AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) Roles, SSO(Single Sign On), SAML(Security Assertion Markup Language), IdP(identity provider), STS(Security Token Service), and ADFS(Active Directory Federation Services)
We'll learn how to make our users to single sign in to the AWS Management Console or to make programmatic calls to AWS APIs by using assertions from a SAML(Security Assertion Markup Language)-compliant IdP(identity provider).
Since there are good materials how to implement the SSO(Single Sign On), in this tutorial, we'll just look into what the work flow looks like via AD FS (Active Directory Federation Services).
SAML is an open standard used by many identity providers. It enables federated single sign-on (SSO), which lets users sign into the AWS Management Console. Many of us are using Windows AD for our corporate directory, and because Windows Server includes ADFS, it's naural to use ADFS as our IdP.
The following diagrams demostrate, at a high level, how an Active Directory (AD) user is federated by AD FS to gain access to AWS resources:
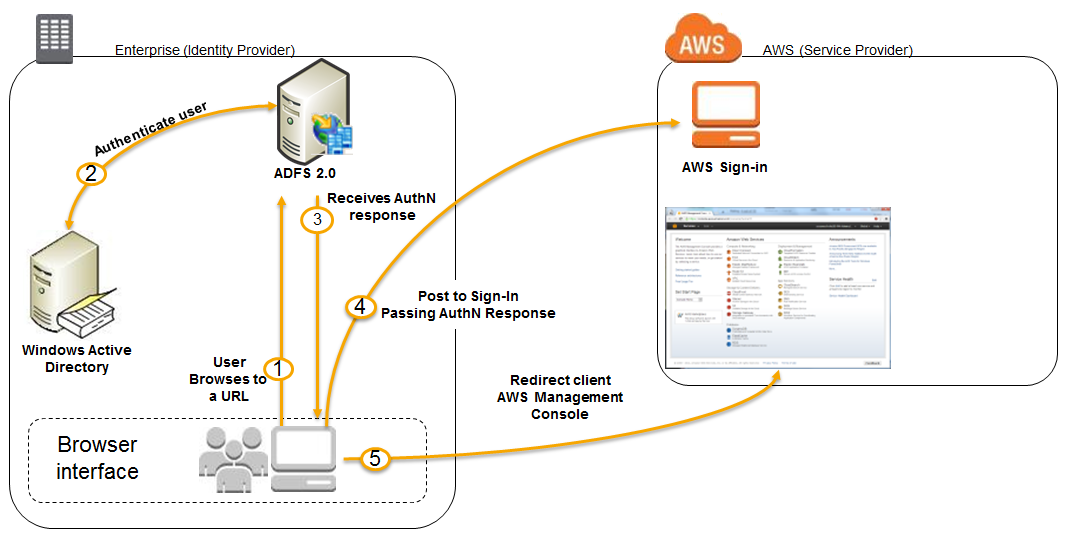
- The flow is initiated when a user (Bob) browses to the ADFS sample site inside his domain.
- The sign-on page authenticates Bob against AD.
- Bob's browser receives a SAML assertion in the form of an authentication response from ADFS. So, this 1,2, and 3 steps are the processes of the federated user authenticates against ADFS. If authentication is successful, the user is sent a SAML assertion.
- Bob's browser posts the SAML assertion to the AWS Security Token Service (STS) in the form of a SAML request. If the SAML request is valid, STS returns a SAML response that contains the user's AWS temporary credentials.
- Bob's browser receives the sign-in URL and is redirected to the console.
Note that the applications or services assume the role (permissions) at run time. This means that AWS is providing to the application or the user temporary security credentials that can be used whenever they need access to those resources.
IAM roles are designed so that our applications can securely make API requests from our instances, without requiring us to manage the security credentials that the applications use. Instead of creating and distributing our AWS credentials, we can delegate permission to make API requests using IAM roles.
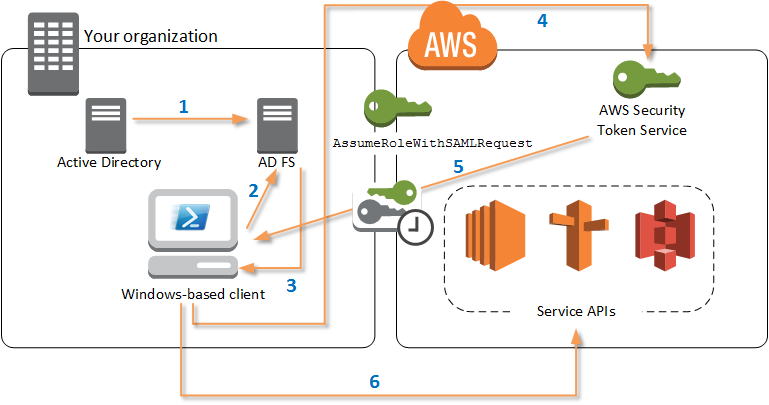
- The Tools for Windows PowerShell authenticate against ADFS by using the Windows user's current credentials, or interactively, when a cmdlet that requires credentials to call into AWS is run.
- ADFS authenticates the user.
- ADFS generates a SAML 2.0 authentication response that includes an assertion; the purpose of the assertion is to identify and provide information about the user. The PowerShell cmdlet extracts the list of the user's authorized roles from the SAML assertion.
- The PowerShell cmdlet forwards the SAML request, including the requested role Amazon Resource Names (ARN), to STS by making the AssumeRoleWithSAMLRequest API call.
- If the SAML request is valid, STS returns a response that contains the AWS AccessKeyId, SecretAccessKey, and SessionToken. These credentials last for 3,600 seconds (1 hour).
- The Tools for Windows PowerShell user now has valid credentials to work with any AWS service APIs that the user's role is authorized to access. The Tools for Windows PowerShell automatically apply these credentials for any subsequent AWS API calls, and renew them automatically when they expire.
Here is a similar diagram:
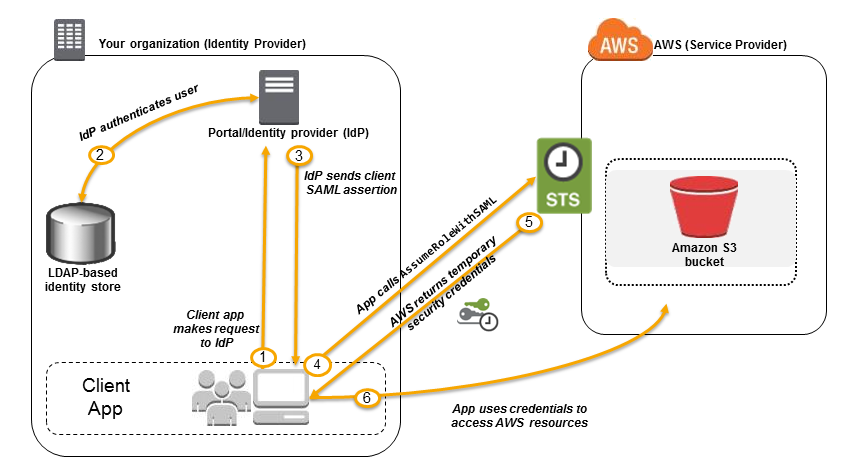
- A user in your organization uses a client app to request authentication from our organization's IdP.
- The IdP authenticates the user against our organization's identity store.
- The IdP constructs a SAML assertion with information about the user and sends the assertion to the client app.
- The client app calls the AWS STS AssumeRoleWithSAML API, passing the ARN of the SAML provider, the ARN of the role to assume, and the SAML assertion from IdP.
- The API response to the client app includes temporary security credentials.
- The client app uses the temporary security credentials to call Amazon S3 APIs.
- AssumeRole
AssumeRole does require us to start with some basic AWS credentials, but those are allowed to be short-term ones as opposed to GetFederationToken. - AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity
AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity requires no AWS credentials to start with. Instead, it takes an external identity (Facebook etc.) and uses the trust policy built into the role to elevate AWS access for a short period of time. - AssumeRoleWithSAML
Same with AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity but it's used within AWS Organizations. - GetFederationToken
We must call the GetFederationToken action using the long-term security credentials of an IAM user. It scopes AWS credentials down in power (weaker) and time (shorter: up to 36h) so they can be handed out to someone else. - GetSessionToken
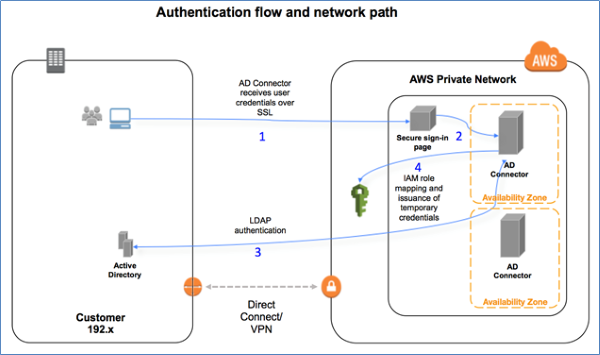
AD Connector is designed to give us an easy way to establish a trusted relationship between our Active Directory and AWS. When AD Connector is configured, the trust allows us to:
- Seamlessly join Windows instances to our Active Directory domain either through the Amazon EC2 launch wizard or programmatically through the EC2 Simple System Manager (SSM) API.
- Provide federated sign-in to the AWS Management Console by mapping Active Directory identities to AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles.
AD Connector forwards sign-in requests to our Active Directory domain controllers for authentication and provides the ability for applications to query the directory for data. When we configure AD Connector, we provide it with service account credentials that are securely stored by AWS. This account is used by AWS to enable single sign-on (SSO).
Given AD Connector's role as a proxy, it does not store or cache user credentials. Rather, all authentication, lookup, and management requests are handled by our Active Directory.
AWS (Amazon Web Services)
- AWS : EKS (Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes)
- AWS : Creating a snapshot (cloning an image)
- AWS : Attaching Amazon EBS volume to an instance
- AWS : Adding swap space to an attached volume via mkswap and swapon
- AWS : Creating an EC2 instance and attaching Amazon EBS volume to the instance using Python boto module with User data
- AWS : Creating an instance to a new region by copying an AMI
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 1
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 2 - Creating and Deleting a Bucket
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 3 - Bucket Versioning
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 4 - Uploading a large file
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 5 - Uploading folders/files recursively
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 6 - Bucket Policy for File/Folder View/Download
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 7 - How to Copy or Move Objects from one region to another
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 8 - Archiving S3 Data to Glacier
- AWS : Creating a CloudFront distribution with an Amazon S3 origin
- AWS : Creating VPC with CloudFormation
- AWS : WAF (Web Application Firewall) with preconfigured CloudFormation template and Web ACL for CloudFront distribution
- AWS : CloudWatch & Logs with Lambda Function / S3
- AWS : Lambda Serverless Computing with EC2, CloudWatch Alarm, SNS
- AWS : Lambda and SNS - cross account
- AWS : CLI (Command Line Interface)
- AWS : CLI (ECS with ALB & autoscaling)
- AWS : ECS with cloudformation and json task definition
- AWS Application Load Balancer (ALB) and ECS with Flask app
- AWS : Load Balancing with HAProxy (High Availability Proxy)
- AWS : VirtualBox on EC2
- AWS : NTP setup on EC2
- AWS: jq with AWS
- AWS & OpenSSL : Creating / Installing a Server SSL Certificate
- AWS : OpenVPN Access Server 2 Install
- AWS : VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) 1 - netmask, subnets, default gateway, and CIDR
- AWS : VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) 2 - VPC Wizard
- AWS : VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) 3 - VPC Wizard with NAT
- DevOps / Sys Admin Q & A (VI) - AWS VPC setup (public/private subnets with NAT)
- AWS - OpenVPN Protocols : PPTP, L2TP/IPsec, and OpenVPN
- AWS : Autoscaling group (ASG)
- AWS : Setting up Autoscaling Alarms and Notifications via CLI and Cloudformation
- AWS : Adding a SSH User Account on Linux Instance
- AWS : Windows Servers - Remote Desktop Connections using RDP
- AWS : Scheduled stopping and starting an instance - python & cron
- AWS : Detecting stopped instance and sending an alert email using Mandrill smtp
- AWS : Elastic Beanstalk with NodeJS
- AWS : Elastic Beanstalk Inplace/Rolling Blue/Green Deploy
- AWS : Identity and Access Management (IAM) Roles for Amazon EC2
- AWS : Identity and Access Management (IAM) Policies, sts AssumeRole, and delegate access across AWS accounts
- AWS : Identity and Access Management (IAM) sts assume role via aws cli2
- AWS : Creating IAM Roles and associating them with EC2 Instances in CloudFormation
- AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) Roles, SSO(Single Sign On), SAML(Security Assertion Markup Language), IdP(identity provider), STS(Security Token Service), and ADFS(Active Directory Federation Services)
- AWS : Amazon Route 53
- AWS : Amazon Route 53 - DNS (Domain Name Server) setup
- AWS : Amazon Route 53 - subdomain setup and virtual host on Nginx
- AWS Amazon Route 53 : Private Hosted Zone
- AWS : SNS (Simple Notification Service) example with ELB and CloudWatch
- AWS : Lambda with AWS CloudTrail
- AWS : SQS (Simple Queue Service) with NodeJS and AWS SDK
- AWS : Redshift data warehouse
- AWS : CloudFormation
- AWS : CloudFormation Bootstrap UserData/Metadata
- AWS : CloudFormation - Creating an ASG with rolling update
- AWS : Cloudformation Cross-stack reference
- AWS : OpsWorks
- AWS : Network Load Balancer (NLB) with Autoscaling group (ASG)
- AWS CodeDeploy : Deploy an Application from GitHub
- AWS EC2 Container Service (ECS)
- AWS EC2 Container Service (ECS) II
- AWS Hello World Lambda Function
- AWS Lambda Function Q & A
- AWS Node.js Lambda Function & API Gateway
- AWS API Gateway endpoint invoking Lambda function
- AWS API Gateway invoking Lambda function with Terraform
- AWS API Gateway invoking Lambda function with Terraform - Lambda Container
- Amazon Kinesis Streams
- AWS: Kinesis Data Firehose with Lambda and ElasticSearch
- Amazon DynamoDB
- Amazon DynamoDB with Lambda and CloudWatch
- Loading DynamoDB stream to AWS Elasticsearch service with Lambda
- Amazon ML (Machine Learning)
- Simple Systems Manager (SSM)
- AWS : RDS Connecting to a DB Instance Running the SQL Server Database Engine
- AWS : RDS Importing and Exporting SQL Server Data
- AWS : RDS PostgreSQL & pgAdmin III
- AWS : RDS PostgreSQL 2 - Creating/Deleting a Table
- AWS : MySQL Replication : Master-slave
- AWS : MySQL backup & restore
- AWS RDS : Cross-Region Read Replicas for MySQL and Snapshots for PostgreSQL
- AWS : Restoring Postgres on EC2 instance from S3 backup
- AWS : Q & A
- AWS : Security
- AWS : Security groups vs. network ACLs
- AWS : Scaling-Up
- AWS : Networking
- AWS : Single Sign-on (SSO) with Okta
- AWS : JIT (Just-in-Time) with Okta
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization