Docker : Kubernetes Service Account
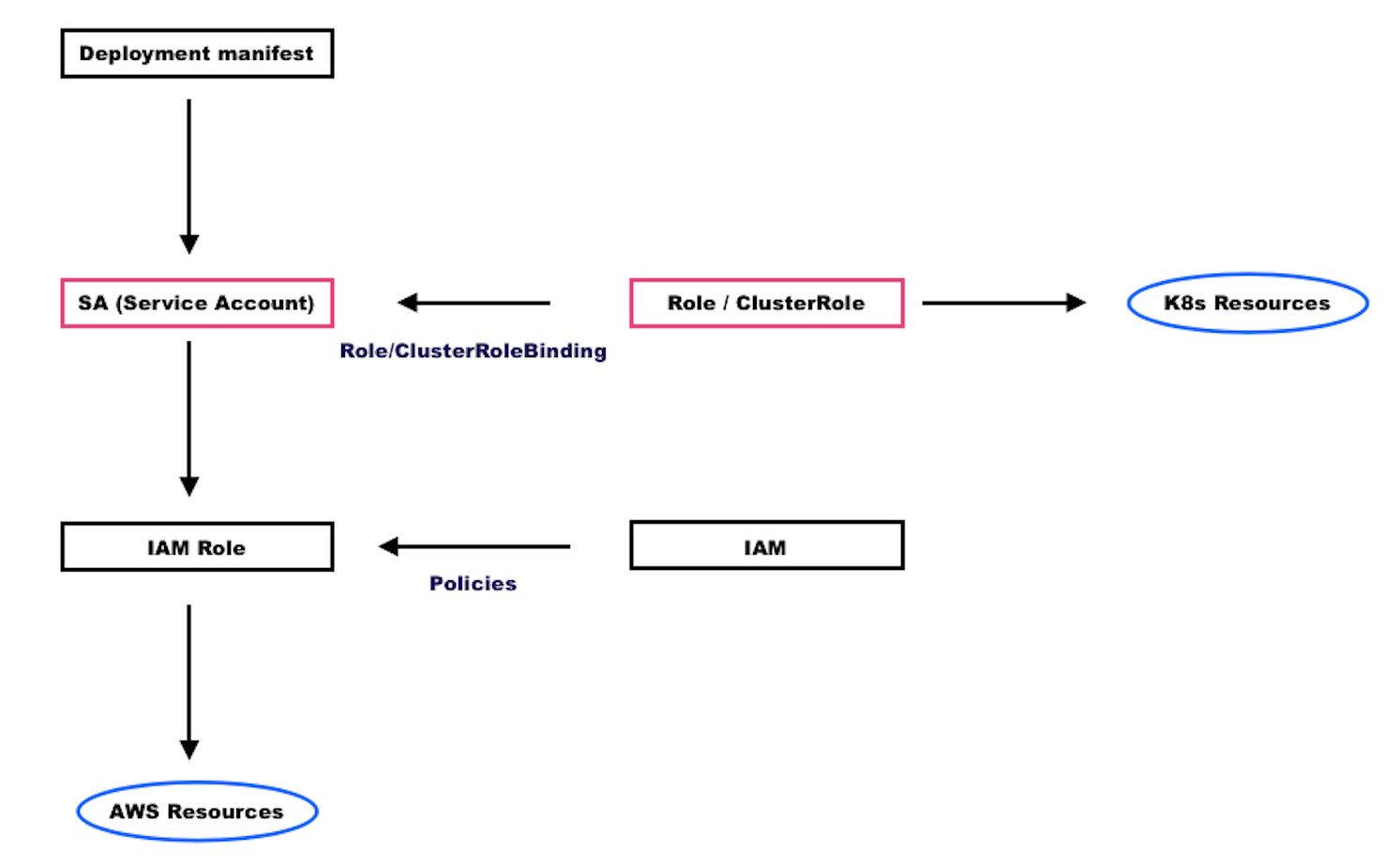
Service account, Role, RoleBinding in EKS
RBAC is based on declarative permissions definitions and cluster API objects. The main objects are roles and cluster roles, both representing a set of permissions on certain objects in the API.
- Role - should work with a namespace
- ClusterRole - without namespace and works across all namespaces
- Both of the roles set permissions
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: Role metadata: namespace: default name: role1 rules: - apiGroups: ['*'] resources: ['nodes','pods', 'pods/log'] verbs: ['get', 'list'] - apiGroups: ['*'] resources: ['configmaps'] resourceNames: ['my-configmap'] verbs: ['get', 'list'] apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRole metadata:namespace: defaultname: clusterRole1 rules: - apiGroups: ['*'] resources: ['nodes', 'pods'] verbs: ['get', 'list'] - nonResourceURLs: ['/api', '/healthz*'] verbs: ['get', 'head']
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: aggregatedClusterRole1
aggregationRule:
clusterRoleSelectors:
- matchLabels:
label1: value1
# The control plane automatically fills in the rules
rules: []
When a pod is created in the Kubernetes cluster with any given namespace, these pods by default creates a service account with the name default. The default service account automatically creates the service token along with the required secret object.
$ kubectl get sa NAME SECRETS AGE consul-consul-client 1 15h consul-consul-server 1 15h default 1 23h vault 1 15h vault-agent-injector 1 15h
To see all Service Account regardless of the namespace, we want to add "-A" flag:
$ kubectl get sa -A NAMESPACE NAME SECRETS AGE default consul-consul-client 1 24h default consul-consul-server 1 24h default default 1 32h default vault 1 24h default vault-agent-injector 1 24h kube-node-lease default 1 32h kube-public default 1 32h kube-system attachdetach-controller 1 32h kube-system bootstrap-signer 1 32h kube-system certificate-controller 1 32h kube-system clusterrole-aggregation-controller 1 32h kube-system coredns 1 32h kube-system cronjob-controller 1 32h kube-system daemon-set-controller 1 32h kube-system default 1 32h kube-system deployment-controller 1 32h kube-system disruption-controller 1 32h kube-system endpoint-controller 1 32h kube-system endpointslice-controller 1 32h kube-system endpointslicemirroring-controller 1 32h kube-system expand-controller 1 32h kube-system generic-garbage-collector 1 32h kube-system horizontal-pod-autoscaler 1 32h kube-system job-controller 1 32h kube-system kube-proxy 1 32h kube-system namespace-controller 1 32h kube-system node-controller 1 32h kube-system persistent-volume-binder 1 32h kube-system pod-garbage-collector 1 32h kube-system pv-protection-controller 1 32h kube-system pvc-protection-controller 1 32h kube-system replicaset-controller 1 32h kube-system replication-controller 1 32h kube-system resourcequota-controller 1 32h kube-system service-account-controller 1 32h kube-system service-controller 1 32h kube-system statefulset-controller 1 32h kube-system storage-provisioner 1 32h kube-system token-cleaner 1 32h kube-system ttl-controller 1 32h
To see the default secret attached with the default token:
$ kubectl get secret NAME TYPE DATA AGE default-token-mdrld kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 23h
We will be able to get the name of default token value, default-token-mdrld, and this automatically gets created when any pod is created in the given node namespace.
To view the secret object detail against the default token:
$ kubectl describe secret default-token-mdrld
Name: default-token-mdrld
Namespace: default
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubernetes.io/service-account.name: default
kubernetes.io/service-account.uid: 11caa5d6-eadb-4554-b7be-af05411703f1
Type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
Data
====
ca.crt: 1066 bytes
namespace: 7 bytes
token: eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6Il9TM1ZBdzNYSUlQclNfQz
...
XkOPIfHgp-0BYr7wuWaPATj3lc_bHOIBhjozQtJSQRk-fa6L5ca0B_83JEKZ_6LQmxC74aYSOkQ
So, for our application hosted in the pod with the same namespace, this default secret object can be used to give access to the API servers lying in the same cluster namespace.
A user. group or a service account to be able to access a resource according to a rule, we need to define bindings between the two, those are RoleBinding and ClusterRoleBinding.
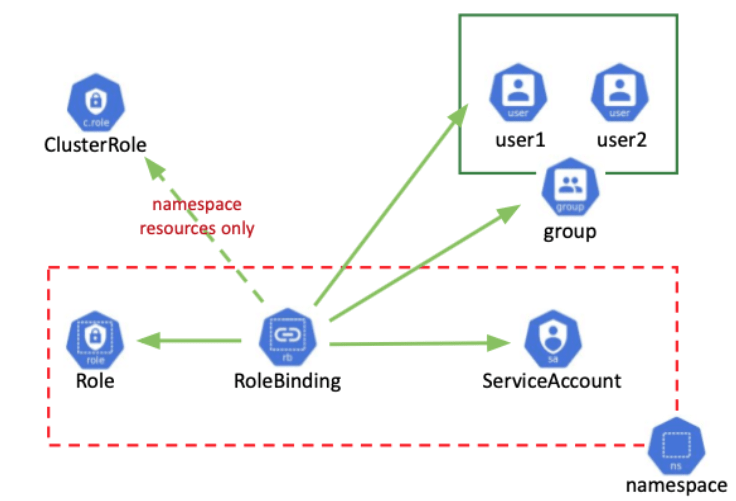
Kubernetes RBAC 101: authorization
RoleBuiding is always created in a specific namespace and ClusterRoleBinding can be associated with either a Role in the same namespace or a ClusterRole.
- Application load balancing on Amazon EKS
- wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/aws-alb-ingress-controller/v1.1.9/docs/examples/alb-ingress-controller.yaml
# Application Load Balancer (ALB) Ingress Controller Deployment Manifest.
# This manifest details sensible defaults for deploying an ALB Ingress Controller.
# GitHub: https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/aws-alb-ingress-controller
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: alb-ingress-controller
name: alb-ingress-controller
# Namespace the ALB Ingress Controller should run in. Does not impact which
# namespaces it's able to resolve ingress resource for. For limiting ingress
# namespace scope, see --watch-namespace.
namespace: kube-system
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: alb-ingress-controller
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: alb-ingress-controller
spec:
containers:
- name: alb-ingress-controller
args:
...
# Repository location of the ALB Ingress Controller.
image: docker.io/amazon/aws-alb-ingress-controller:v1.1.9
serviceAccountName: alb-ingress-controller
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: alb-ingress-controller
name: alb-ingress-controller
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
- extensions
resources:
- configmaps
- endpoints
- events
- ingresses
- ingresses/status
- services
- pods/status
verbs:
- create
- get
- list
- update
- watch
- patch
- apiGroups:
- ""
- extensions
resources:
- nodes
- pods
- secrets
- services
- namespaces
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: alb-ingress-controller
name: alb-ingress-controller
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: alb-ingress-controller
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: alb-ingress-controller
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: alb-ingress-controller
annotations: # Add the annotations line
eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn: arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/role-name # Add the IAM role
name: alb-ingress-controller
namespace: kube-system
Docker & K8s
- Docker install on Amazon Linux AMI
- Docker install on EC2 Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker container vs Virtual Machine
- Docker install on Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker Hello World Application
- Nginx image - share/copy files, Dockerfile
- Working with Docker images : brief introduction
- Docker image and container via docker commands (search, pull, run, ps, restart, attach, and rm)
- More on docker run command (docker run -it, docker run --rm, etc.)
- Docker Networks - Bridge Driver Network
- Docker Persistent Storage
- File sharing between host and container (docker run -d -p -v)
- Linking containers and volume for datastore
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically I - FROM, MAINTAINER, and build context
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically II - revisiting FROM, MAINTAINER, build context, and caching
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically III - RUN
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically IV - CMD
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically V - WORKDIR, ENV, ADD, and ENTRYPOINT
- Docker - Apache Tomcat
- Docker - NodeJS
- Docker - NodeJS with hostname
- Docker Compose - NodeJS with MongoDB
- Docker - Prometheus and Grafana with Docker-compose
- Docker - StatsD/Graphite/Grafana
- Docker - Deploying a Java EE JBoss/WildFly Application on AWS Elastic Beanstalk Using Docker Containers
- Docker : NodeJS with GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker : Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline with Jenkinsfile and Github
- Docker : Jenkins Master and Slave
- Docker - ELK : ElasticSearch, Logstash, and Kibana
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elasticsearch on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Filebeat on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Logstash on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Kibana on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elastic Stack with Docker Compose
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK) via Elasticsearch operator on minikube
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Stack via Helm on minikube
- Docker Compose - A gentle introduction with WordPress
- Docker Compose - MySQL
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services via docker-compose
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part A (install vault, unsealing, static secrets, and policies)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part B (EaaS, dynamic secrets, leases, and revocation)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part C (Consul)
- Docker Compose with two containers - Flask REST API service container and an Apache server container
- Docker compose : Nginx reverse proxy with multiple containers
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Getting started
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Front Proxy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ambassador - Envoy API Gateway on Kubernetes
- Docker Packer
- Docker Cheat Sheet
- Docker Q & A #1
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part I
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part II
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker II (snapshot app with nginx)
- Docker - NodeJS and MySQL app with React in a docker
- Docker - Step by Step NodeJS and MySQL app with React - I
- Installing LAMP via puppet on Docker
- Docker install via Puppet
- Nginx Docker install via Ansible
- Apache Hadoop CDH 5.8 Install with QuickStarts Docker
- Docker - Deploying Flask app to ECS
- Docker Compose - Deploying WordPress to AWS
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI EC2 type)
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI Fargate type)
- Docker - ECS Fargate
- Docker - AWS ECS service discovery with Flask and Redis
- Docker & Kubernetes : minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes 2 : minikube Django with Postgres - persistent volume
- Docker & Kubernetes 3 : minikube Django with Redis and Celery
- Docker & Kubernetes 4 : Django with RDS via AWS Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kops on AWS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ingress controller on AWS with Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul - Auto-unseal using Transit Secrets Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes & Persistent Volumes Claims - hostPath and annotations
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes - Dynamic volume provisioning
- Docker & Kubernetes : DaemonSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Secrets
- Docker & Kubernetes : kubectl command
- Docker & Kubernetes : Assign a Kubernetes Pod to a particular node in a Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : Configure a Pod to Use a ConfigMap
- AWS : EKS (Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Run a React app in a minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Minikube install on AWS EC2
- Docker & Kubernetes : Cassandra with a StatefulSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Terraform and AWS EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Pods and Service definitions
- Docker & Kubernetes : Service IP and the Service Type
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes DNS with Pods and Services
- Docker & Kubernetes : Headless service and discovering pods
- Docker & Kubernetes : Scaling and Updating application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Horizontal pod autoscaler on minikubes
- Docker & Kubernetes : From a monolithic app to micro services on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Rolling updates
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deployments to GKE (Rolling update, Canary and Blue-green deployments)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Slack Chat Bot with NodeJS on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery with Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline for Dev, Canary, and Production Environments on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : NodePort vs LoadBalancer vs Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB / MongoExpress on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Load Testing with Locust on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB with StatefulSets on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up Ingress with NGINX Controller on Minikube (Mac)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller for Dashboard service on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Ingress with AWS ALB Ingress Controller in EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up a private cluster on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Namespaces (default, kube-public, kube-system) and switching namespaces (kubens)
- Docker & Kubernetes : StatefulSets on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : RBAC
- Docker & Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, and IAM
- Docker & Kubernetes - Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, IAM with EKS ALB, Part 1
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : My first Helm deploy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Readiness and Liveness Probes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm chart repository with Github pages
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB with Ingress to Minikube using Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 2 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 3 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart for Node/Express and MySQL with Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using Helm and Prometheus Operator - Monitoring Kubernetes node resources out of the box
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using kube-prometheus-stack Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio (service mesh) sidecar proxy on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on Minikube with AWS EC2 for Bookinfo Application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part I)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part II - Prometheus, Grafana, pin a service, split traffic, and inject faults)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Package Manager with MySQL on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying Memcached on Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : EKS Control Plane (API server) Metrics with Prometheus
- Docker & Kubernetes : Spinnaker on EKS with Halyard
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery Pipelines with Spinnaker and Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-dind (docker-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-kind (k8s-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : nodeSelector, nodeAffinity, taints/tolerations, pod affinity and anti-affinity - Assigning Pods to Nodes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Jenkins-X on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD App of Apps with Heml on Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD on Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : GitOps with ArgoCD for Continuous Delivery to Kubernetes clusters (minikube) - guestbook
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization