Dockerfiles : building Docker images automatically IV - CMD
Continued from Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically III - RUN
In this chapter, we're going to learn more on how to automate this process via instructions in Dockerfiles. We'll be focused on CMD.
This section is from http://docs.docker.com/reference/builder/.
CMD has 3 forms:
- CMD ["executable","param1","param2"] (exec form, this is the preferred form)
- CMD ["param1","param2"] (as default parameters to ENTRYPOINT)
- CMD command param1 param2 (shell form)
There can only be one CMD instruction in a Dockerfile. If we list more than one CMD then only the last CMD will take effect.
The main purpose of a CMD is to provide defaults for an executing container. These defaults can include an executable, or they can omit the executable, in which case we must specify an ENTRYPOINT instruction as well.
- Note: If CMD is used to provide default arguments for the ENTRYPOINT instruction, both the CMD and ENTRYPOINT instructions should be specified with the JSON array format.
- Note: The exec form is parsed as a JSON array, which means that you must use double-quotes (") around words not single-quotes (').
- Note: Unlike the shell form, the exec form does not invoke a command shell. This means that normal shell processing does not happen. For example, CMD [ "echo", "$HOME" ] will not do variable substitution on $HOME. If you want shell processing then either use the shell form or execute a shell directly, for example: CMD [ "sh", "-c", "echo", "$HOME" ].
Here is our Dockerfile that we're going to play with in this chapter. We'll run instructions from this file step by step by uncommenting and commenting each line.
FROM debian:latest MAINTAINER devops@bogotobogo.com # 1 - RUN RUN apt-get update && DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -yq apt-utils RUN DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -yq htop RUN apt-get clean # 2 - CMD CMD ["htop"]
We have one instruction for CMD, and at the completion of the CMD, it will become an image.
$ docker image build -t bogodevops/demo . Sending build context to Docker daemon 33.56 MB Sending build context to Docker daemon Step 0 : FROM debian:latest ---> f6fab3b798be Step 1 : MAINTAINER k@bogotobogo.com ---> Using cache ---> 511bcbdd59ba Step 2 : RUN apt-get update && DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -yq apt-utils ---> Using cache ---> e6e2c03b8efc Step 3 : RUN DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -yq htop ---> Using cache ---> fac6e3168cfe Step 4 : RUN apt-get clean ---> Using cache ---> 358b5cc4b9fa Step 5 : CMD htop ---> Running in d31a73253846 ---> b64547129d16 Removing intermediate container d31a73253846 Successfully built b64547129d16
But unlike in the previous chapter where we ran htop explicitly within the container, this time, it becomes a default environment.
So, even though we issue docker run without passing in any command, we have htop running automatically when the container is created:
$ docker container run -it --rm bogodevops/demo
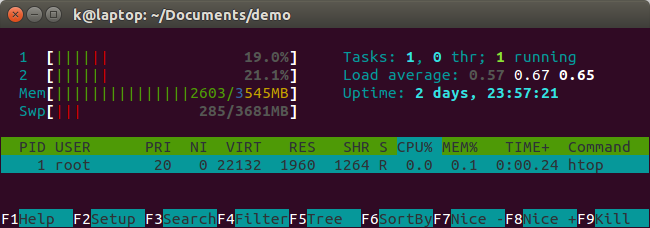
We get the htop as soon as we're in the container. It's given us as an environment.
If we pass in /bin/bash, then we'll have bash instead of htop:
$ docker container run -it --rm bogodevops/demo /bin/bash root@00e40007ed7d:/# exit exit
Before we start new thing, we need to remove 'testimage' in our directory:
$ ls Dockerfile testimage $ rm testimage
Then, let's switch our CMD instruction to CMD ["ls", "l"]. Here is our new Dockerfile:
FROM debian:latest MAINTAINER k@bogotobogo.com # 1 - RUN RUN apt-get update && DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -yq apt-utils RUN DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -yq htop RUN apt-get clean # 2 - CMD #CMD ["htop"] CMD ["ls", "l"]
Build a new image with the new CMD ["ls", "l"]:
$ docker image build -t bogodevops/demo . Sending build context to Docker daemon 2.56 kB Sending build context to Docker daemon Step 0 : FROM debian:latest ---> f6fab3b798be Step 1 : MAINTAINER k@bogotobogo.com ---> Using cache ---> 511bcbdd59ba Step 2 : RUN apt-get update && DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -yq apt-utils ---> Using cache ---> e6e2c03b8efc Step 3 : RUN DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -yq htop ---> Using cache ---> fac6e3168cfe Step 4 : RUN apt-get clean ---> Using cache ---> 358b5cc4b9fa Step 5 : CMD ls -l ---> Running in 717df1a3baa2 ---> d2f3de97b6ef Removing intermediate container 717df1a3baa2 Successfully built d2f3de97b6ef
If we go in our container, it will automatically gives the output from ls -a:
$ docker container run -it --rm bogodevops/demo total 68 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 5 21:37 bin drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Sep 21 18:17 boot drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 360 Nov 25 05:25 dev drwxr-xr-x 32 root root 4096 Nov 25 05:25 etc drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Sep 21 18:17 home drwxr-xr-x 8 root root 4096 Nov 25 02:27 lib drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 5 21:33 lib64 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 5 21:31 media drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Sep 21 18:17 mnt drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 5 21:31 opt dr-xr-xr-x 253 root root 0 Nov 25 05:25 proc drwx------ 2 root root 4096 Nov 5 21:31 root drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 Nov 5 21:37 run drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 5 21:37 sbin drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 10 2012 selinux drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 5 21:31 srv dr-xr-xr-x 13 root root 0 Nov 25 05:25 sys drwxrwxrwt 2 root root 4096 Nov 5 21:37 tmp drwxr-xr-x 16 root root 4096 Nov 25 02:27 usr drwxr-xr-x 17 root root 4096 Nov 25 02:27 var
Docker & K8s
- Docker install on Amazon Linux AMI
- Docker install on EC2 Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker container vs Virtual Machine
- Docker install on Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker Hello World Application
- Nginx image - share/copy files, Dockerfile
- Working with Docker images : brief introduction
- Docker image and container via docker commands (search, pull, run, ps, restart, attach, and rm)
- More on docker run command (docker run -it, docker run --rm, etc.)
- Docker Networks - Bridge Driver Network
- Docker Persistent Storage
- File sharing between host and container (docker run -d -p -v)
- Linking containers and volume for datastore
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically I - FROM, MAINTAINER, and build context
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically II - revisiting FROM, MAINTAINER, build context, and caching
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically III - RUN
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically IV - CMD
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically V - WORKDIR, ENV, ADD, and ENTRYPOINT
- Docker - Apache Tomcat
- Docker - NodeJS
- Docker - NodeJS with hostname
- Docker Compose - NodeJS with MongoDB
- Docker - Prometheus and Grafana with Docker-compose
- Docker - StatsD/Graphite/Grafana
- Docker - Deploying a Java EE JBoss/WildFly Application on AWS Elastic Beanstalk Using Docker Containers
- Docker : NodeJS with GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker : Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline with Jenkinsfile and Github
- Docker : Jenkins Master and Slave
- Docker - ELK : ElasticSearch, Logstash, and Kibana
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elasticsearch on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Filebeat on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Logstash on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Kibana on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elastic Stack with Docker Compose
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK) via Elasticsearch operator on minikube
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Stack via Helm on minikube
- Docker Compose - A gentle introduction with WordPress
- Docker Compose - MySQL
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services via docker-compose
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part A (install vault, unsealing, static secrets, and policies)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part B (EaaS, dynamic secrets, leases, and revocation)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part C (Consul)
- Docker Compose with two containers - Flask REST API service container and an Apache server container
- Docker compose : Nginx reverse proxy with multiple containers
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Getting started
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Front Proxy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ambassador - Envoy API Gateway on Kubernetes
- Docker Packer
- Docker Cheat Sheet
- Docker Q & A #1
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part I
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part II
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker II (snapshot app with nginx)
- Docker - NodeJS and MySQL app with React in a docker
- Docker - Step by Step NodeJS and MySQL app with React - I
- Installing LAMP via puppet on Docker
- Docker install via Puppet
- Nginx Docker install via Ansible
- Apache Hadoop CDH 5.8 Install with QuickStarts Docker
- Docker - Deploying Flask app to ECS
- Docker Compose - Deploying WordPress to AWS
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI EC2 type)
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI Fargate type)
- Docker - ECS Fargate
- Docker - AWS ECS service discovery with Flask and Redis
- Docker & Kubernetes : minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes 2 : minikube Django with Postgres - persistent volume
- Docker & Kubernetes 3 : minikube Django with Redis and Celery
- Docker & Kubernetes 4 : Django with RDS via AWS Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kops on AWS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ingress controller on AWS with Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul - Auto-unseal using Transit Secrets Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes & Persistent Volumes Claims - hostPath and annotations
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes - Dynamic volume provisioning
- Docker & Kubernetes : DaemonSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Secrets
- Docker & Kubernetes : kubectl command
- Docker & Kubernetes : Assign a Kubernetes Pod to a particular node in a Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : Configure a Pod to Use a ConfigMap
- AWS : EKS (Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Run a React app in a minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Minikube install on AWS EC2
- Docker & Kubernetes : Cassandra with a StatefulSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Terraform and AWS EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Pods and Service definitions
- Docker & Kubernetes : Service IP and the Service Type
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes DNS with Pods and Services
- Docker & Kubernetes : Headless service and discovering pods
- Docker & Kubernetes : Scaling and Updating application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Horizontal pod autoscaler on minikubes
- Docker & Kubernetes : From a monolithic app to micro services on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Rolling updates
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deployments to GKE (Rolling update, Canary and Blue-green deployments)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Slack Chat Bot with NodeJS on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery with Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline for Dev, Canary, and Production Environments on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : NodePort vs LoadBalancer vs Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB / MongoExpress on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Load Testing with Locust on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB with StatefulSets on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up Ingress with NGINX Controller on Minikube (Mac)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller for Dashboard service on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Ingress with AWS ALB Ingress Controller in EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up a private cluster on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Namespaces (default, kube-public, kube-system) and switching namespaces (kubens)
- Docker & Kubernetes : StatefulSets on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : RBAC
- Docker & Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, and IAM
- Docker & Kubernetes - Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, IAM with EKS ALB, Part 1
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : My first Helm deploy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Readiness and Liveness Probes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm chart repository with Github pages
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB with Ingress to Minikube using Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 2 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 3 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart for Node/Express and MySQL with Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using Helm and Prometheus Operator - Monitoring Kubernetes node resources out of the box
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using kube-prometheus-stack Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio (service mesh) sidecar proxy on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on Minikube with AWS EC2 for Bookinfo Application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part I)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part II - Prometheus, Grafana, pin a service, split traffic, and inject faults)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Package Manager with MySQL on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying Memcached on Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : EKS Control Plane (API server) Metrics with Prometheus
- Docker & Kubernetes : Spinnaker on EKS with Halyard
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery Pipelines with Spinnaker and Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-dind (docker-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-kind (k8s-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : nodeSelector, nodeAffinity, taints/tolerations, pod affinity and anti-affinity - Assigning Pods to Nodes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Jenkins-X on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD App of Apps with Heml on Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD on Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : GitOps with ArgoCD for Continuous Delivery to Kubernetes clusters (minikube) - guestbook
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization