn=kubelet
Type client
LegacyFormat false
Keypair/kubelet-api
Signer name:ca id:cn=kubernetes
Subject cn=kubelet-api
Type client
LegacyFormat false
Keypair/master
AlternateNames [100.64.0.1, 127.0.0.1, api.internal.useast1.dev.pykey.com, api.useast1.dev.pykey.com, kubernetes, kubernetes.default, kubernetes.default.svc, kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local]
Signer name:ca id:cn=kubernetes
Subject cn=kubernetes-master
Type server
LegacyFormat false
LaunchConfiguration/master-us-east-1a.masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
AssociatePublicIP true
IAMInstanceProfile name:masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com id:masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
ImageID 099720109477/ubuntu/images/hvm-ssd/ubuntu-focal-20.04-amd64-server-20200716
InstanceType t3.medium
RootVolumeDeleteOnTermination true
RootVolumeSize 64
RootVolumeType gp2
SSHKey name:kubernetes.useast1.dev.pykey.com-f4:e6:ca:e1:b3:ee:fc:6c:91:13:3b:a8:f5:36:e4:92 id:kubernetes.useast1.dev.pykey.com-f4:e6:ca:e1:b3:ee:fc:6c:91:13:3b:a8:f5:36:e4:92
SecurityGroups [name:masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com]
SpotPrice
LaunchConfiguration/nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
AssociatePublicIP true
IAMInstanceProfile name:nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com id:nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
ImageID 099720109477/ubuntu/images/hvm-ssd/ubuntu-focal-20.04-amd64-server-20200716
InstanceType t3.medium
RootVolumeDeleteOnTermination true
RootVolumeSize 128
RootVolumeType gp2
SSHKey name:kubernetes.useast1.dev.pykey.com-f4:e6:ca:e1:b3:ee:fc:6c:91:13:3b:a8:f5:36:e4:92 id:kubernetes.useast1.dev.pykey.com-f4:e6:ca:e1:b3:ee:fc:6c:91:13:3b:a8:f5:36:e4:92
SecurityGroups [name:nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com]
SpotPrice
ManagedFile/etcd-cluster-spec-events
Base s3://clusters.dev.pykey.com/useast1.dev.pykey.com/backups/etcd/events
Location /control/etcd-cluster-spec
ManagedFile/etcd-cluster-spec-main
Base s3://clusters.dev.pykey.com/useast1.dev.pykey.com/backups/etcd/main
Location /control/etcd-cluster-spec
ManagedFile/manifests-etcdmanager-events
Location manifests/etcd/events.yaml
ManagedFile/manifests-etcdmanager-main
Location manifests/etcd/main.yaml
ManagedFile/manifests-static-kube-apiserver-healthcheck
Location manifests/static/kube-apiserver-healthcheck.yaml
ManagedFile/useast1.dev.pykey.com-addons-bootstrap
Location addons/bootstrap-channel.yaml
ManagedFile/useast1.dev.pykey.com-addons-core.addons.k8s.io
Location addons/core.addons.k8s.io/v1.4.0.yaml
ManagedFile/useast1.dev.pykey.com-addons-dns-controller.addons.k8s.io-k8s-1.12
Location addons/dns-controller.addons.k8s.io/k8s-1.12.yaml
ManagedFile/useast1.dev.pykey.com-addons-dns-controller.addons.k8s.io-k8s-1.6
Location addons/dns-controller.addons.k8s.io/k8s-1.6.yaml
ManagedFile/useast1.dev.pykey.com-addons-kops-controller.addons.k8s.io-k8s-1.16
Location addons/kops-controller.addons.k8s.io/k8s-1.16.yaml
ManagedFile/useast1.dev.pykey.com-addons-kube-dns.addons.k8s.io-k8s-1.12
Location addons/kube-dns.addons.k8s.io/k8s-1.12.yaml
ManagedFile/useast1.dev.pykey.com-addons-kube-dns.addons.k8s.io-k8s-1.6
Location addons/kube-dns.addons.k8s.io/k8s-1.6.yaml
ManagedFile/useast1.dev.pykey.com-addons-kubelet-api.rbac.addons.k8s.io-k8s-1.9
Location addons/kubelet-api.rbac.addons.k8s.io/k8s-1.9.yaml
ManagedFile/useast1.dev.pykey.com-addons-limit-range.addons.k8s.io
Location addons/limit-range.addons.k8s.io/v1.5.0.yaml
ManagedFile/useast1.dev.pykey.com-addons-rbac.addons.k8s.io-k8s-1.8
Location addons/rbac.addons.k8s.io/k8s-1.8.yaml
ManagedFile/useast1.dev.pykey.com-addons-storage-aws.addons.k8s.io-v1.15.0
Location addons/storage-aws.addons.k8s.io/v1.15.0.yaml
ManagedFile/useast1.dev.pykey.com-addons-storage-aws.addons.k8s.io-v1.7.0
Location addons/storage-aws.addons.k8s.io/v1.7.0.yaml
Route/0.0.0.0/0
RouteTable name:useast1.dev.pykey.com
CIDR 0.0.0.0/0
InternetGateway name:useast1.dev.pykey.com
RouteTable/useast1.dev.pykey.com
VPC name:useast1.dev.pykey.com
Shared false
Tags {kubernetes.io/cluster/useast1.dev.pykey.com: owned, kubernetes.io/kops/role: public, Name: useast1.dev.pykey.com, KubernetesCluster: useast1.dev.pykey.com}
RouteTableAssociation/us-east-1a.useast1.dev.pykey.com
RouteTable name:useast1.dev.pykey.com
Subnet name:us-east-1a.useast1.dev.pykey.com
RouteTableAssociation/us-east-1b.useast1.dev.pykey.com
RouteTable name:useast1.dev.pykey.com
Subnet name:us-east-1b.useast1.dev.pykey.com
RouteTableAssociation/us-east-1c.useast1.dev.pykey.com
RouteTable name:useast1.dev.pykey.com
Subnet name:us-east-1c.useast1.dev.pykey.com
SSHKey/kubernetes.useast1.dev.pykey.com-f4:e6:ca:e1:b3:ee:fc:6c:91:13:3b:a8:f5:36:e4:92
KeyFingerprint 99:18:2b:e4:dd:e8:4c:87:fb:b7:4d:ba:94:74:3a:bb
Secret/admin
Secret/kube
Secret/kube-proxy
Secret/kubelet
Secret/system:controller_manager
Secret/system:dns
Secret/system:logging
Secret/system:monitoring
Secret/system:scheduler
SecurityGroup/masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
Description Security group for masters
VPC name:useast1.dev.pykey.com
RemoveExtraRules [port=22, port=443, port=2380, port=2381, port=4001, port=4002, port=4789, port=179]
Tags {Name: masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com, KubernetesCluster: useast1.dev.pykey.com, kubernetes.io/cluster/useast1.dev.pykey.com: owned}
SecurityGroup/nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
Description Security group for nodes
VPC name:useast1.dev.pykey.com
RemoveExtraRules [port=22]
Tags {Name: nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com, KubernetesCluster: useast1.dev.pykey.com, kubernetes.io/cluster/useast1.dev.pykey.com: owned}
SecurityGroupRule/all-master-to-master
SecurityGroup name:masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
SourceGroup name:masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
SecurityGroupRule/all-master-to-node
SecurityGroup name:nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
SourceGroup name:masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
SecurityGroupRule/all-node-to-node
SecurityGroup name:nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
SourceGroup name:nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
SecurityGroupRule/https-external-to-master-0.0.0.0/0
SecurityGroup name:masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
CIDR 0.0.0.0/0
Protocol tcp
FromPort 443
ToPort 443
SecurityGroupRule/master-egress
SecurityGroup name:masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
CIDR 0.0.0.0/0
Egress true
SecurityGroupRule/node-egress
SecurityGroup name:nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
CIDR 0.0.0.0/0
Egress true
SecurityGroupRule/node-to-master-tcp-1-2379
SecurityGroup name:masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
Protocol tcp
FromPort 1
ToPort 2379
SourceGroup name:nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
SecurityGroupRule/node-to-master-tcp-2382-4000
SecurityGroup name:masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
Protocol tcp
FromPort 2382
ToPort 4000
SourceGroup name:nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
SecurityGroupRule/node-to-master-tcp-4003-65535
SecurityGroup name:masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
Protocol tcp
FromPort 4003
ToPort 65535
SourceGroup name:nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
SecurityGroupRule/node-to-master-udp-1-65535
SecurityGroup name:masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
Protocol udp
FromPort 1
ToPort 65535
SourceGroup name:nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
SecurityGroupRule/ssh-external-to-master-0.0.0.0/0
SecurityGroup name:masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com
CIDR 0.0.0.0/0
Protocol tcp
FromPort 22
ToPort 22
SecurityGroupRule/ssh-external-to-node-0.0.0.0/0
SecurityGroup name:nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com
CIDR 0.0.0.0/0
Protocol tcp
FromPort 22
ToPort 22
Subnet/us-east-1a.useast1.dev.pykey.com
ShortName us-east-1a
VPC name:useast1.dev.pykey.com
AvailabilityZone us-east-1a
CIDR 172.20.32.0/19
Shared false
Tags {SubnetType: Public, kubernetes.io/role/elb: 1, Name: us-east-1a.useast1.dev.pykey.com, KubernetesCluster: useast1.dev.pykey.com, kubernetes.io/cluster/useast1.dev.pykey.com: owned}
Subnet/us-east-1b.useast1.dev.pykey.com
ShortName us-east-1b
VPC name:useast1.dev.pykey.com
AvailabilityZone us-east-1b
CIDR 172.20.64.0/19
Shared false
Tags {kubernetes.io/role/elb: 1, Name: us-east-1b.useast1.dev.pykey.com, KubernetesCluster: useast1.dev.pykey.com, kubernetes.io/cluster/useast1.dev.pykey.com: owned, SubnetType: Public}
Subnet/us-east-1c.useast1.dev.pykey.com
ShortName us-east-1c
VPC name:useast1.dev.pykey.com
AvailabilityZone us-east-1c
CIDR 172.20.96.0/19
Shared false
Tags {Name: us-east-1c.useast1.dev.pykey.com, KubernetesCluster: useast1.dev.pykey.com, kubernetes.io/cluster/useast1.dev.pykey.com: owned, SubnetType: Public, kubernetes.io/role/elb: 1}
VPC/useast1.dev.pykey.com
CIDR 172.20.0.0/16
EnableDNSHostnames true
EnableDNSSupport true
Shared false
Tags {Name: useast1.dev.pykey.com, KubernetesCluster: useast1.dev.pykey.com, kubernetes.io/cluster/useast1.dev.pykey.com: owned}
VPCDHCPOptionsAssociation/useast1.dev.pykey.com
VPC name:useast1.dev.pykey.com
DHCPOptions name:useast1.dev.pykey.com
Must specify --yes to apply changes
Cluster configuration has been created.
Suggestions:
* list clusters with: kops get cluster
* edit this cluster with: kops edit cluster useast1.dev.pykey.com
* edit your node instance group: kops edit ig --name=useast1.dev.pykey.com nodes
* edit your master instance group: kops edit ig --name=useast1.dev.pykey.com master-us-east-1a
Finally configure your cluster with: kops update cluster --name useast1.dev.pykey.com --yes
The kops create cluster command created the configuration for our cluster.
Note that it only created the configuration, it did not actually create the cloud resources - we'll do that in the next step with a kops update cluster.
This gives us an opportunity to review the configuration or change it.
It prints commands we can use to explore further:
- list clusters with:
kops get cluster:
$ kops get cluster --state s3://clusters.dev.pykey.com NAME CLOUD ZONES useast1.dev.pykey.com aws us-east-1a,us-east-1b,us-east-1c
Or after setting export KOPS_STATE_STOR=s3://clusters.dev.pykey.com:
$ kops get cluster NAME CLOUD ZONES useast1.dev.pykey.com aws us-east-1a,us-east-1b,us-east-1c
- edit this cluster with:
kops edit cluster useast1.dev.pykey.com:
# Please edit the object below. Lines beginning with a '#' will be ignored, # and an empty file will abort the edit. If an error occurs while saving this file will be # reopened with the relevant failures. # apiVersion: kops.k8s.io/v1alpha2 kind: Cluster metadata: creationTimestamp: "2020-09-03T21:24:06Z" name: useast1.dev.pykey.com spec: api: dns: {} authorization: rbac: {} channel: stable cloudProvider: aws configBase: s3://clusters.dev.pykey.com/useast1.dev.pykey.com containerRuntime: docker etcdClusters: - cpuRequest: 200m etcdMembers: - instanceGroup: master-us-east-1a name: a memoryRequest: 100Mi name: main - cpuRequest: 100m etcdMembers: - instanceGroup: master-us-east-1a name: a memoryRequest: 100Mi name: events iam: allowContainerRegistry: true legacy: false kubelet: anonymousAuth: false kubernetesApiAccess: - 0.0.0.0/0 kubernetesVersion: 1.18.8 masterInternalName: api.internal.useast1.dev.pykey.com masterPublicName: api.useast1.dev.pykey.com networkCIDR: 172.20.0.0/16 networking: kubenet: {} nonMasqueradeCIDR: 100.64.0.0/10 sshAccess: - 0.0.0.0/0 subnets: - cidr: 172.20.32.0/19 name: us-east-1a type: Public zone: us-east-1a - cidr: 172.20.64.0/19 name: us-east-1b type: Public zone: us-east-1b - cidr: 172.20.96.0/19 name: us-east-1c type: Public zone: us-east-1c topology: dns: type: Public masters: public nodes: public - edit node instance group:
kops edit ig --name=useast1.dev.pykey.com nodes:
apiVersion: kops.k8s.io/v1alpha2 kind: InstanceGroup metadata: creationTimestamp: "2020-09-01T23:17:45Z" labels: kops.k8s.io/cluster: useast1.dev.pykey.com name: nodes spec: image: 099720109477/ubuntu/images/hvm-ssd/ubuntu-focal-20.04-amd64-server-20200716 machineType: t3.medium maxSize: 2 minSize: 2 nodeLabels: kops.k8s.io/instancegroup: nodes role: Node subnets: - us-east-1a - us-east-1b - us-east-1c
Modify it:
machineType: t3.medium maxSize: 2 minSize: 2 => machineType: t2.nano maxSize: 1 minSize: 1
- edit master instance group:
kops edit ig --name=useast1.dev.pykey.com master-us-east-1a:
apiVersion: kops.k8s.io/v1alpha2 kind: InstanceGroup metadata: creationTimestamp: "2020-09-03T21:24:06Z" labels: kops.k8s.io/cluster: useast1.dev.pykey.com name: master-us-east-1a spec: image: 099720109477/ubuntu/images/hvm-ssd/ubuntu-focal-20.04-amd64-server-20200716 machineType: t3.medium maxSize: 1 minSize: 1 nodeLabels: kops.k8s.io/instancegroup: master-us-east-1a role: Master subnets: - us-east-1a
- Finally configure cluster with:
kops update cluster --name useast1.dev.pykey.com --yesSee next section.
If this is the first time using kops, do spend a few minutes to try those out! An instance group is a set of instances, which will be registered as kubernetes nodes. On AWS this is implemented via auto-scaling-groups.
Run kops update cluster to preview what it is going to do our cluster in AWS:
$ kops update cluster useast1.dev.pykey.com ...
Now we'll use the same command, kops update cluster but with --yes to actually create the cluster:
$ kops update cluster useast1.dev.pykey.com --yes I0903 14:44:07.068796 49581 executor.go:103] Tasks: 0 done / 91 total; 43 can run I0903 14:44:08.166320 49581 vfs_castore.go:590] Issuing new certificate: "ca" I0903 14:44:08.232347 49581 vfs_castore.go:590] Issuing new certificate: "apiserver-aggregator-ca" I0903 14:44:08.345192 49581 vfs_castore.go:590] Issuing new certificate: "etcd-manager-ca-events" I0903 14:44:08.417344 49581 vfs_castore.go:590] Issuing new certificate: "etcd-manager-ca-main" I0903 14:44:08.483010 49581 vfs_castore.go:590] Issuing new certificate: "etcd-clients-ca" I0903 14:44:08.638627 49581 vfs_castore.go:590] Issuing new certificate: "etcd-peers-ca-main" I0903 14:44:08.725188 49581 vfs_castore.go:590] Issuing new certificate: "etcd-peers-ca-events" I0903 14:44:10.040967 49581 executor.go:103] Tasks: 43 done / 91 total; 28 can run I0903 14:44:11.128125 49581 vfs_castore.go:590] Issuing new certificate: "kube-controller-manager" I0903 14:44:11.263449 49581 vfs_castore.go:590] Issuing new certificate: "kubelet" I0903 14:44:11.308451 49581 vfs_castore.go:590] Issuing new certificate: "master" I0903 14:44:11.571119 49581 vfs_castore.go:590] Issuing new certificate: "kube-proxy" I0903 14:44:11.590496 49581 vfs_castore.go:590] Issuing new certificate: "kube-scheduler" I0903 14:44:11.687091 49581 vfs_castore.go:590] Issuing new certificate: "kops" I0903 14:44:11.910723 49581 vfs_castore.go:590] Issuing new certificate: "apiserver-proxy-client" I0903 14:44:11.937927 49581 vfs_castore.go:590] Issuing new certificate: "kubelet-api" I0903 14:44:11.988192 49581 vfs_castore.go:590] Issuing new certificate: "apiserver-aggregator" I0903 14:44:11.988308 49581 vfs_castore.go:590] Issuing new certificate: "kubecfg" I0903 14:44:13.140444 49581 executor.go:103] Tasks: 71 done / 91 total; 18 can run I0903 14:44:14.250941 49581 launchconfiguration.go:375] waiting for IAM instance profile "nodes.useast1.dev.pykey.com" to be ready I0903 14:44:14.296649 49581 launchconfiguration.go:375] waiting for IAM instance profile "masters.useast1.dev.pykey.com" to be ready I0903 14:44:25.409587 49581 executor.go:103] Tasks: 89 done / 91 total; 2 can run I0903 14:44:26.361856 49581 executor.go:103] Tasks: 91 done / 91 total; 0 can run I0903 14:44:26.364272 49581 dns.go:156] Pre-creating DNS records I0903 14:44:27.953961 49581 update_cluster.go:308] Exporting kubecfg for cluster kops has set your kubectl context to useast1.dev.pykey.com Cluster is starting. It should be ready in a few minutes. Suggestions: * validate cluster: kops validate cluster --wait 10m * list nodes: kubectl get nodes --show-labels * ssh to the master: ssh -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa ubuntu@api.useast1.dev.pykey.com * the ubuntu user is specific to Ubuntu. If not using Ubuntu please use the appropriate user based on your OS. * read about installing addons at: https://kops.sigs.k8s.io/operations/addons.
This may take a few seconds to run, but then our cluster will likely take a few minutes to actually be ready.
The kops update cluster will be the tool we'll use whenever we change the configuration of our cluster.
It applies the changes we have made to the configuration to our cluster - reconfiguring AWS or kubernetes as needed.
For example, after we kops edit ig nodes, then kops update cluster --yes to apply our configuration,
and sometimes we will also have to kops rolling-update cluster to roll out the configuration immediately.
Now that our cluster is ready, let's check:
$ kops validate cluster Using cluster from kubectl context: useast1.dev.pykey.com Validating cluster useast1.dev.pykey.com INSTANCE GROUPS NAME ROLE MACHINETYPE MIN MAX SUBNETS master-us-east-1a Master t3.medium 1 1 us-east-1a nodes Node t2.nano 2 2 us-east-1a,us-east-1b,us-east-1c NODE STATUS NAME ROLE READY ip-172-20-42-41.ec2.internal master True ip-172-20-63-75.ec2.internal node True ip-172-20-97-84.ec2.internal node True Your cluster useast1.dev.pykey.com is ready
list nodes:
$ kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION ip-172-20-42-41.ec2.internal Ready master 4m14s v1.18.8 ip-172-20-63-75.ec2.internal Ready node 2m48s v1.18.8 ip-172-20-97-84.ec2.internal Ready node 2m52s v1.18.8 $ kubectl get nodes --show-labels NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION LABELS ip-172-20-42-41.ec2.internal Ready master 4m35s v1.18.8 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/instance-type=t3.medium,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/region=us-east-1,failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/zone=us-east-1a,kops.k8s.io/instancegroup=master-us-east-1a,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=ip-172-20-42-41.ec2.internal,kubernetes.io/os=linux,kubernetes.io/role=master,node-role.kubernetes.io/master=,node.kubernetes.io/instance-type=t3.medium,topology.kubernetes.io/region=us-east-1,topology.kubernetes.io/zone=us-east-1a ip-172-20-63-75.ec2.internal Ready node 3m9s v1.18.8 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/instance-type=t2.nano,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/region=us-east-1,failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/zone=us-east-1a,kops.k8s.io/instancegroup=nodes,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=ip-172-20-63-75.ec2.internal,kubernetes.io/os=linux,kubernetes.io/role=node,node-role.kubernetes.io/node=,node.kubernetes.io/instance-type=t2.nano,topology.kubernetes.io/region=us-east-1,topology.kubernetes.io/zone=us-east-1a ip-172-20-97-84.ec2.internal Ready node 3m13s v1.18.8 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/instance-type=t2.nano,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/region=us-east-1,failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/zone=us-east-1c,kops.k8s.io/instancegroup=nodes,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=ip-172-20-97-84.ec2.internal,kubernetes.io/os=linux,kubernetes.io/role=node,node-role.kubernetes.io/node=,node.kubernetes.io/instance-type=t2.nano,topology.kubernetes.io/region=us-east-1,topology.kubernetes.io/zone=us-east-1c
ssh to the master:
$ ssh -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa ubuntu@api.useast1.dev.pykey.com The authenticity of host 'api.useast1.dev.pykey.com (3.218.244.1)' can't be established. ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:96RKZe6hI555FhPZloK0O5B21+7lO2nDY7YshB7UAcE. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes Warning: Permanently added 'api.useast1.dev.pykey.com,3.218.244.1' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts. Welcome to Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (GNU/Linux 5.4.0-1018-aws x86_64) * Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com * Management: https://landscape.canonical.com * Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage System information as of Thu Sep 3 21:56:13 UTC 2020 System load: 0.08 Processes: 160 Usage of /: 6.4% of 61.98GB Users logged in: 0 Memory usage: 24% IPv4 address for docker0: 172.17.0.1 Swap usage: 0% IPv4 address for ens5: 172.20.42.41 55 updates can be installed immediately. 29 of these updates are security updates. To see these additional updates run: apt list --upgradable The programs included with the Ubuntu system are free software; the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright. Ubuntu comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by applicable law. To run a command as administrator (user "root"), use "sudo". See "man sudo_root" for details. ubuntu@ip-172-20-42-41:~$
$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE kube-system dns-controller-78f77977f-bxtsg 1/1 Running 0 8m57s kube-system etcd-manager-events-ip-172-20-42-41.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 0 8m10s kube-system etcd-manager-main-ip-172-20-42-41.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 0 8m29s kube-system kops-controller-9ncgv 1/1 Running 0 8m1s kube-system kube-apiserver-ip-172-20-42-41.ec2.internal 2/2 Running 0 8m12s kube-system kube-controller-manager-ip-172-20-42-41.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 0 7m34s kube-system kube-dns-64f86fb8dd-9p8p4 3/3 Running 0 7m22s kube-system kube-dns-64f86fb8dd-9q22z 3/3 Running 0 8m57s kube-system kube-dns-autoscaler-cd7778b7b-xsxsx 1/1 Running 0 8m57s kube-system kube-proxy-ip-172-20-42-41.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 0 7m8s kube-system kube-proxy-ip-172-20-63-75.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 0 6m56s kube-system kube-proxy-ip-172-20-97-84.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 0 6m50s kube-system kube-scheduler-ip-172-20-42-41.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 0 8m19s
We now have two instances - 1 master and 1 node:
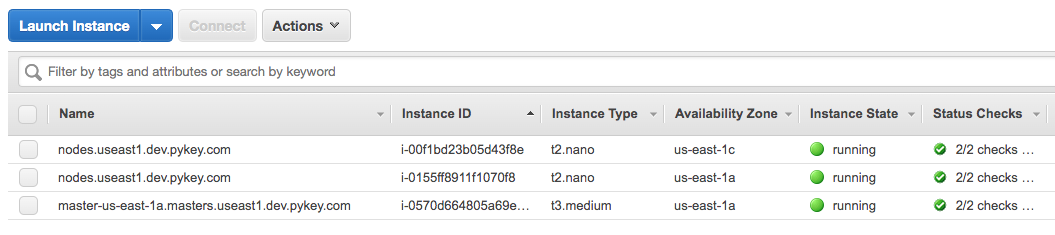
Cluster info at S3:
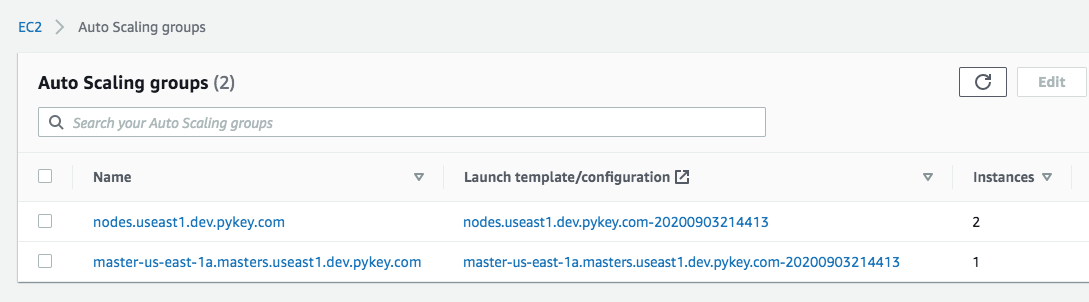
Autoscaling Group:
Dashboard is a web interface for Kubernetes.
Let's check if the dashboard is deployed:
$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces | grep dashboard
Looks like the dashboard is missing, so we need to install the latest stable release by running the following command:
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.0.0/aio/deploy/recommended.yaml namespace/kubernetes-dashboard created serviceaccount/kubernetes-dashboard created service/kubernetes-dashboard created secret/kubernetes-dashboard-certs created secret/kubernetes-dashboard-csrf created secret/kubernetes-dashboard-key-holder created configmap/kubernetes-dashboard-settings created role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created deployment.apps/kubernetes-dashboard created service/dashboard-metrics-scraper created deployment.apps/dashboard-metrics-scraper created $ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE kube-system dns-controller-78f77977f-6t6fz 1/1 Running 0 72m kube-system etcd-manager-events-ip-172-20-54-121.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 0 72m kube-system etcd-manager-main-ip-172-20-54-121.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 0 72m kube-system kops-controller-pgpjc 1/1 Running 0 72m kube-system kube-apiserver-ip-172-20-54-121.ec2.internal 2/2 Running 1 72m kube-system kube-controller-manager-ip-172-20-54-121.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 0 72m kube-system kube-dns-64f86fb8dd-7zsk8 3/3 Running 0 71m kube-system kube-dns-64f86fb8dd-zw785 3/3 Running 0 72m kube-system kube-dns-autoscaler-cd7778b7b-btv4j 1/1 Running 0 72m kube-system kube-proxy-ip-172-20-49-53.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 0 71m kube-system kube-proxy-ip-172-20-54-121.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 0 72m kube-system kube-scheduler-ip-172-20-54-121.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 0 72m kubernetes-dashboard dashboard-metrics-scraper-6b4884c9d5-l68cf 1/1 Running 0 12m kubernetes-dashboard kubernetes-dashboard-7b544877d5-c58gh 1/1 Running 0 12m
By default, the Kubernetes Dashboard user has limited permissions. In this section, we create a kops-admin service account and cluster role binding that we can use to securely connect to the dashboard with admin-level permissions.
- Create a file called kops-admin-service-account.yaml:
apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: kops-admin namespace: kube-system --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: ClusterRoleBinding metadata: name: kops-admin roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole name: cluster-admin subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: kops-admin namespace: kube-system
This manifest defines a service account and cluster role binding called kops-admin (we can name whatever we want).
-
Apply the service account and cluster role binding to our cluster:
$ kubectl apply -f kops-admin-service-account.yaml serviceaccount/kops-admin created clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kops-admin created $ kubectl get serviceaccounts --all-namespaces NAMESPACE NAME SECRETS AGE default default 1 28m kube-node-lease default 1 28m kube-public default 1 28m kube-system attachdetach-controller 1 28m kube-system aws-cloud-provider 1 28m kube-system certificate-controller 1 28m kube-system clusterrole-aggregation-controller 1 28m kube-system cronjob-controller 1 28m kube-system daemon-set-controller 1 28m kube-system default 1 28m kube-system deployment-controller 1 28m kube-system disruption-controller 1 28m kube-system dns-controller 1 28m kube-system endpoint-controller 1 28m kube-system endpointslice-controller 1 28m kube-system expand-controller 1 28m kube-system generic-garbage-collector 1 28m kube-system horizontal-pod-autoscaler 1 28m kube-system job-controller 1 28m kube-system kops-admin 1 2m23s kube-system kops-controller 1 28m kube-system kube-dns 1 28m kube-system kube-dns-autoscaler 1 28m kube-system kube-proxy 1 28m kube-system namespace-controller 1 28m kube-system node-controller 1 28m kube-system persistent-volume-binder 1 28m kube-system pod-garbage-collector 1 28m kube-system pv-protection-controller 1 28m kube-system pvc-protection-controller 1 28m kube-system replicaset-controller 1 28m kube-system replication-controller 1 28m kube-system resourcequota-controller 1 28m kube-system route-controller 1 28m kube-system service-account-controller 1 28m kube-system service-controller 1 28m kube-system statefulset-controller 1 28m kube-system ttl-controller 1 28m kubernetes-dashboard default 1 10m kubernetes-dashboard kubernetes-dashboard 1 10m
Now that the Kubernetes Dashboard is deployed to our cluster, and we have an administrator service account that we can use to view and control our cluster, we can connect to the dashboard with that service account.
Retrieve an authentication token for the kops-admin service account. Copy the "authentication_token" value from the output. We use this token to connect to the dashboard:
$ kubectl -n kube-system describe secret $(kubectl -n kube-system get secret | grep kops-admin | awk '{print $1}')
Name: kops-admin-token-ffbm6
Namespace: kube-system
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubernetes.io/service-account.name: kops-admin
kubernetes.io/service-account.uid: 8ea467e6-fe18-40de-a288-ccb9a07bdd24
Type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
Data
====
ca.crt: 1042 bytes
namespace: 11 bytes
token: eyJhbGc...MImg
Start the kubectl proxy:
$ kubectl proxy
To access the dashboard endpoint, open the following link with a web browser: http://localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/kubernetes-dashboard/services/https:kubernetes-dashboard:/proxy/#!/login
Choose Token, paste the "authentication_token" output from the previous command into the Token field, and choose SIGN IN:
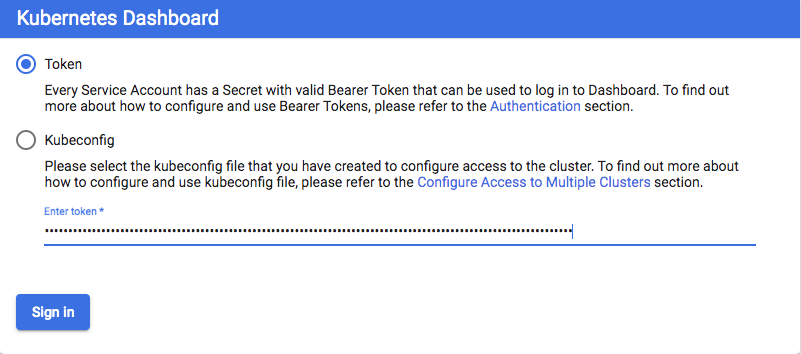
After we have connected to our Kubernetes Dashboard, we can view and control your cluster using your kops-admin service account.
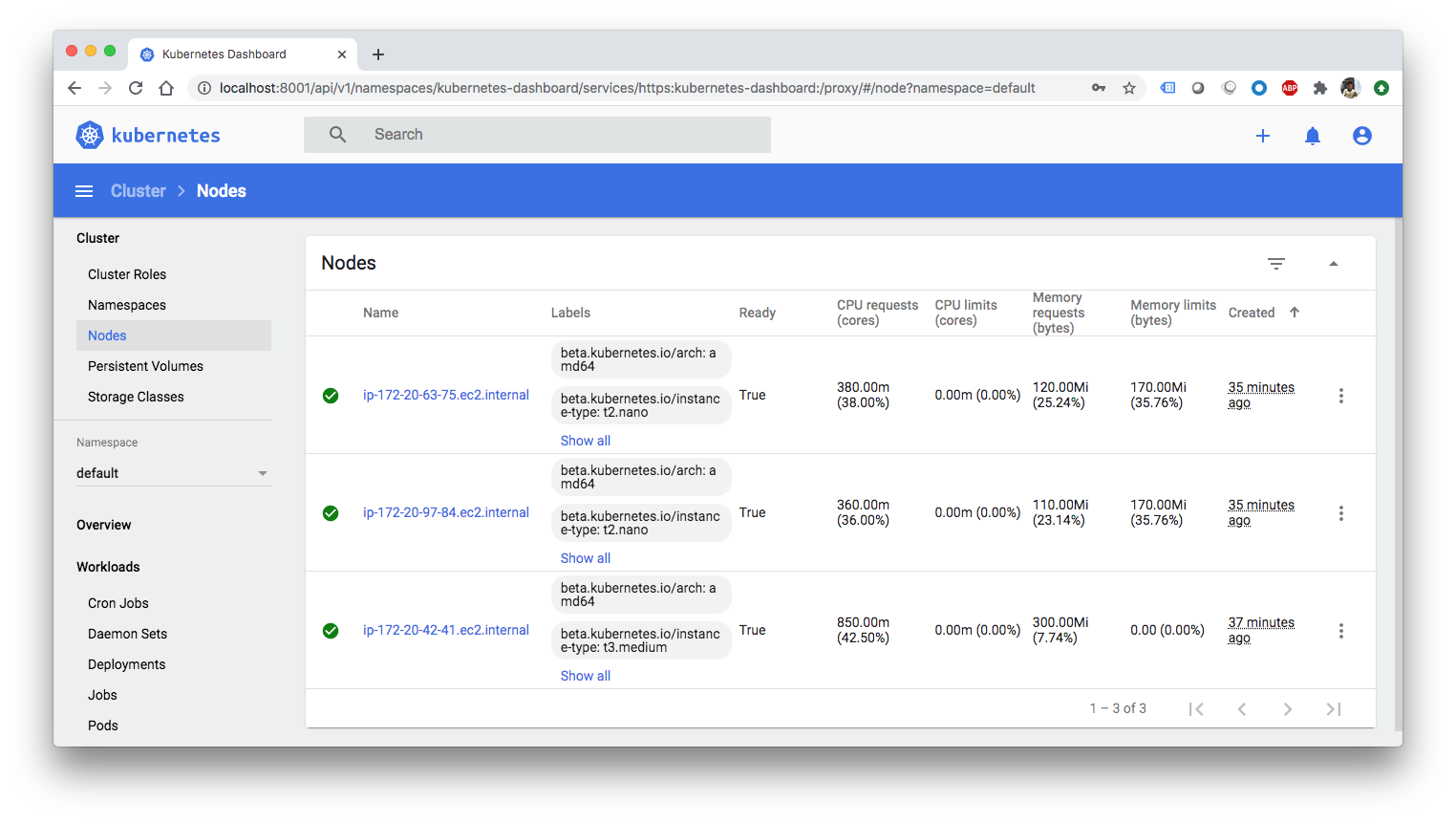
At this point, we haven't deployed any apps:
$ kubectl get pods No resources found in default namespace.
Now, we may want to deploy a simple service using this deployment (hello.yaml):
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hello-world
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
run: load-balancer-example
replicas: 2
template:
metadata:
labels:
run: load-balancer-example
spec:
containers:
- name: hello-world
image: gcr.io/google-samples/node-hello:1.0
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
Run a Hello World application in our cluster. Create the application deployment:
$ kubectl apply -f hello.yaml deployment.apps/hello-world created $ kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE hello-world-86d6c6f84d-nkm2d 1/1 Running 0 2m42s hello-world-86d6c6f84d-qw95v 1/1 Running 0 2m42s $ kubectl get deployment NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE hello-world 2/2 2 2 2m50s $ kubectl get rs NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE hello-world-86d6c6f84d 2 2 2 4m46s
The command created a Deployment and an associated ReplicaSet. The ReplicaSet has two Pods each of which runs the Hello World application.
Create a Service object that exposes the deployment:
$ kubectl expose deployment hello-world --type=NodePort --name=example-service service/example-service exposed $ kubectl get services -o wide NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR example-service NodePort 100.71.100.203 <none> 8080:32438/TCP 49s run=load-balancer-example kubernetes ClusterIP 100.64.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 5h27m <none>
List the pods that are running the Hello World application:
$ kubectl get pods --selector="run=load-balancer-example" --output=wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES hello-world-86d6c6f84d-9m6gc 1/1 Running 0 10m 100.96.1.3 ip-172-20-97-84.ec2.internal <none> <none> hello-world-86d6c6f84d-zw287 1/1 Running 0 10m 100.96.2.4 ip-172-20-63-75.ec2.internal <none> <none>
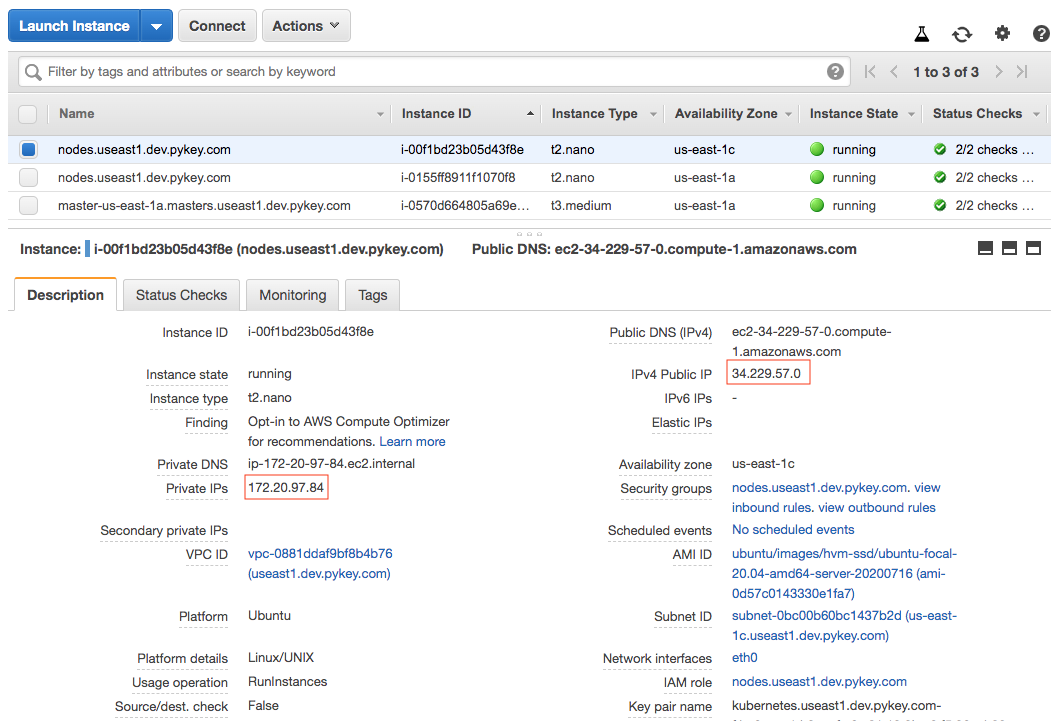
Get the public IP address of one of our nodes that is running a Hello World pod. Use the node address and node port to access the Hello World application:
curl http://<public-node-ip>:<node-port>
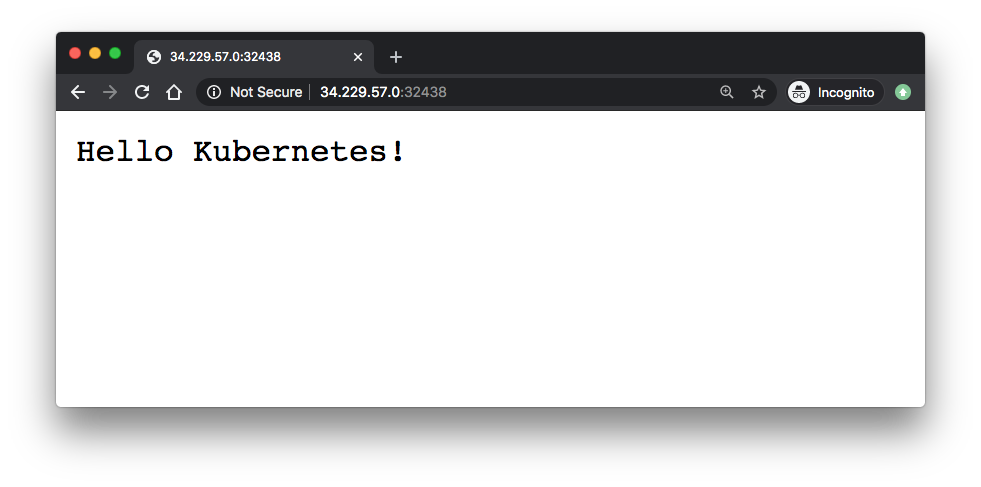
After modifying the inbound rule to allow TCP from the :node-port, we get the following page:
We can see the pods/services/deployments/replicasets on Web-UI:
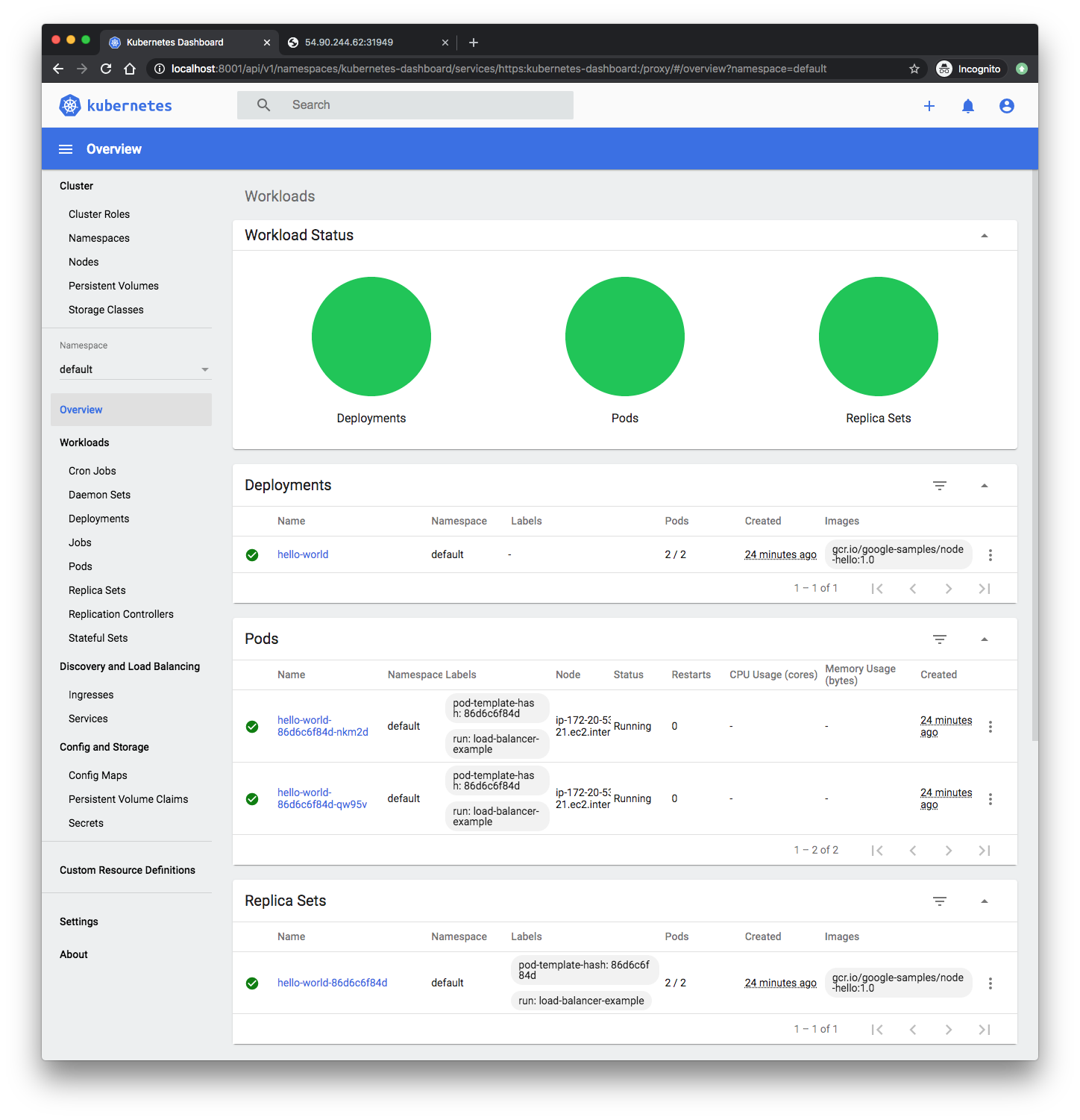
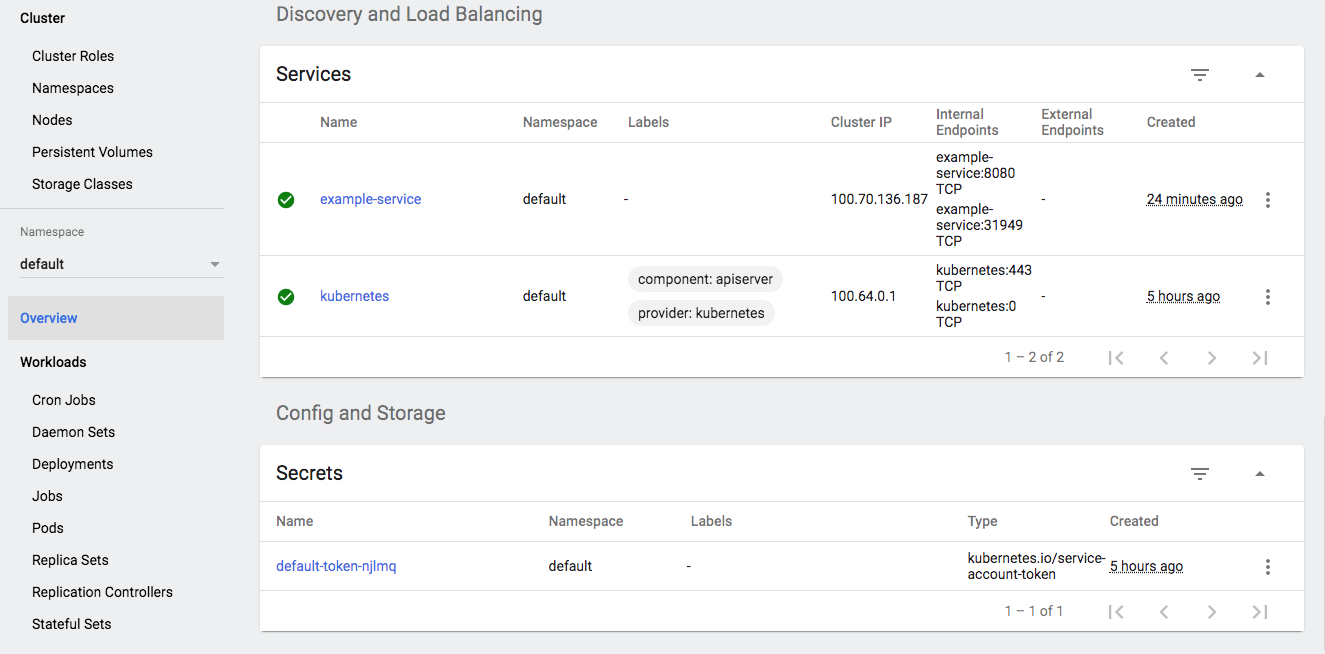
To delete the Service, enter this command:
$ kubectl delete services example-service service "example-service" deleted
To delete the Deployment, the ReplicaSet, and the Pods that are running the Hello World application, enter this command:
$ kubectl delete -f hello.yaml deployment.apps "hello-world" deleted
nginx-deploy.yam:
kind: Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: "nginxdemos/hello"
---
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: nginx-elb
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
nodePort: 30008
Deploy:
$ kubectl apply -f nginx-deploy.yaml deployment.apps/nginx created service/nginx-elb created $ kubectl get pods -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES nginx-66d58cb8c4-8mdr9 1/1 Running 0 43m 100.96.2.5 ip-172-20-63-75.ec2.internal <none> <none> nginx-66d58cb8c4-nxjfw 1/1 Running 0 44m 100.96.1.4 ip-172-20-97-84.ec2.internal <none> <none> $ kubectl get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kubernetes ClusterIP 100.64.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 105m nginx-elb LoadBalancer 100.67.53.146 aa09b8bc3ffb4483ebb29442642c1a2b-1326065343.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80:30008/TCP 2m5s $ kubectl describe svc nginx-elb Name: nginx-elb Namespace: default Labels: <none> Annotations: Selector: app=nginx Type: LoadBalancer IP: 100.67.53.146 LoadBalancer Ingress: aa09b8bc3ffb4483ebb29442642c1a2b-1326065343.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com Port: http 80/TCP TargetPort: 80/TCP NodePort: http 30008/TCP Endpoints: 100.96.1.4:80,100.96.2.5:80 Session Affinity: None External Traffic Policy: Cluster Events: Type Reason Age From Message ---- ------ ---- ---- ------- Normal EnsuringLoadBalancer 9m15s service-controller Ensuring load balancer Normal EnsuredLoadBalancer 9m13s service-controller Ensured load balancer
In the description of the LoadBalancer service, we see the LoadBalancer Ingress property, which is the DNS name we'll use to connect to our web service. The load balancer exposes the port 80 and redirects this traffic to the kubernetes node port 30008. This node will then redirect the traffic to the nginx container.
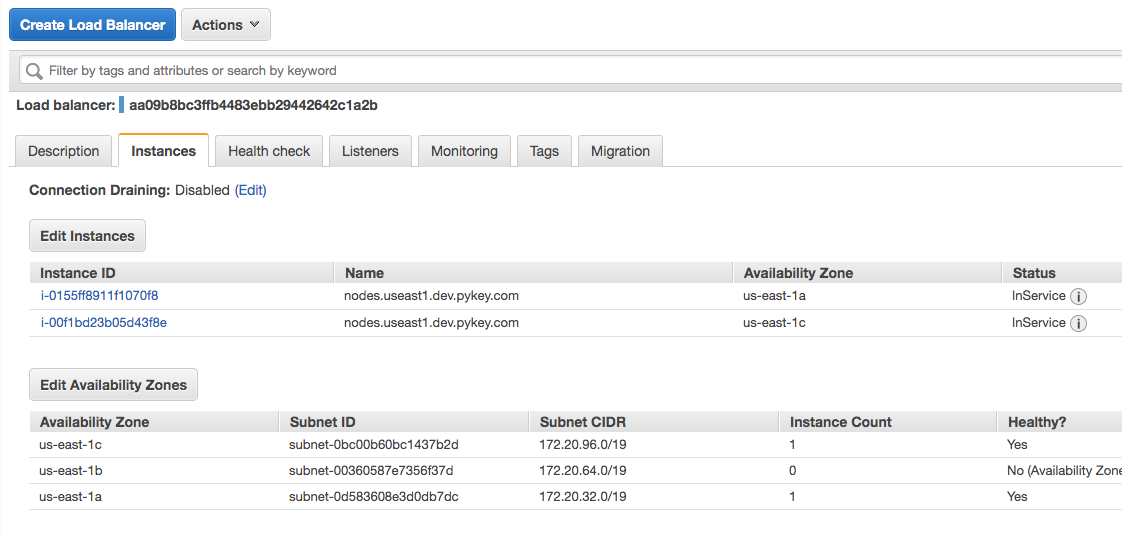
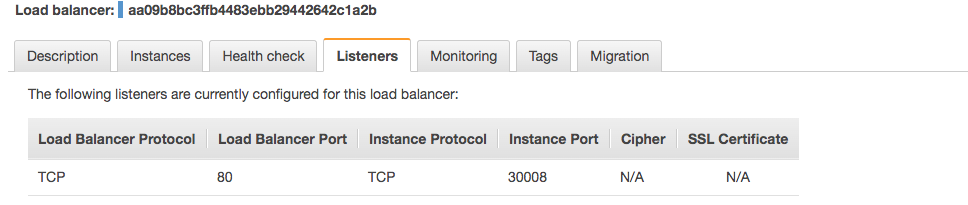
To test if the DNS works we just need to use the LoadBalancer Ingress address:
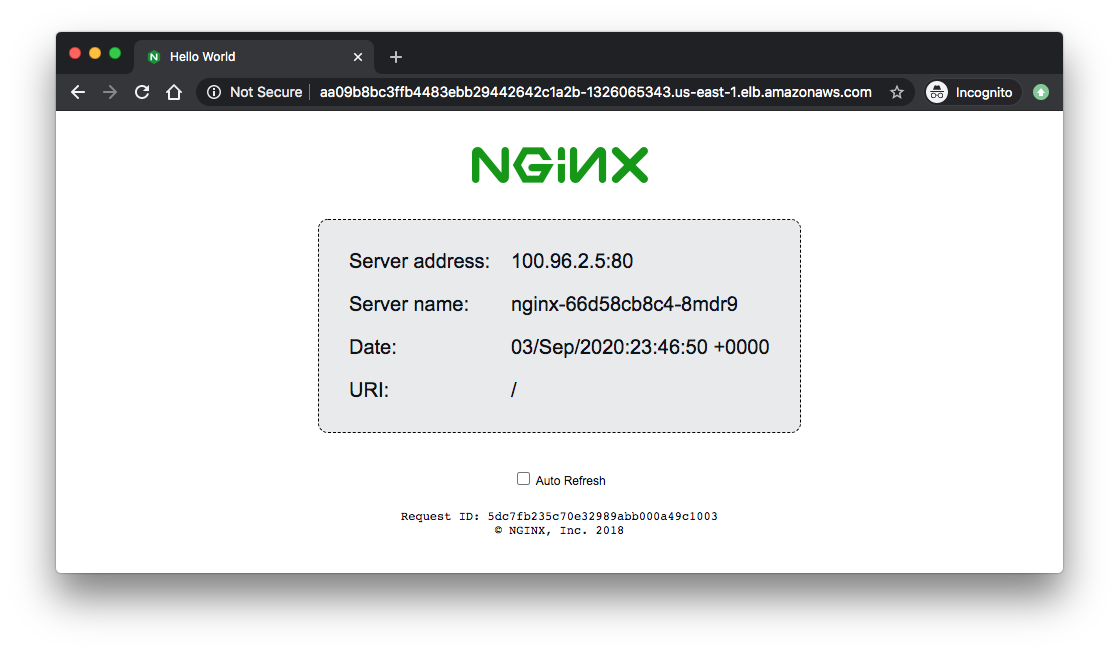
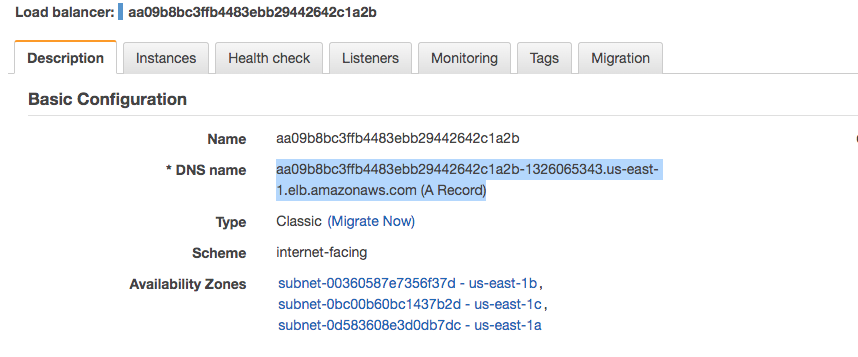
Usually we don't use LoadBalancer Ingress directly, instead we create a CNAME record with a domain (like dev.pykey.com) which points to the load balancer dns name:
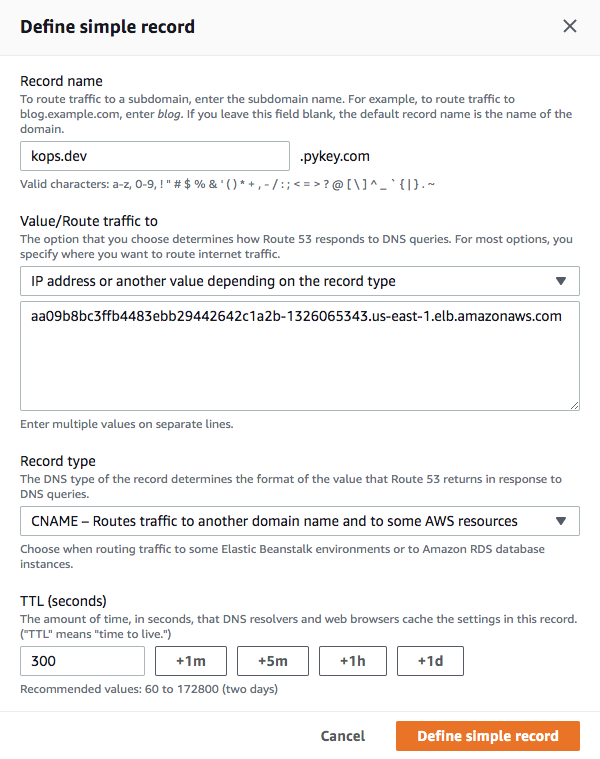
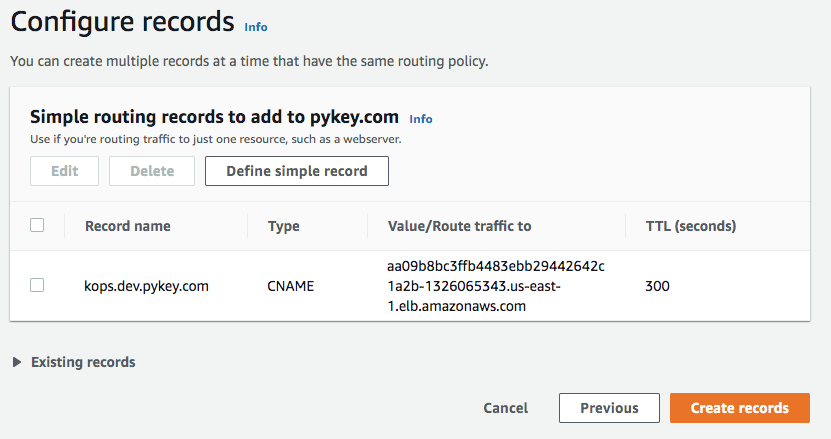
Now that our CNAME for kops.dev.pykey.com is pointing to the LB address, let's try it:
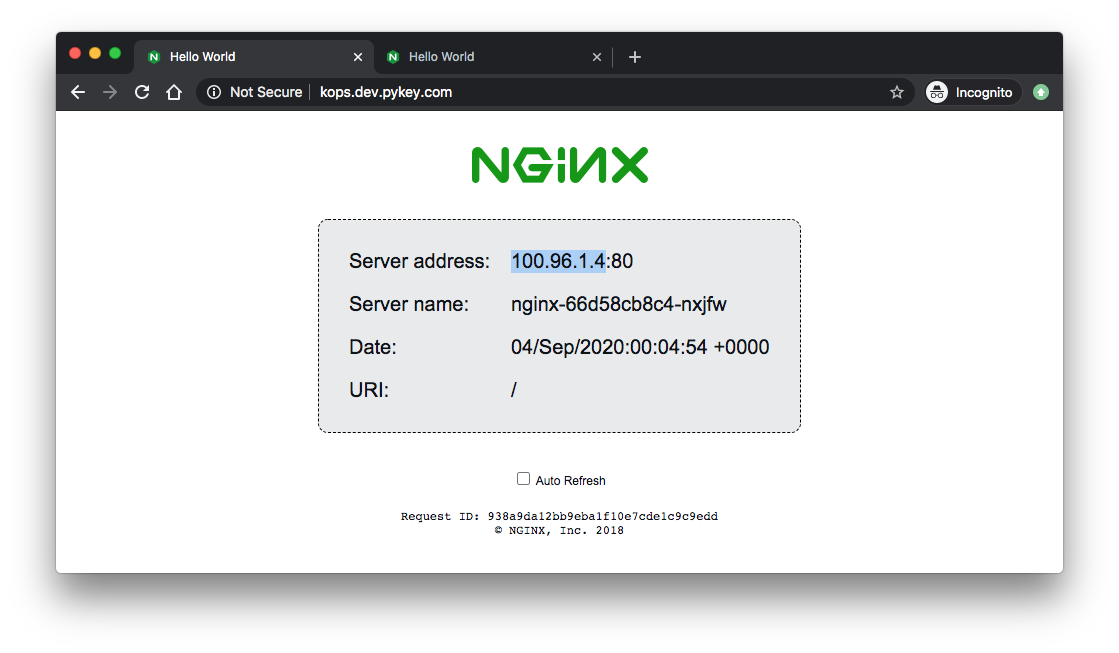
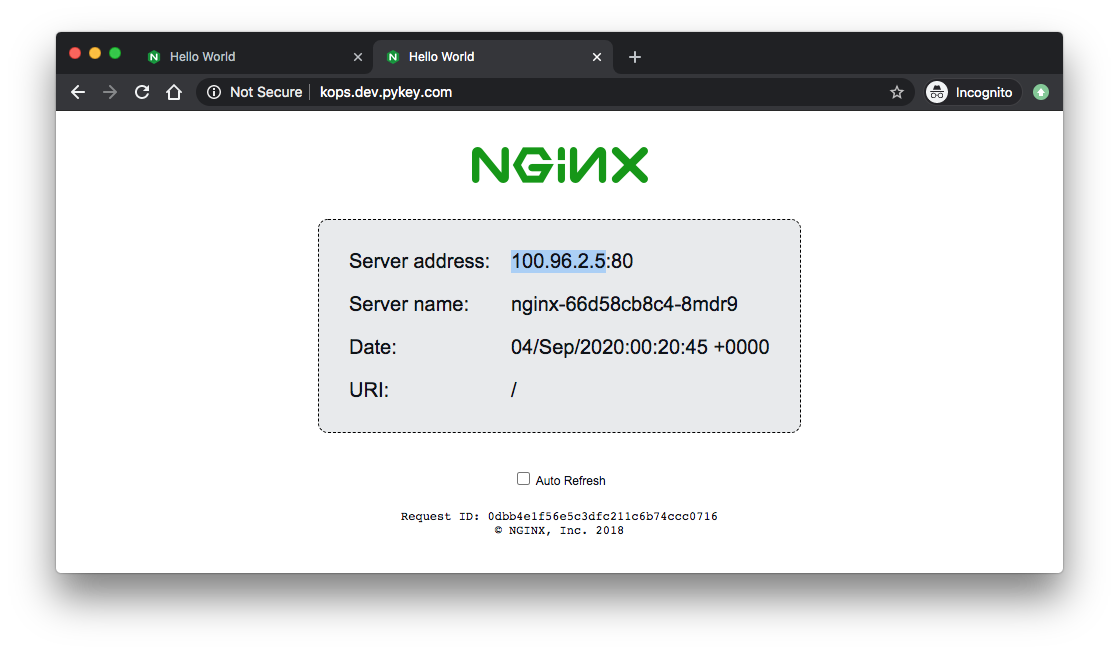
We can also see the load balancing is working. Compare the IPs with the server addresses of the browser:
$ kubectl get pods -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES nginx-66d58cb8c4-8mdr9 1/1 Running 0 43m 100.96.2.5 ip-172-20-63-75.ec2.internal <none> <none> nginx-66d58cb8c4-nxjfw 1/1 Running 0 44m 100.96.1.4 ip-172-20-97-84.ec2.internal <none> <none>
To delete our cluster:
$ kops delete cluster useast1.dev.pykey.com --yes
Delete S3 bucket:
$ aws s3 rb s3://clusters.dev.pykey.com
For Nginx controller / Ingress with LoadBalancer type service on AWS, check Docker & Kubernetes - Ingress controller on AWS with Kops
- Installing Kubernetes with kops
- kubernetes/kops
- Getting Started with kops on AWS
- Install and Set Up kubectl
- Tutorial: Deploy the Kubernetes Dashboard (web UI)
- Use a Service to Access an Application in a Cluster
- https://github.com/nginxinc/NGINX-Demos/tree/master/nginx-hello
Docker & K8s
- Docker install on Amazon Linux AMI
- Docker install on EC2 Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker container vs Virtual Machine
- Docker install on Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker Hello World Application
- Nginx image - share/copy files, Dockerfile
- Working with Docker images : brief introduction
- Docker image and container via docker commands (search, pull, run, ps, restart, attach, and rm)
- More on docker run command (docker run -it, docker run --rm, etc.)
- Docker Networks - Bridge Driver Network
- Docker Persistent Storage
- File sharing between host and container (docker run -d -p -v)
- Linking containers and volume for datastore
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically I - FROM, MAINTAINER, and build context
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically II - revisiting FROM, MAINTAINER, build context, and caching
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically III - RUN
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically IV - CMD
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically V - WORKDIR, ENV, ADD, and ENTRYPOINT
- Docker - Apache Tomcat
- Docker - NodeJS
- Docker - NodeJS with hostname
- Docker Compose - NodeJS with MongoDB
- Docker - Prometheus and Grafana with Docker-compose
- Docker - StatsD/Graphite/Grafana
- Docker - Deploying a Java EE JBoss/WildFly Application on AWS Elastic Beanstalk Using Docker Containers
- Docker : NodeJS with GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker : Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline with Jenkinsfile and Github
- Docker : Jenkins Master and Slave
- Docker - ELK : ElasticSearch, Logstash, and Kibana
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elasticsearch on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Filebeat on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Logstash on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Kibana on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elastic Stack with Docker Compose
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK) via Elasticsearch operator on minikube
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Stack via Helm on minikube
- Docker Compose - A gentle introduction with WordPress
- Docker Compose - MySQL
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services via docker-compose
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part A (install vault, unsealing, static secrets, and policies)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part B (EaaS, dynamic secrets, leases, and revocation)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part C (Consul)
- Docker Compose with two containers - Flask REST API service container and an Apache server container
- Docker compose : Nginx reverse proxy with multiple containers
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Getting started
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Front Proxy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ambassador - Envoy API Gateway on Kubernetes
- Docker Packer
- Docker Cheat Sheet
- Docker Q & A #1
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part I
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part II
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker II (snapshot app with nginx)
- Docker - NodeJS and MySQL app with React in a docker
- Docker - Step by Step NodeJS and MySQL app with React - I
- Installing LAMP via puppet on Docker
- Docker install via Puppet
- Nginx Docker install via Ansible
- Apache Hadoop CDH 5.8 Install with QuickStarts Docker
- Docker - Deploying Flask app to ECS
- Docker Compose - Deploying WordPress to AWS
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI EC2 type)
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI Fargate type)
- Docker - ECS Fargate
- Docker - AWS ECS service discovery with Flask and Redis
- Docker & Kubernetes : minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes 2 : minikube Django with Postgres - persistent volume
- Docker & Kubernetes 3 : minikube Django with Redis and Celery
- Docker & Kubernetes 4 : Django with RDS via AWS Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kops on AWS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ingress controller on AWS with Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul - Auto-unseal using Transit Secrets Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes & Persistent Volumes Claims - hostPath and annotations
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes - Dynamic volume provisioning
- Docker & Kubernetes : DaemonSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Secrets
- Docker & Kubernetes : kubectl command
- Docker & Kubernetes : Assign a Kubernetes Pod to a particular node in a Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : Configure a Pod to Use a ConfigMap
- AWS : EKS (Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Run a React app in a minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Minikube install on AWS EC2
- Docker & Kubernetes : Cassandra with a StatefulSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Terraform and AWS EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Pods and Service definitions
- Docker & Kubernetes : Service IP and the Service Type
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes DNS with Pods and Services
- Docker & Kubernetes : Headless service and discovering pods
- Docker & Kubernetes : Scaling and Updating application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Horizontal pod autoscaler on minikubes
- Docker & Kubernetes : From a monolithic app to micro services on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Rolling updates
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deployments to GKE (Rolling update, Canary and Blue-green deployments)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Slack Chat Bot with NodeJS on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery with Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline for Dev, Canary, and Production Environments on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : NodePort vs LoadBalancer vs Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB / MongoExpress on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Load Testing with Locust on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB with StatefulSets on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up Ingress with NGINX Controller on Minikube (Mac)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller for Dashboard service on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Ingress with AWS ALB Ingress Controller in EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up a private cluster on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Namespaces (default, kube-public, kube-system) and switching namespaces (kubens)
- Docker & Kubernetes : StatefulSets on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : RBAC
- Docker & Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, and IAM
- Docker & Kubernetes - Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, IAM with EKS ALB, Part 1
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : My first Helm deploy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Readiness and Liveness Probes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm chart repository with Github pages
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB with Ingress to Minikube using Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 2 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 3 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart for Node/Express and MySQL with Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using Helm and Prometheus Operator - Monitoring Kubernetes node resources out of the box
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using kube-prometheus-stack Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio (service mesh) sidecar proxy on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on Minikube with AWS EC2 for Bookinfo Application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part I)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part II - Prometheus, Grafana, pin a service, split traffic, and inject faults)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Package Manager with MySQL on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying Memcached on Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : EKS Control Plane (API server) Metrics with Prometheus
- Docker & Kubernetes : Spinnaker on EKS with Halyard
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery Pipelines with Spinnaker and Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-dind (docker-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-kind (k8s-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : nodeSelector, nodeAffinity, taints/tolerations, pod affinity and anti-affinity - Assigning Pods to Nodes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Jenkins-X on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD App of Apps with Heml on Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD on Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : GitOps with ArgoCD for Continuous Delivery to Kubernetes clusters (minikube) - guestbook
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization