Docker : Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline with Jenkinsfile and Github
In this post, we'll setup Jenkins from scratch in a Docker container. Then, we'll create a Multibranch pipeline with git that runs a Jenkinsfile.
The official Jenkins image for Docker is available from https://hub.docker.com/r/jenkins/jenkins/.
This is a fully functional Jenkins server, based on the weekly and LTS releases.
To use the latest LTS: docker pull jenkins/jenkins:lts.
To run container in a detached mode and to create a 'jenkins_home' docker volume attached to the host machine volume as shown in https://github.com/jenkinsci/docker/blob/master/README.md, we do the fillowing:
$ docker run -d -v jenkins_home:/var/jenkins_home -p 8080:8080 -p 5000:5000 jenkins/jenkins:lts ... hudson.WebAppMain$3#run: Jenkins is fully up and running $ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 666101198dd0 jenkins/jenkins:lts "/sbin/tini -- /usr/…" 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes 0.0.0.0:8080->8080/tcp, 0.0.0.0:50000->50000/tcp dazzling_euclid
The mapping (i.e. "publish") port 8080 of the current container to port 8080 on the host machine. The first number represents the port on the host while the last represents the container's port.
This is optional but we map port 5000 of the current container to port 5000 on the host machine. This is only necessary if we have set up one or more inbound Jenkins agents on other machines, which in turn interact with our jenkins container (the Jenkins "controller"). Inbound Jenkins agents communicate with the Jenkins controller through TCP port 50000 by default.
We're also mapping the /var/jenkins_home directory in the container to the Docker volume with the name jenkins_home. Instead of mapping the /var/jenkins_home directory to a Docker volume, we could also map this directory to one on our machine's local file system. For example, specifying the option --volume $HOME/jenkins:/var/jenkins_home would map the container's /var/jenkins_home directory to the jenkins subdirectory within the $HOME directory on our local machine, which would typically be /Users/<username>/jenkins or /home/<username>/jenkins.
Thanks to the volume, we will survive the container stop/restart/deletion. Also, by making an explicit volume, we can manage it and attach to another container for upgrades.
Note: On a Mac host, the volume, jenkins_home, is located on vm where the docker in running:
$ screen ~/Library/Containers/com.docker.docker/Data/vms/0/tty docker-desktop:~# ls /var/lib/docker/volumes ... jenkins_home ...
We can access our Jenkins running on the container:
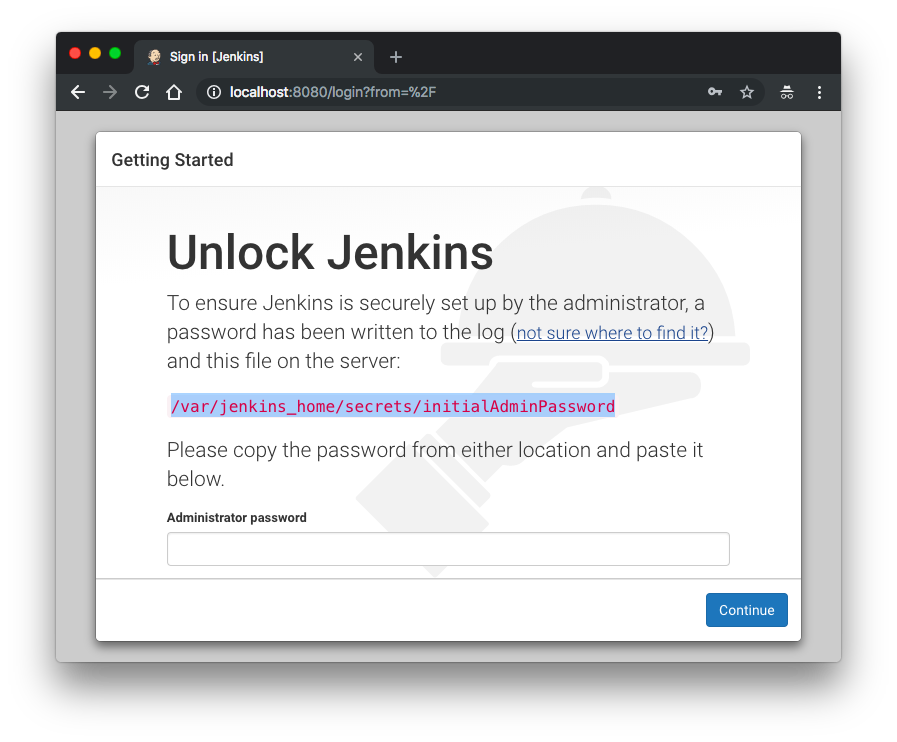
Let's go into the running Jenkins container and retrieve an initial password to unlock Jenkins:
$ docker exec -i -t --user root 666101198dd0 /bin/bash root@666101198dd0:/# root@666101198dd0:/# cat /var/jenkins_home/secrets/initialAdminPassword 56316ef50c714872a210ee44564cbe40
As instructed, paste the password and click "Continue":
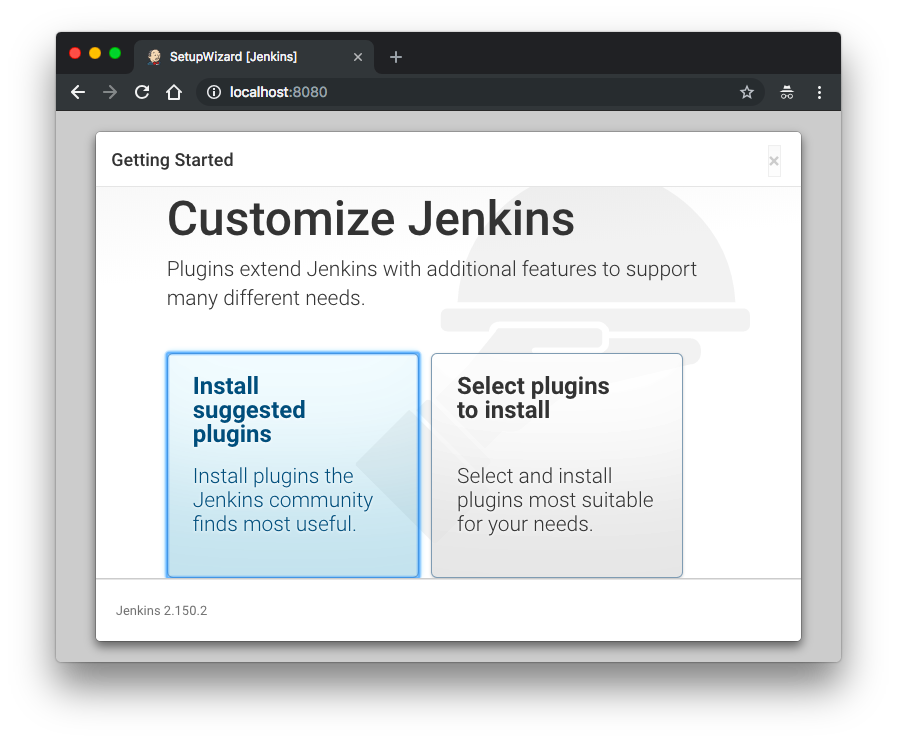
After unlocking Jenkins, the Customize Jenkins page appears. Here we can install any number of useful plugins as part of our initial setup.
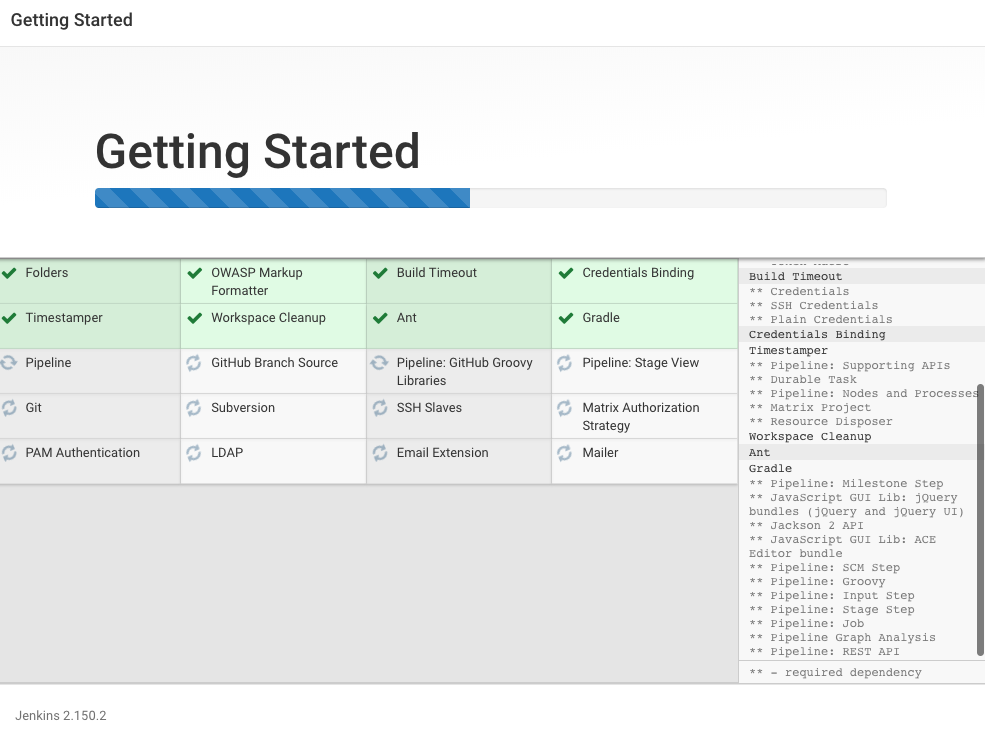
Select "Install suggested plugins", then the setup wizard shows the progression of Jenkins being configured:
After customizing Jenkins with plugins, Jenkins asks us to create our first administrator user:
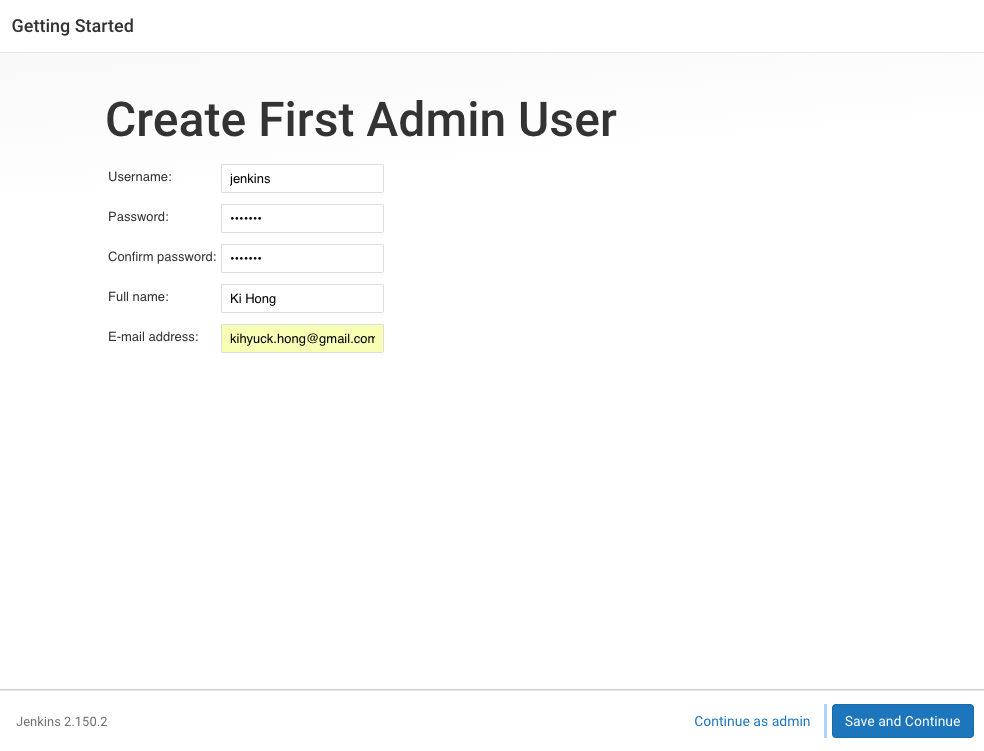
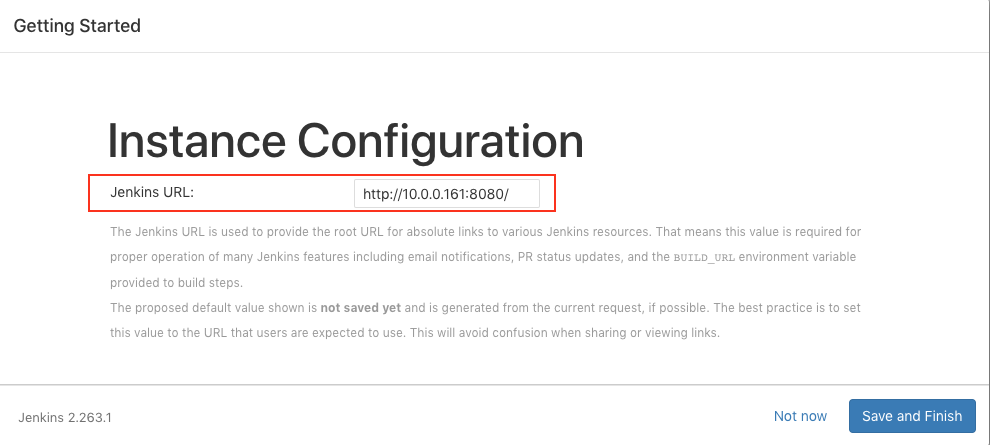
Click "Save and Finish" and "Start using Jenkins":
Credentials in Jenkins have three scopes depending where this credential can be used:
- Global(for Jenkins instances such as email auth, slave connection, etc) scope
- System (job related) scope
- Per project
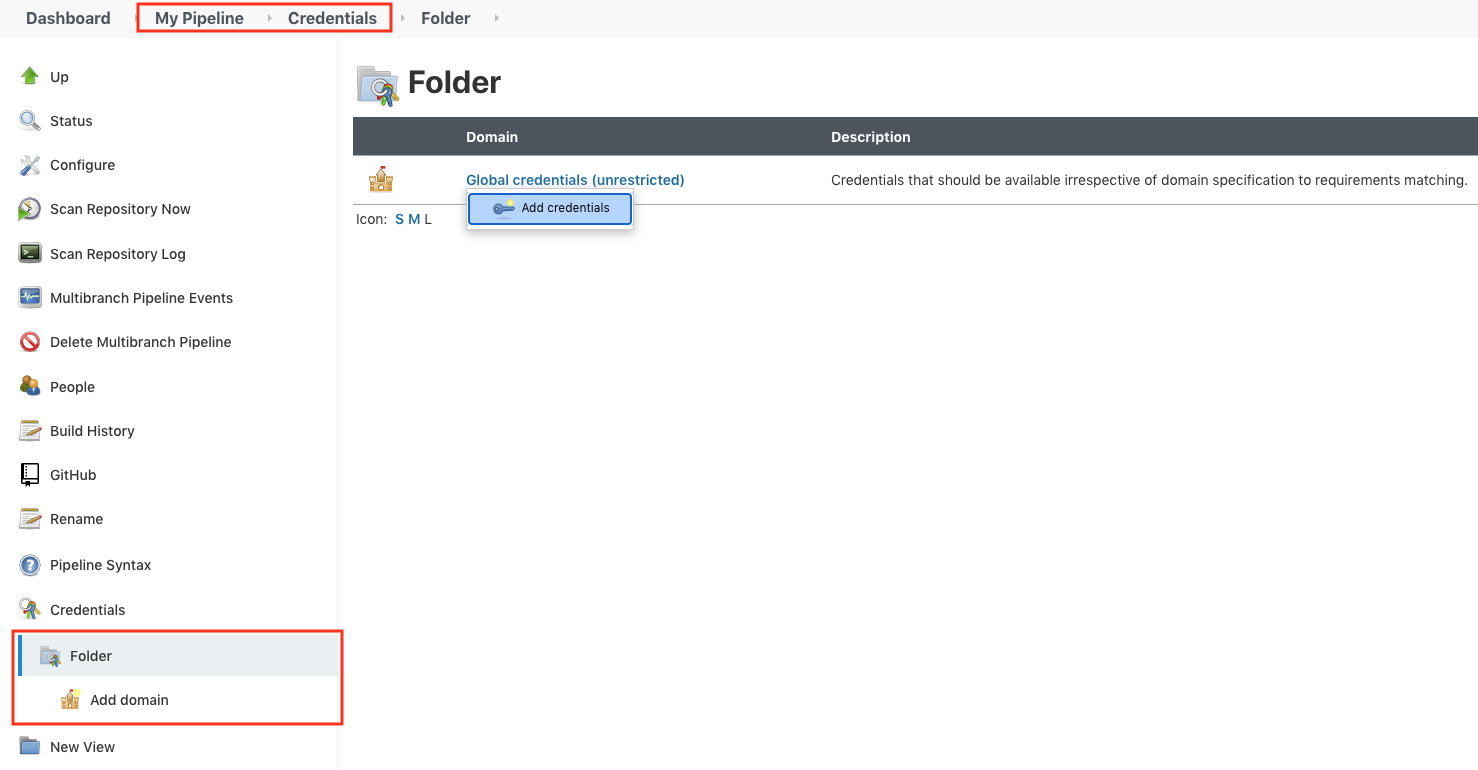
For our Multibranch project, the following needs to be set:
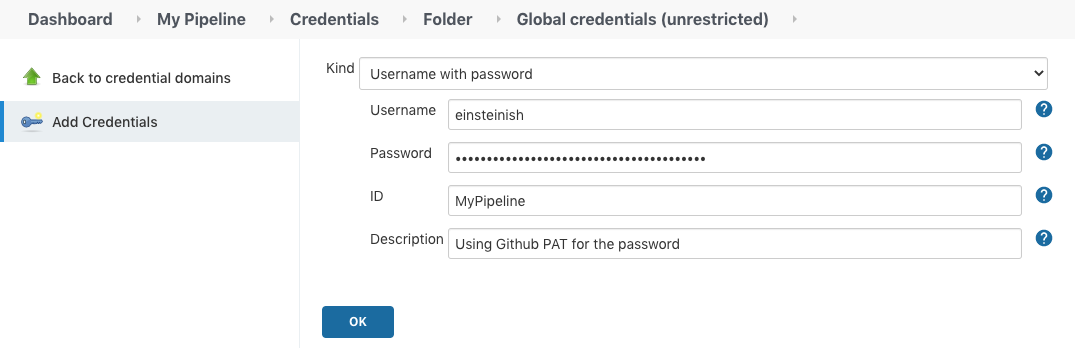
Note that we used PAT (Personal Access Token) for the password.
Here is the git repo.
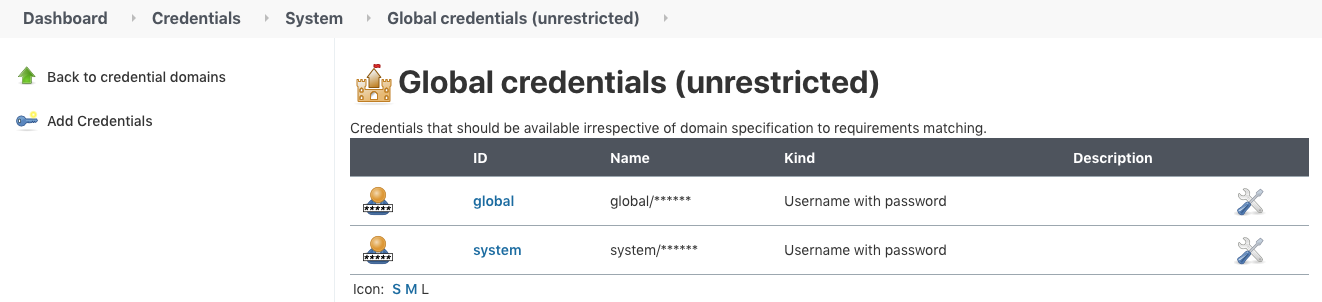
Here are the credentials so far.
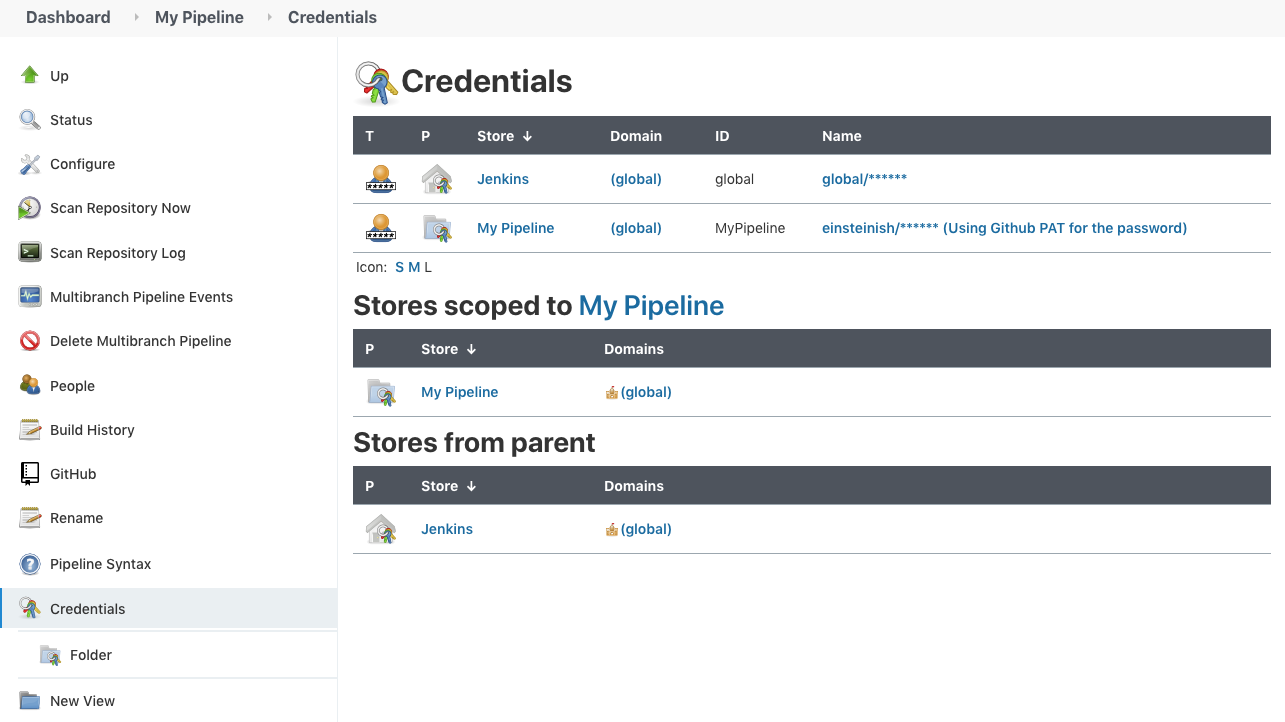
As we can see the credentials for the 'My Pipeline" won't be visible to other project. Each project can have its own credentials that are not visible to other projects.
Note also that the System credentials are hidden from our project, 'My Pipeline", and we only see the Jenkins/Global scope.
Configure the project with the credentials we put in the previous section:
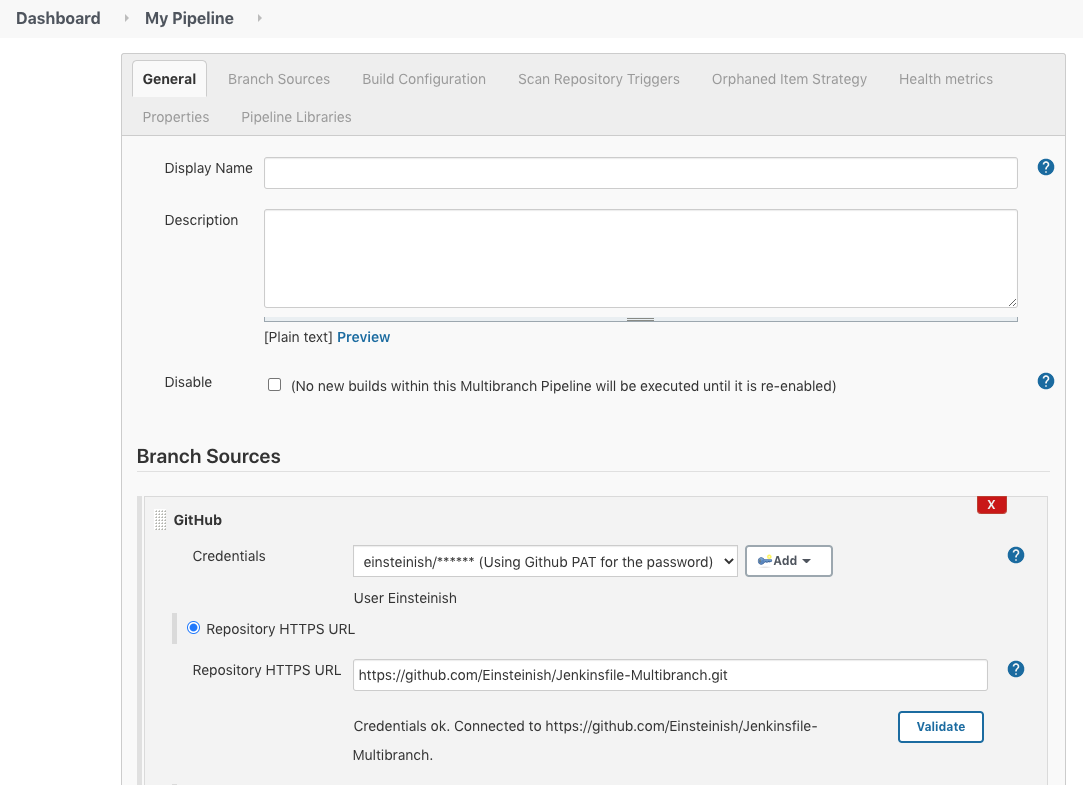
Hit "Save", then it will run. From the "Console Output", we see it was successfully built:
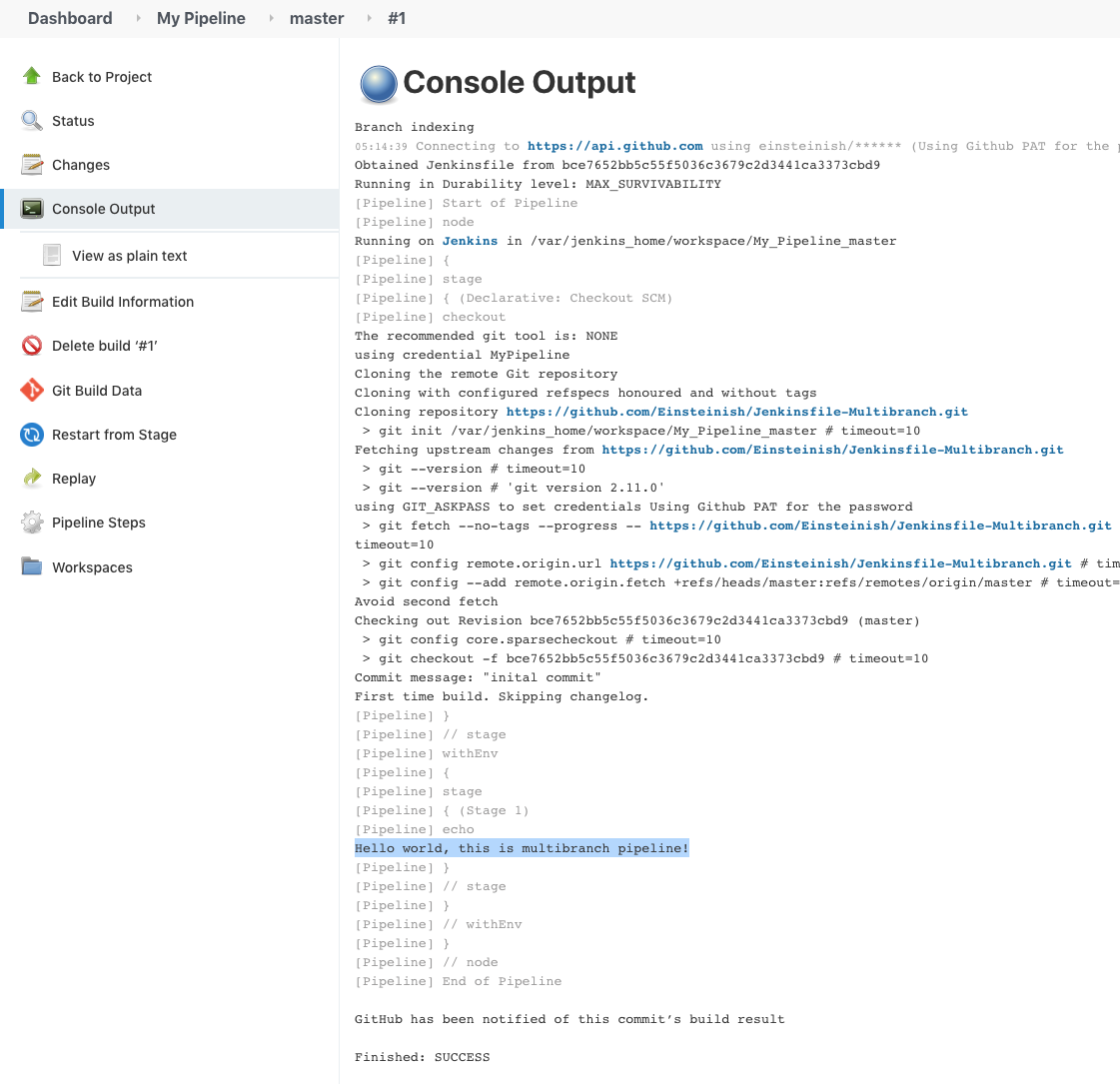
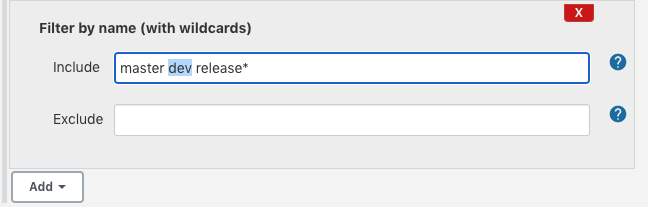
As the project name suggests the Multibranch Pipeline can do several branches not just the master branch as in the previous example. In the project configuration page, we can set the branches we want by adding filter for the behavior of repo discovery:
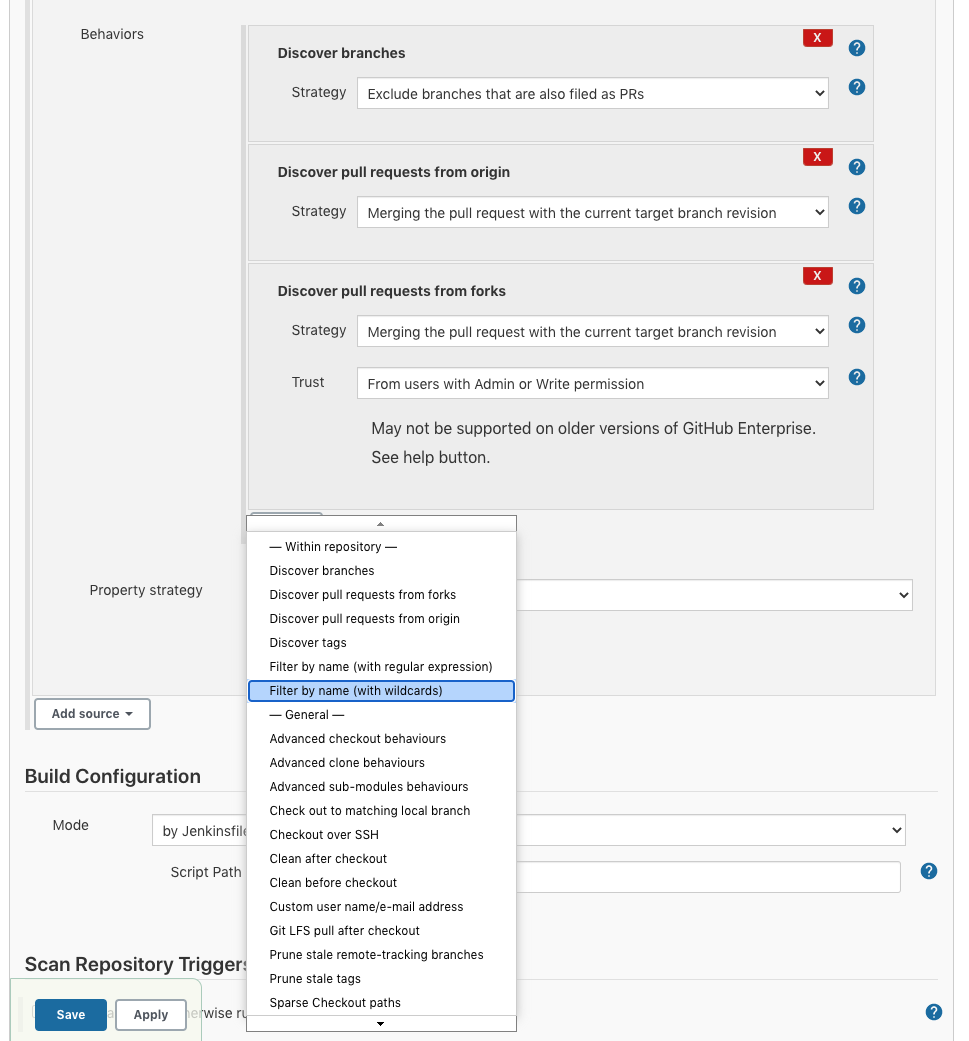
The added filter should look like this:
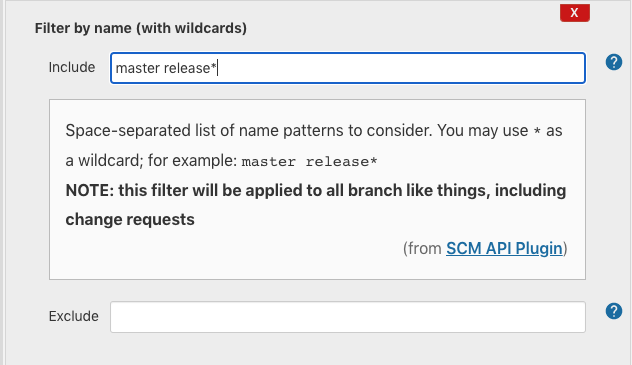
Note that we have another option to use the filter by name with regular expression (for example, we can use ".*" to apply to all branches).
Hit "Save" button, then w'll have the following "Console Output" that ran against the release branch with a newly updated Jenkinsfile:
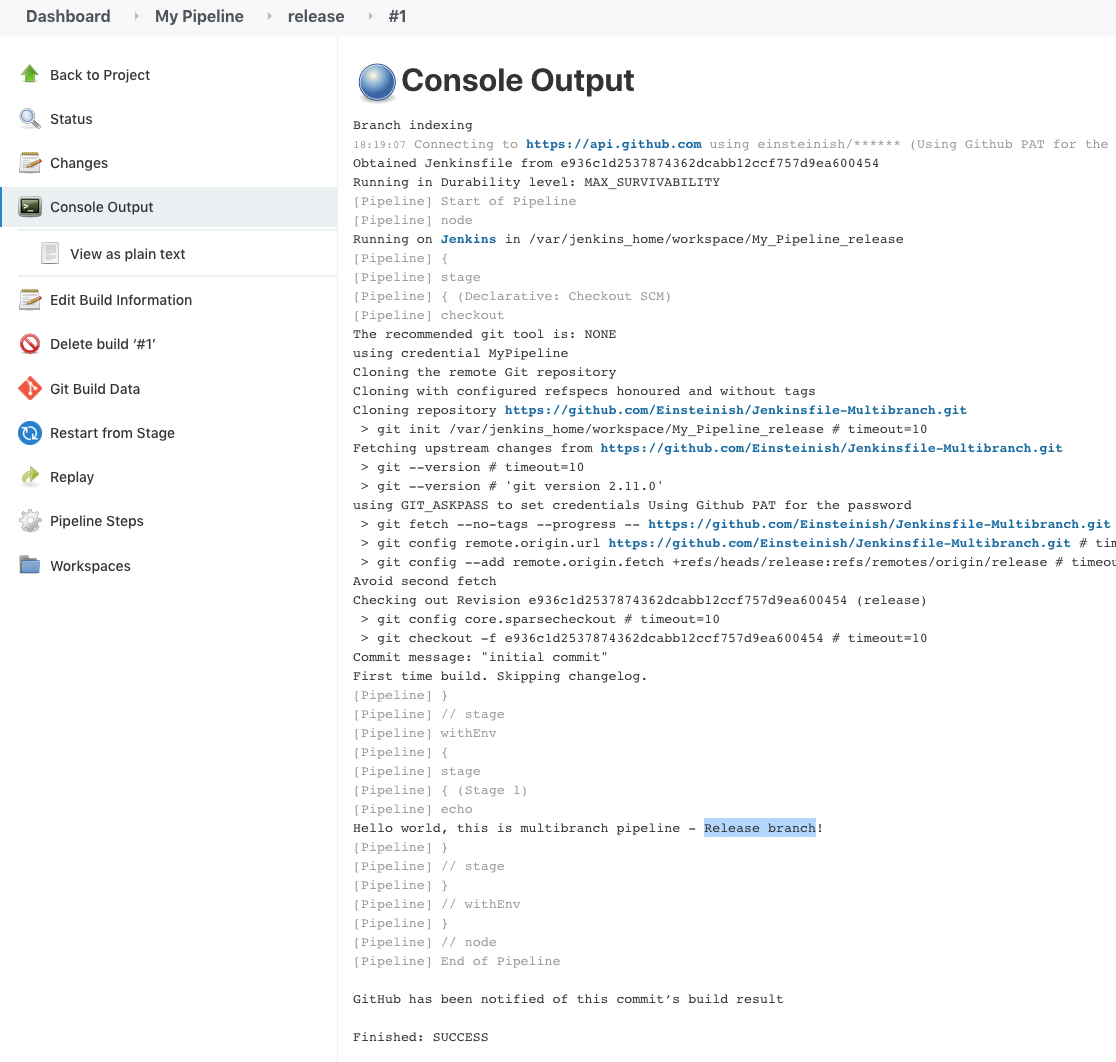
We can also check it from "Scan Repository Log":
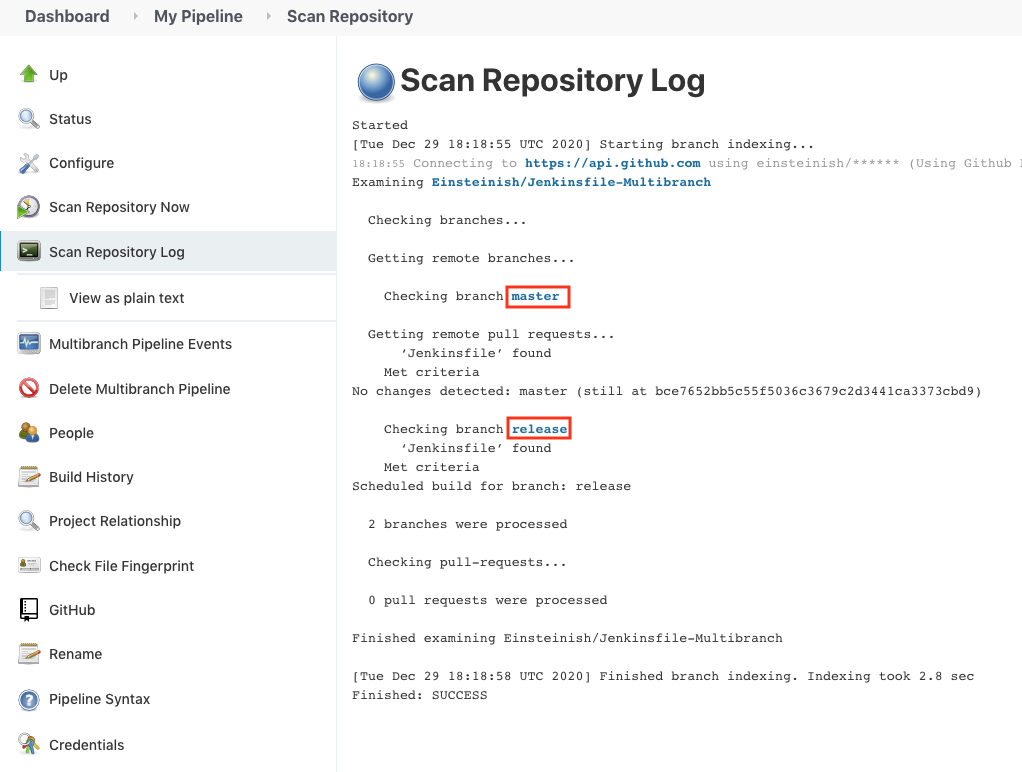
Jenkinsfile is a script that defines a pipeline configuration instead of using Jenkins UI. So, simply put, it is a "Pipeline as a Code".
The Jenkinsfile Pipeline syntax can be found in Pipeline Syntax.
There are two types of Jenkinsfile:
- Declarative Pipeline - we''ll use're using it in this post.
- Scripted Pipeline - it is effectively a general-purpose DSL built with Groovy.
Here is a basic Jenkins file:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('build') {
steps {
echo 'Hello world, this is multibranch pipeline for Dev branch'
}
}
stage('test') {
steps {
echo 'testing Dev...'
}
}
stage('deploy') {
steps {
echo 'deploying Dev...'
}
}
}
}
Here are the requiremed fields of a Jenkinsfile:
- "pipeline" - should be top level
- "agent" - where to execute
- "stages" - where the works are done
- "stage" and "steps"
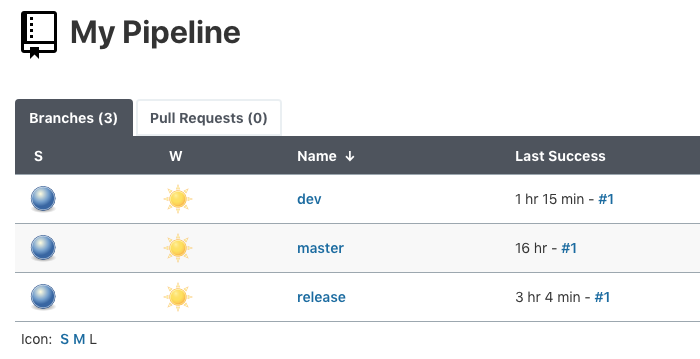
We also need to add the "dev" branch to our pipeline conf:
Then, click "Save" to run the Jenkinsfile.
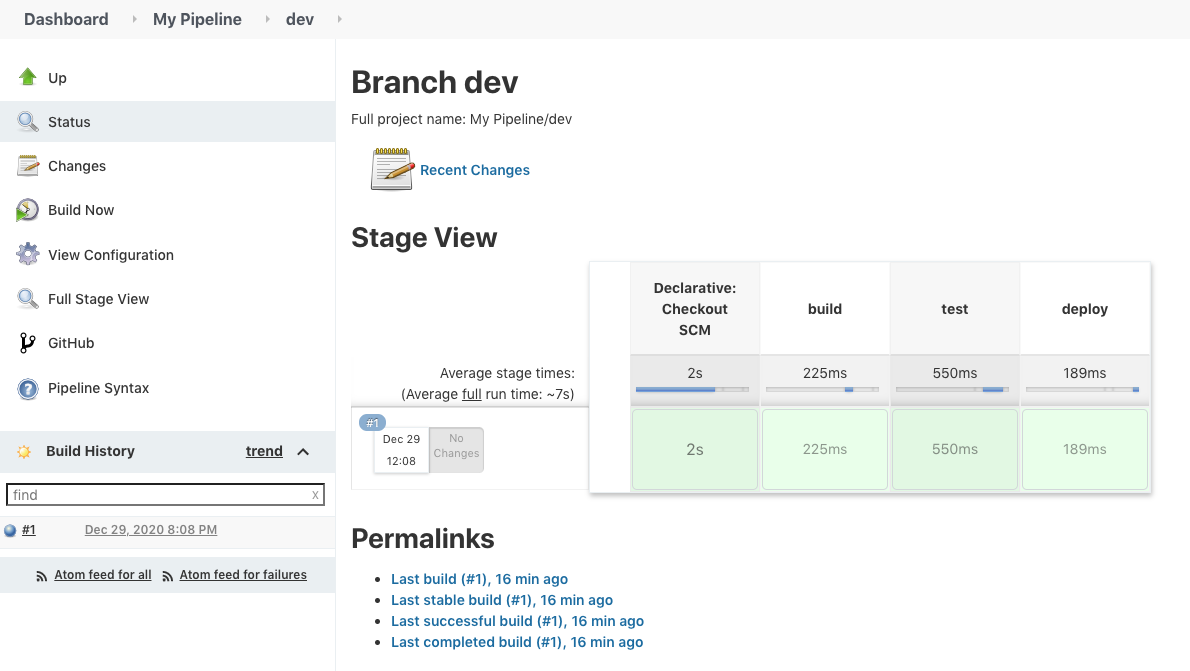
What if we want to test the Jenkinsfile without actually commit it to our repo?
Here is a "Replay" feature in Jenkins.
Just go back to the dev build and select "Replay":
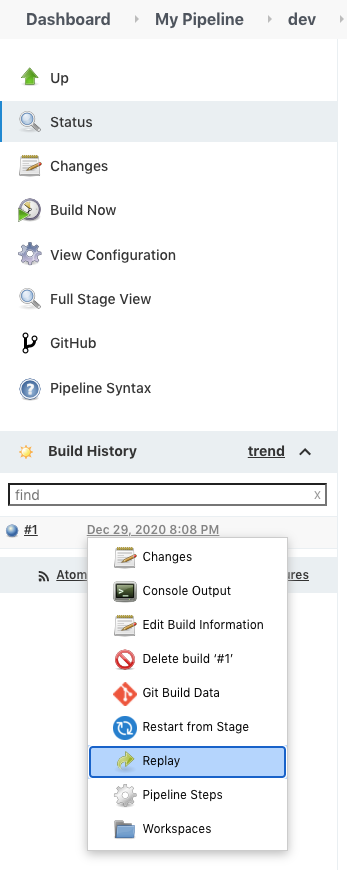
It will show our Jenkinsfile and we just want to add Groovy script withing the "build" step:
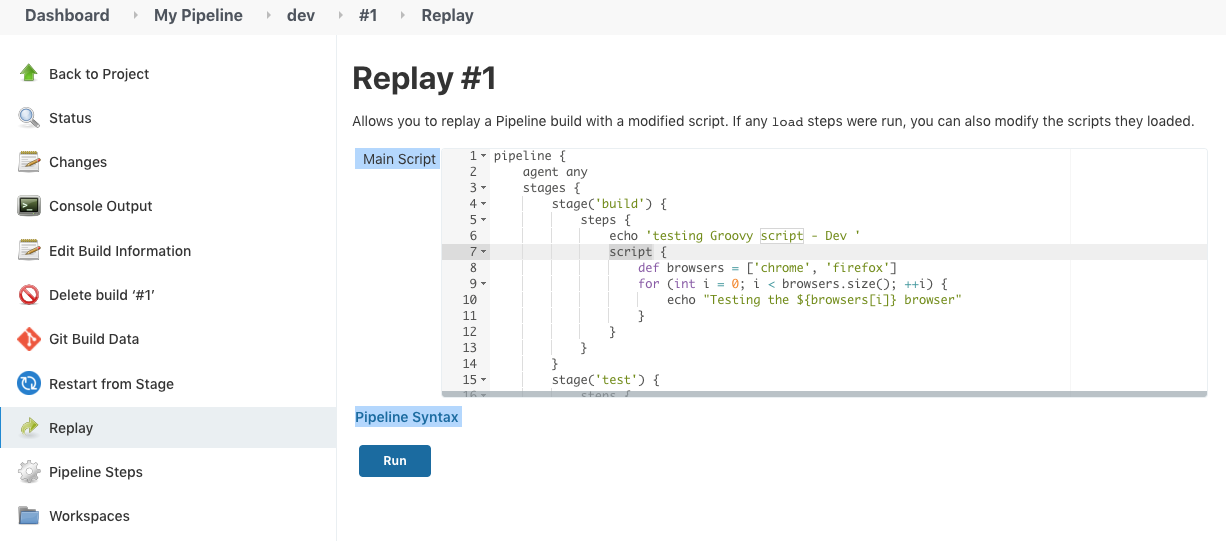
Hit "Run":
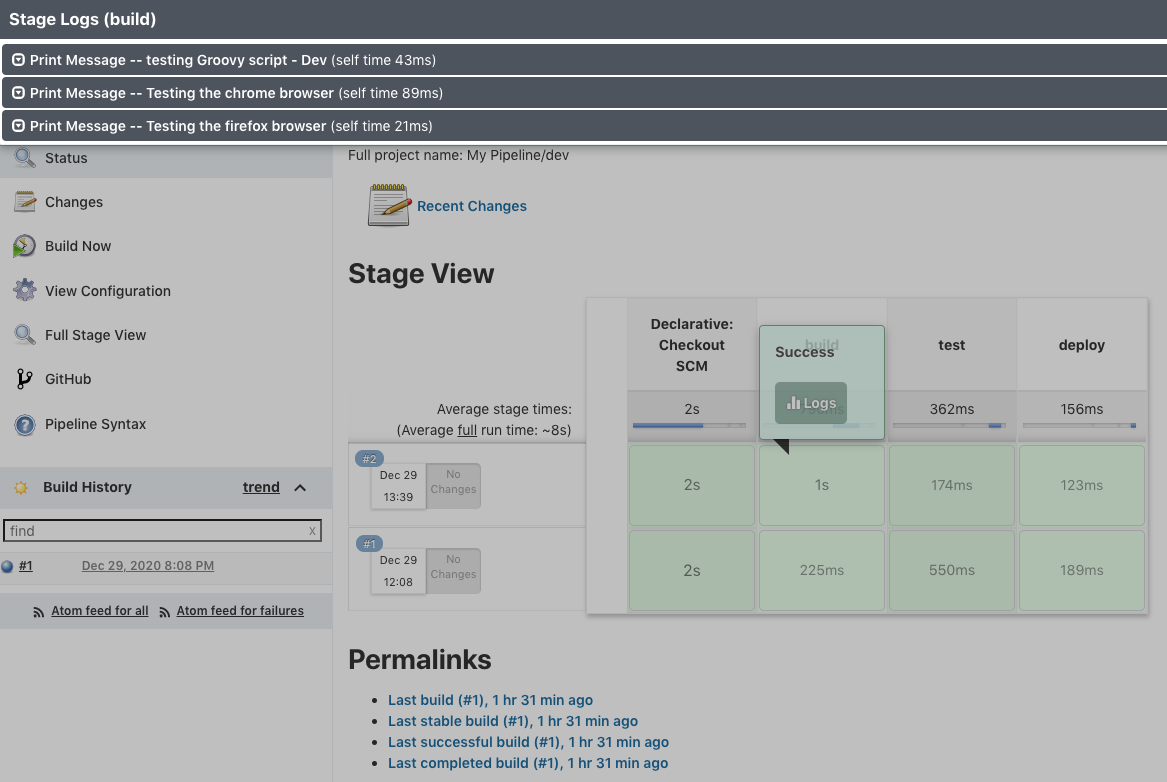
As we can see, the logs show that the run was successful!
There is another feature that we can specify stages. For example, in our case we have three stages: build, test, deploy.
Let's just do the 'deploy" skipping the prevous other two stages:
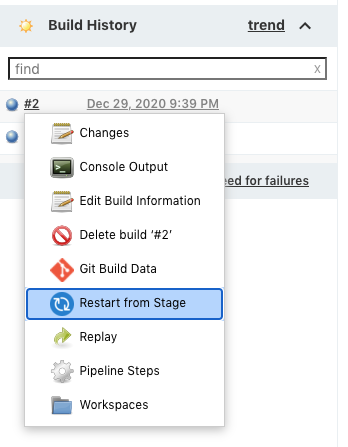
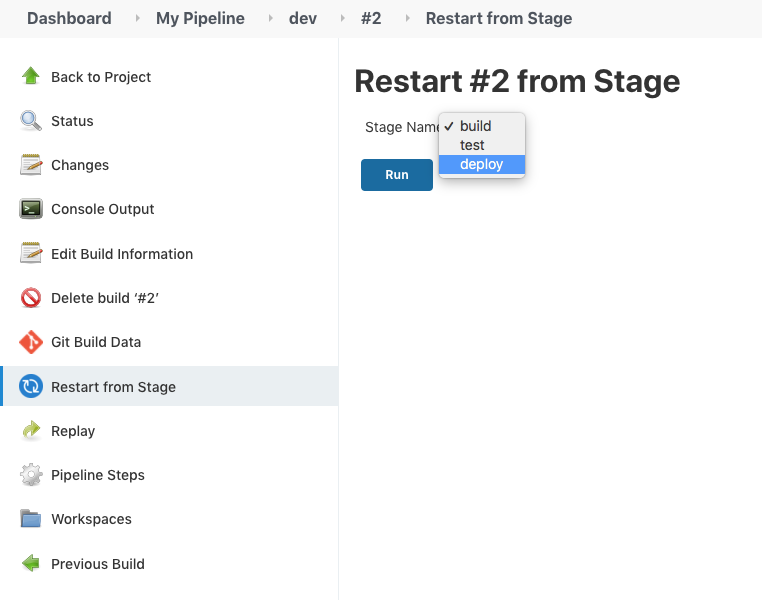
Now we can build the "deploy" stage only as shown below:

To trigger Jenkins job automatically, we may want to setup for push notification and polling for changes in the Git.
- Push notification - Version Control notifies Jenkins on a new commit. More efficient than polling by Jenkins.
- Polling - Jenkins itself polls Git in regular intervals.
Since we're working on local environmanet, the Github cannot connect to our Jenkins. So, we need a proxy that give us a public ip by doing remote port forawrding.
Follow the steps in https://dashboard.ngrok.com/get-started/setup.
$ ./ngrok http 8080
then, we get the following:
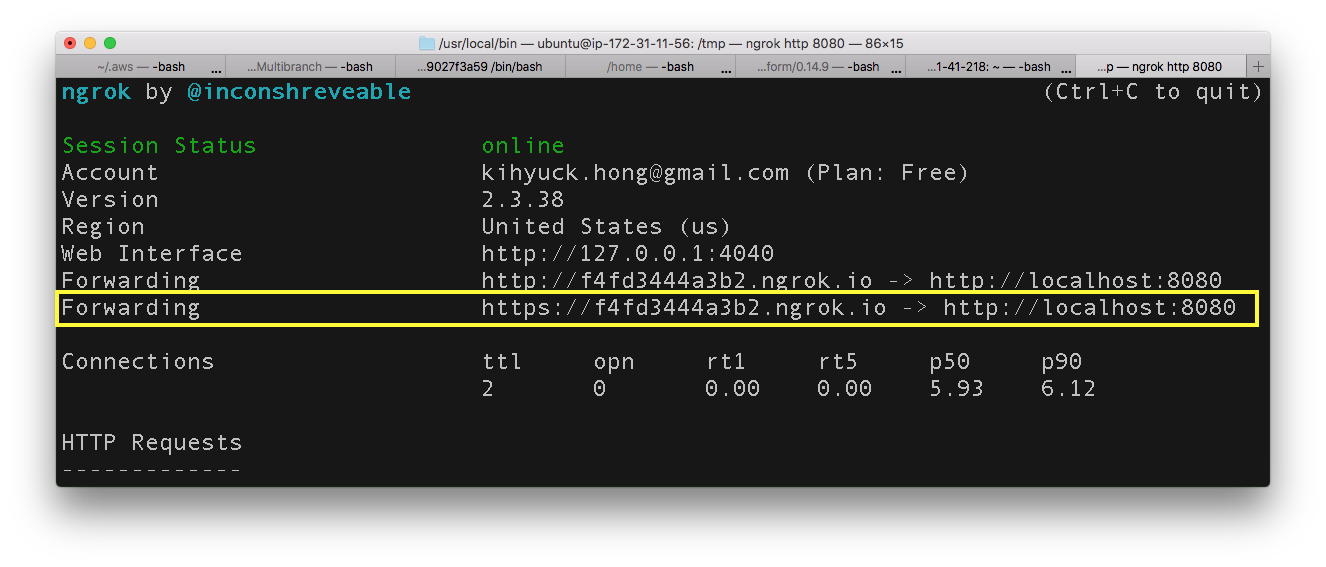
We're going to use https://f4fd3444a3b2.ngrok.io as our public ip from now on.
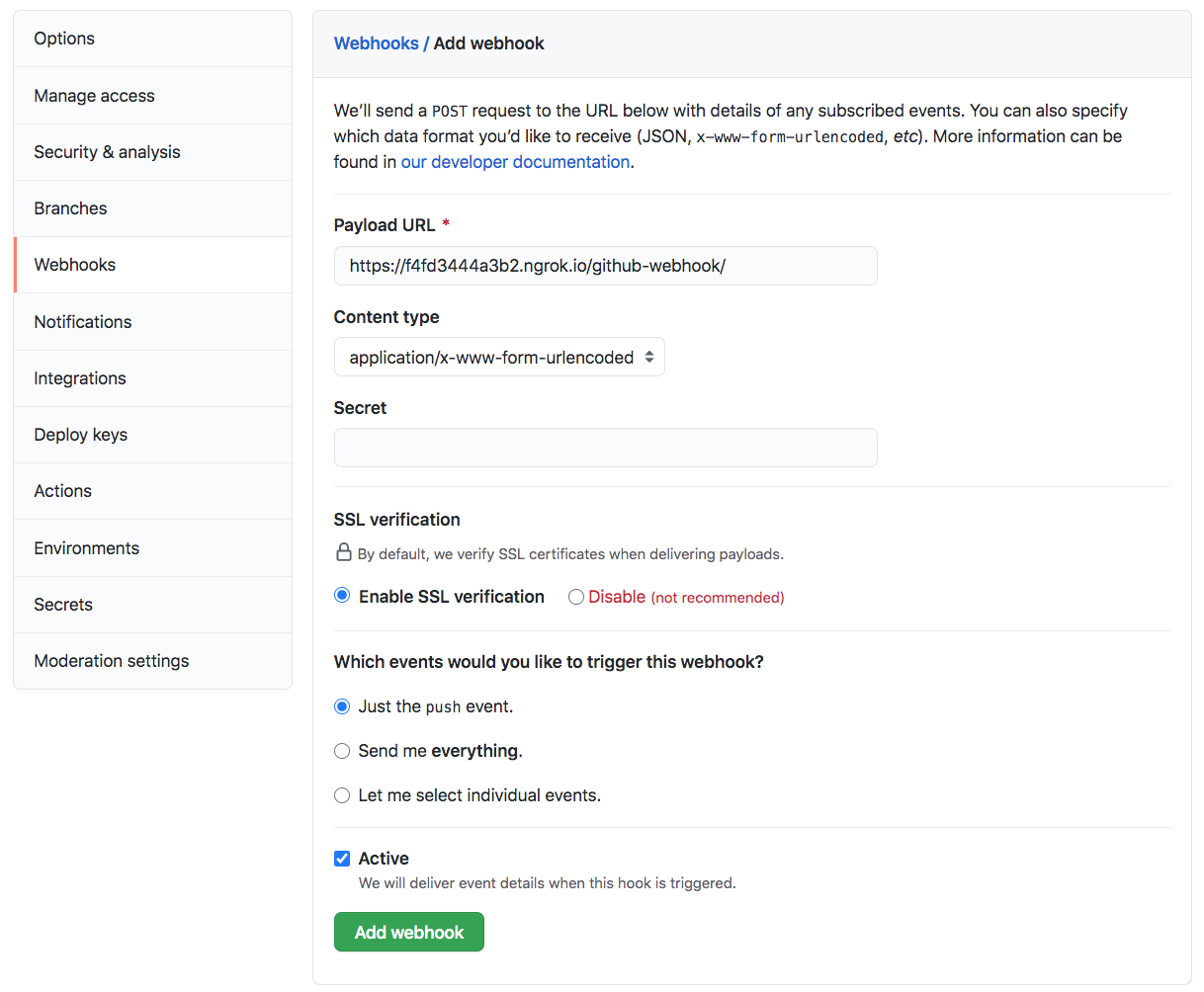
Now, while the ngrok terminal opened, let's setup a webhook.
Navigate to our Github repository (https://github.com/Einsteinish/webhook-demo.git) that we want Jenkins to monitor for pushes. Click on Settings > Webhooks:
Once we click Add Webhook, the Github Server will send a request to our Jenkins server and if successful it will show a green check mark next to the URL when we go back to the Webhooks section of our repository:
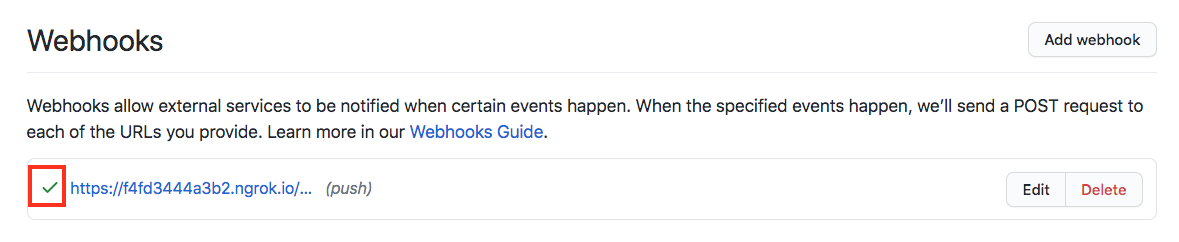
Now let’s see how to use this webhook in Jenkins:
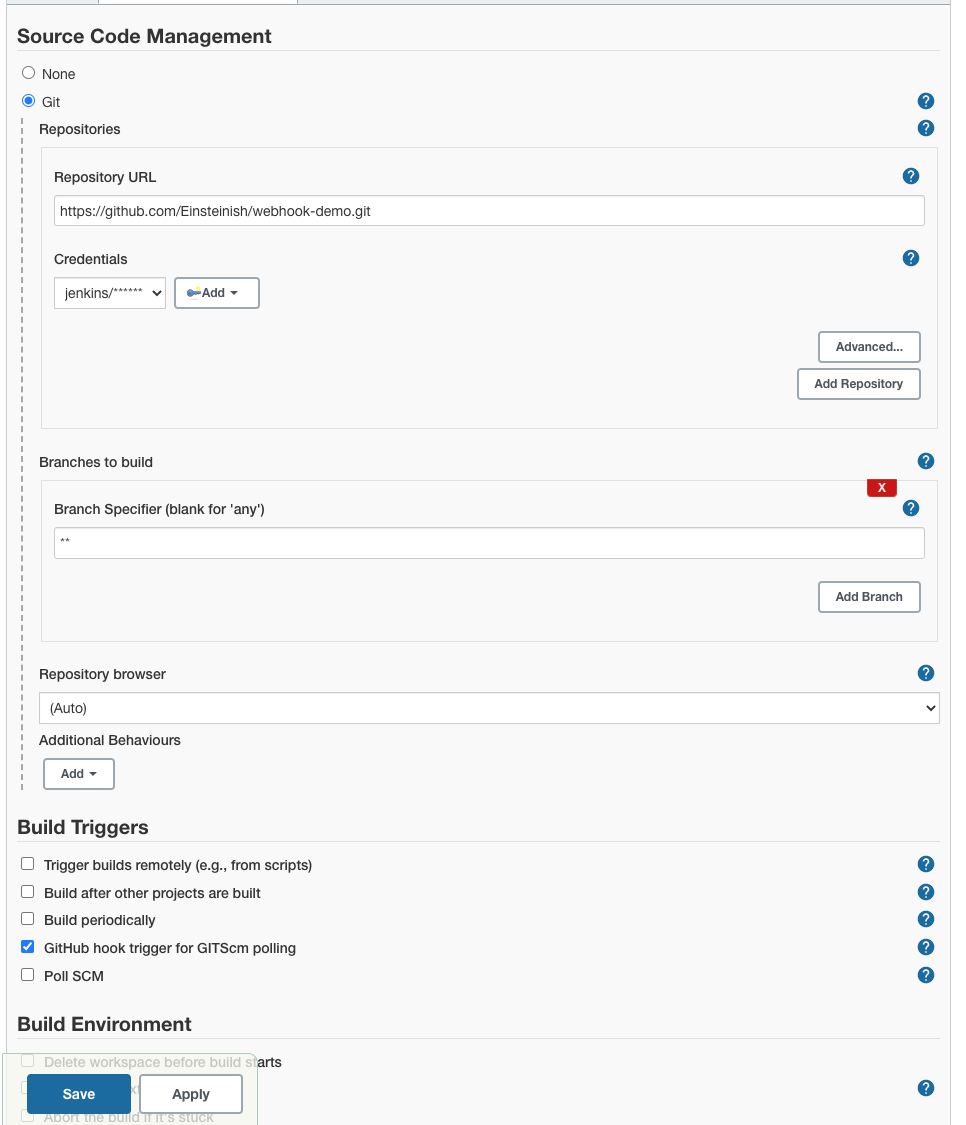
- Select "FreeEstyle" project.
- Click on the 'Source Code Management' tab.
- Click on Git and paste the GitHub repository URL in the 'Repository URL' field.
- Note that we do not need to put in the "Credentials" here.
- On the 'GitHub hook trigger for GITScm polling'.
- Click on "Save."
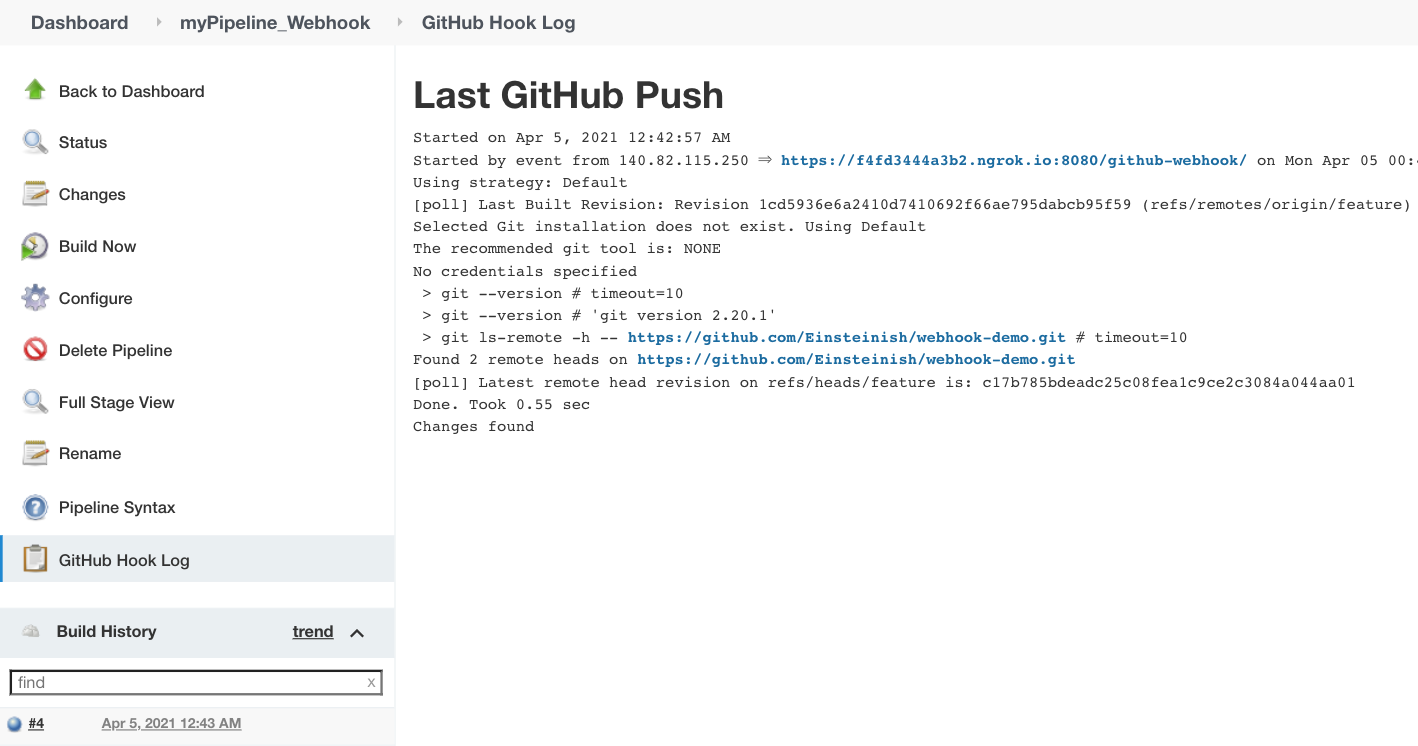
Now, whenever a new push to Github, our Jenkins task will get triggered:

Of course, we can use the Webhook with other type of projects such as Pipeline.
Here, we're using the "feature" branch of the same repo.
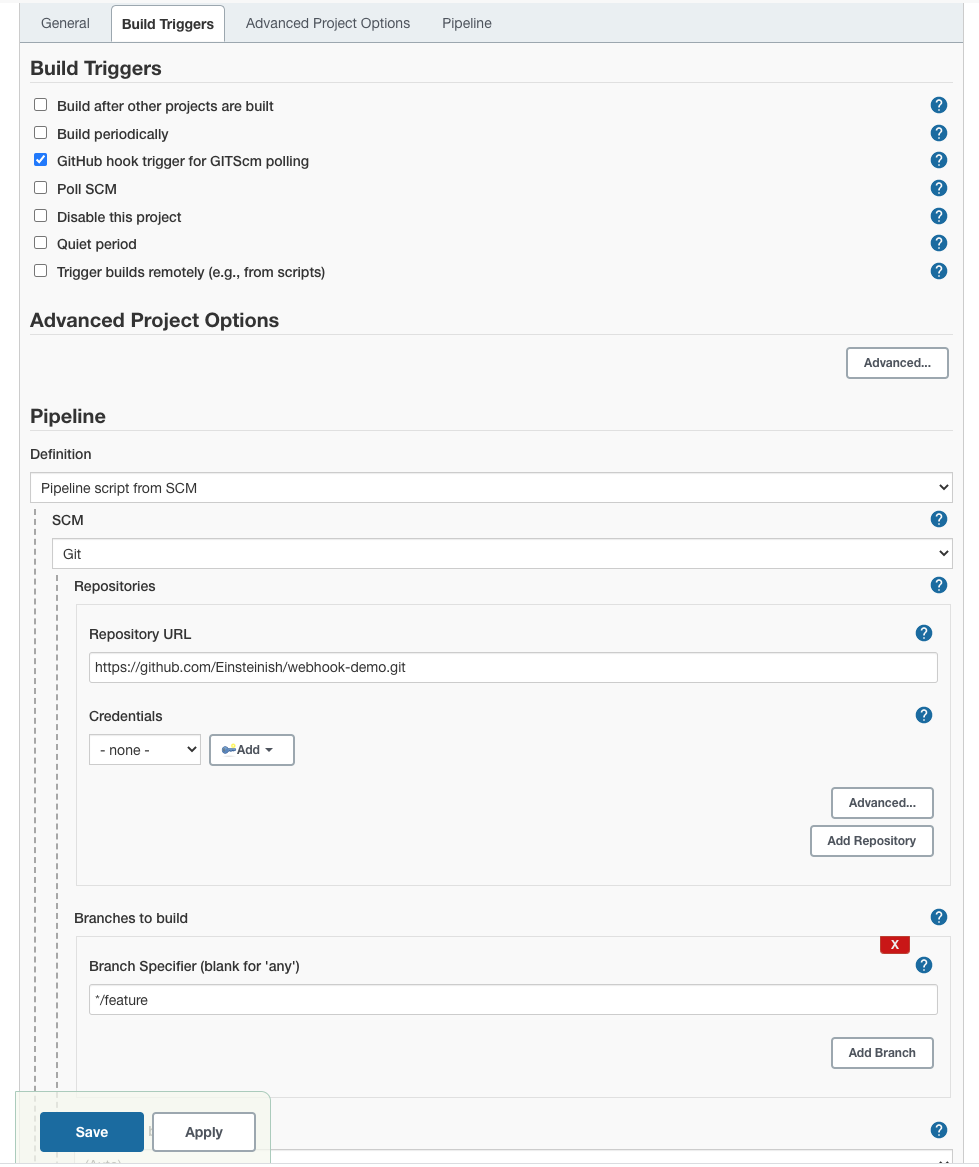
Just a sample Jenkinsfile:
pipeline {
agent {
docker {
image 'maven:3-alpine'
args '-v /root/.m2:/root/.m2'
}
}
stages {
stage('Build') {
steps {
sh 'mvn -B -DskipTests clean package'
}
}
stage('Test') {
steps {
sh 'mvn test'
}
post {
always {
junit 'target/surefire-reports/*.xml'
}
}
}
stage('Deliver') {
steps {
sh './jenkins/scripts/deliver.sh'
}
}
}
}
Docker & K8s
- Docker install on Amazon Linux AMI
- Docker install on EC2 Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker container vs Virtual Machine
- Docker install on Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker Hello World Application
- Nginx image - share/copy files, Dockerfile
- Working with Docker images : brief introduction
- Docker image and container via docker commands (search, pull, run, ps, restart, attach, and rm)
- More on docker run command (docker run -it, docker run --rm, etc.)
- Docker Networks - Bridge Driver Network
- Docker Persistent Storage
- File sharing between host and container (docker run -d -p -v)
- Linking containers and volume for datastore
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically I - FROM, MAINTAINER, and build context
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically II - revisiting FROM, MAINTAINER, build context, and caching
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically III - RUN
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically IV - CMD
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically V - WORKDIR, ENV, ADD, and ENTRYPOINT
- Docker - Apache Tomcat
- Docker - NodeJS
- Docker - NodeJS with hostname
- Docker Compose - NodeJS with MongoDB
- Docker - Prometheus and Grafana with Docker-compose
- Docker - StatsD/Graphite/Grafana
- Docker - Deploying a Java EE JBoss/WildFly Application on AWS Elastic Beanstalk Using Docker Containers
- Docker : NodeJS with GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker : Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline with Jenkinsfile and Github
- Docker : Jenkins Master and Slave
- Docker - ELK : ElasticSearch, Logstash, and Kibana
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elasticsearch on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Filebeat on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Logstash on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Kibana on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elastic Stack with Docker Compose
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK) via Elasticsearch operator on minikube
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Stack via Helm on minikube
- Docker Compose - A gentle introduction with WordPress
- Docker Compose - MySQL
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services via docker-compose
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part A (install vault, unsealing, static secrets, and policies)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part B (EaaS, dynamic secrets, leases, and revocation)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part C (Consul)
- Docker Compose with two containers - Flask REST API service container and an Apache server container
- Docker compose : Nginx reverse proxy with multiple containers
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Getting started
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Front Proxy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ambassador - Envoy API Gateway on Kubernetes
- Docker Packer
- Docker Cheat Sheet
- Docker Q & A #1
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part I
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part II
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker II (snapshot app with nginx)
- Docker - NodeJS and MySQL app with React in a docker
- Docker - Step by Step NodeJS and MySQL app with React - I
- Installing LAMP via puppet on Docker
- Docker install via Puppet
- Nginx Docker install via Ansible
- Apache Hadoop CDH 5.8 Install with QuickStarts Docker
- Docker - Deploying Flask app to ECS
- Docker Compose - Deploying WordPress to AWS
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI EC2 type)
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI Fargate type)
- Docker - ECS Fargate
- Docker - AWS ECS service discovery with Flask and Redis
- Docker & Kubernetes : minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes 2 : minikube Django with Postgres - persistent volume
- Docker & Kubernetes 3 : minikube Django with Redis and Celery
- Docker & Kubernetes 4 : Django with RDS via AWS Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kops on AWS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ingress controller on AWS with Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul - Auto-unseal using Transit Secrets Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes & Persistent Volumes Claims - hostPath and annotations
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes - Dynamic volume provisioning
- Docker & Kubernetes : DaemonSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Secrets
- Docker & Kubernetes : kubectl command
- Docker & Kubernetes : Assign a Kubernetes Pod to a particular node in a Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : Configure a Pod to Use a ConfigMap
- AWS : EKS (Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Run a React app in a minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Minikube install on AWS EC2
- Docker & Kubernetes : Cassandra with a StatefulSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Terraform and AWS EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Pods and Service definitions
- Docker & Kubernetes : Service IP and the Service Type
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes DNS with Pods and Services
- Docker & Kubernetes : Headless service and discovering pods
- Docker & Kubernetes : Scaling and Updating application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Horizontal pod autoscaler on minikubes
- Docker & Kubernetes : From a monolithic app to micro services on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Rolling updates
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deployments to GKE (Rolling update, Canary and Blue-green deployments)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Slack Chat Bot with NodeJS on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery with Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline for Dev, Canary, and Production Environments on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : NodePort vs LoadBalancer vs Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB / MongoExpress on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Load Testing with Locust on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB with StatefulSets on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up Ingress with NGINX Controller on Minikube (Mac)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller for Dashboard service on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Ingress with AWS ALB Ingress Controller in EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up a private cluster on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Namespaces (default, kube-public, kube-system) and switching namespaces (kubens)
- Docker & Kubernetes : StatefulSets on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : RBAC
- Docker & Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, and IAM
- Docker & Kubernetes - Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, IAM with EKS ALB, Part 1
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : My first Helm deploy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Readiness and Liveness Probes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm chart repository with Github pages
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB with Ingress to Minikube using Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 2 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 3 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart for Node/Express and MySQL with Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using Helm and Prometheus Operator - Monitoring Kubernetes node resources out of the box
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using kube-prometheus-stack Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio (service mesh) sidecar proxy on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on Minikube with AWS EC2 for Bookinfo Application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part I)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part II - Prometheus, Grafana, pin a service, split traffic, and inject faults)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Package Manager with MySQL on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying Memcached on Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : EKS Control Plane (API server) Metrics with Prometheus
- Docker & Kubernetes : Spinnaker on EKS with Halyard
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery Pipelines with Spinnaker and Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-dind (docker-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-kind (k8s-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : nodeSelector, nodeAffinity, taints/tolerations, pod affinity and anti-affinity - Assigning Pods to Nodes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Jenkins-X on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD App of Apps with Heml on Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD on Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : GitOps with ArgoCD for Continuous Delivery to Kubernetes clusters (minikube) - guestbook
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization