Amazon EC2 Container Service (ECS)
Amazon EC2 Container Service (Amazon ECS) is a highly scalable, fast, container management service that makes it easy to run, stop, and manage Docker containers on a cluster of Amazon EC2 instances.
Amazon ECS uses Docker images in task definitions to launch containers on EC2 instances in our clusters.
Docker is a technology that allows us to build, run, test, and deploy distributed applications that are based on Linux containers.
ECS is basically a set of APIs that turn EC2 instances into compute cluster for container management:
- EC2 instances must call RegisterContainerInstance API to signal that they are ready to run containers.
- Need to call RegisterTaskDefinition API to define the tasks (setting an image, command and memory for docker run etc.)
- We use RunTask API to start a new task.
- Lastly, we make a CreateService API call to run a long-running container.
We can start using Amazon EC2 Container Service (Amazon ECS) by creating a task definition, scheduling tasks, and configuring a cluster in the Amazon ECS console. Note that we do not need any orchestration tools such as Mesos, Kubernetes or Docker Swarm.
Open the Amazon ECS console first run wizard at https://console.aws.amazon.com/ecs/home#/firstRun.
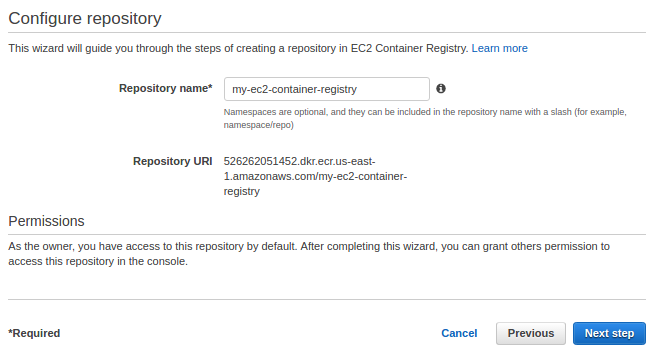
Step 2: Build, tag, and push Docker image
Now that our repository exists, we can push a Docker image by following these steps:
- Retrieve the docker login command that we can use to authenticate our Docker client to our registry:
- Run the docker login command that was returned in the previous step.
- Flask Dockerfile:
FROM tiangolo/uwsgi-nginx-flask:flask # copy over our requirements.txt file COPY requirements.txt /tmp/ # upgrade pip and install required python packages RUN pip install -U pip RUN pip install -r /tmp/requirements.txt # copy over our app code COPY ./app /app # set an environmental variable, MESSAGE, # which the app will use and display ENV MESSAGE "hello from Docker"
app/main.py:
from pyfiglet import Figlet import os from flask import Flask app = Flask(__name__) font = Figlet(font="starwars") @app.route("/") def main(): # get the message from the environmental variable $MESSAGE # or fall back to the string "no message specified" message = os.getenv("MESSAGE", "Flask on AWS ECS") # render plain text nicely in HTML html_text = font.renderText(message)\ .replace(" "," ")\ .replace(">",">")\ .replace("<","<")\ .replace("\n","<br>") # use a monospace font so everything lines up as expected return "<html><body style='font-family: mono;'>" + html_text + "</body></html>" if __name__ == "__main__": app.run(host="0.0.0.0", port=5000)
requirements.txt:
Flask==0.11.1 pyfiglet==0.7.5
- Now we're ready for our Flask app. On our local machine, let's build our Docker image using the following command:
- After the build completes, tag our image so we can push the image to this repository:
- Run the following command to push this image to our newly created AWS repository:
- We can check if the image has been pushed into ECR:
$ aws ecr get-login --region us-east-1
Or we can combine the two commands:
$ eval $(aws ecr get-login --region us-east-1) Login Succeeded
$ docker build -t my_flask_app . Sending build context to Docker daemon 25.43 MB Step 1/6 : FROM tiangolo/uwsgi-nginx-flask:flask Step 2/6 : COPY requirements.txt /tmp/ Step 3/6 : RUN pip install -U pip Step 4/6 : RUN pip install -r /tmp/requirements.txt Step 5/6 : COPY ./app /app Step 6/6 : ENV MESSAGE "hello from Docker" Successfully built 1ff7f5314a23 $ docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID my_flask_app latest 1ff7f5314a23
$ docker tag my_flask_app:latest 526262051452.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/my-ec2-container-registry:latest
$ docker push 526262051452.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/my-ec2-container-registry:latest The push refers to a repository [526262051452.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/my-ec2-container-registry] ... latest: digest: sha256:5de6f7cb5ed272746dad4fc6e7168e6855ad8f40b13c56c4c811d1ff18d9da2b size: 5344
A task definition is like a blue print for an application.
Every time we launch a task in Amazon ECS, we specify a task definition so the service knows which Docker image to use for containers, how many containers to use in the task, and the resource allocation for each container.
Task definitions created in the first run wizard are limited to a single container for simplicity's sake:
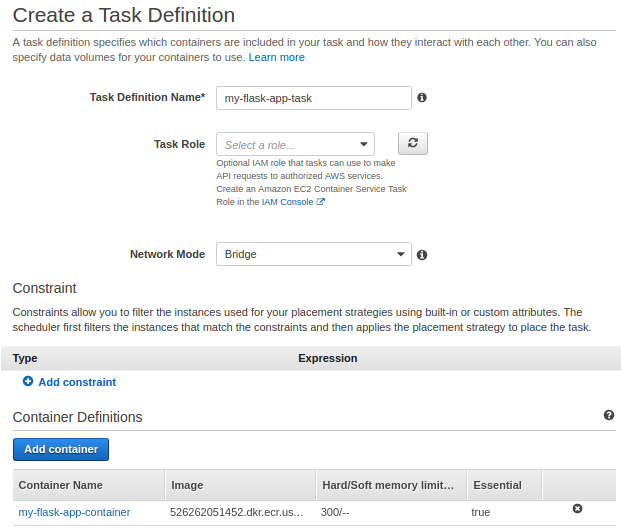
Actually, to complete the definition, we need to click "Add Container" and fill out the following as shown below:
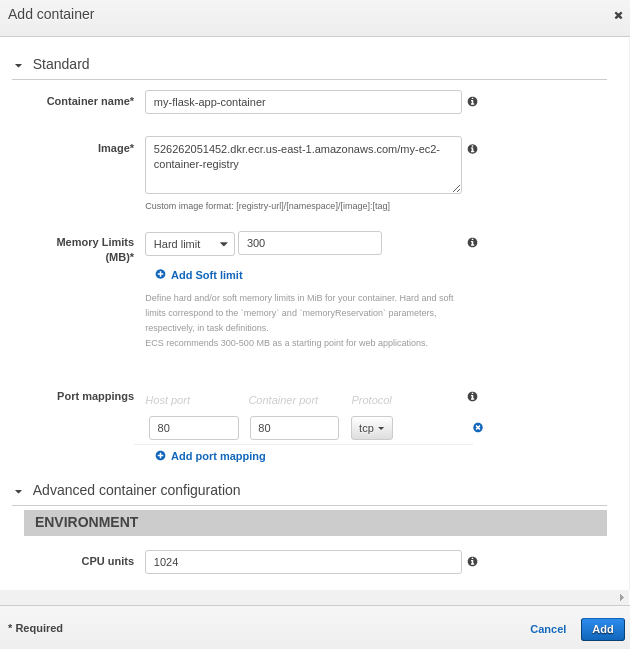
A service launches and maintains a specified number of copies of the task definition in our cluster.
The Amazon ECS sample application is a web-based "Hello World" style application that is meant to run indefinitely, so by running it as a service, it will restart if the task becomes unhealthy or unexpectedly stops.
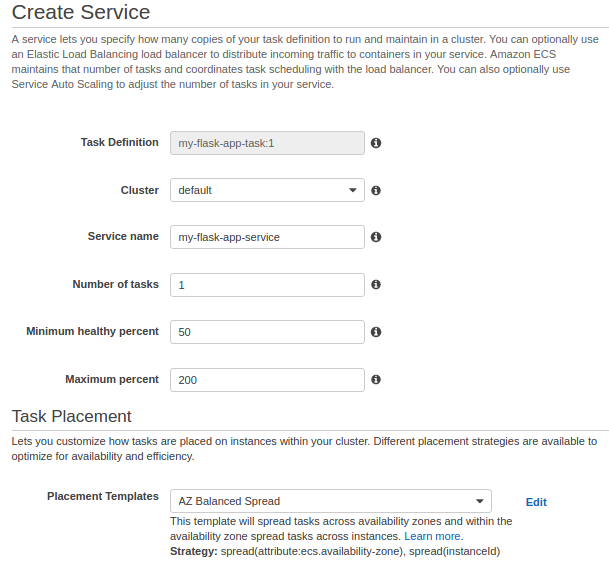
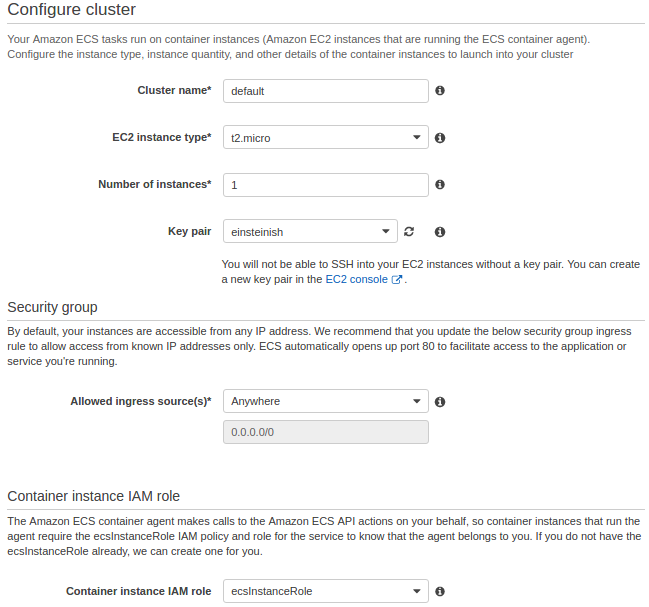
In this section of the wizard, we name our cluster, and then configure the container instances that our tasks can be placed on, the address range that we can reach our instances and load balancer from, and the IAM roles to use with our container instances that let Amazon ECS take care of this configuration for us.
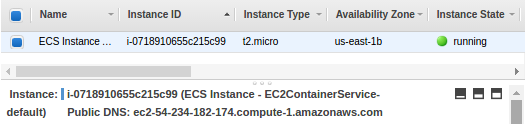
Now, our docker is running on this agent node:
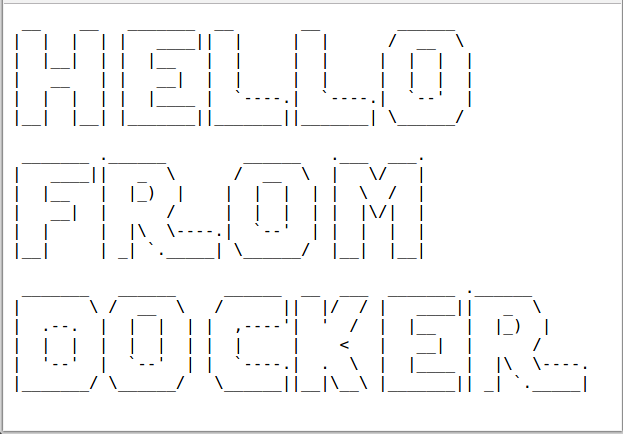
- Scale Down Services
If our cluster contains any services, we should first scale down the desired count of tasks in these services to 0 so that Amazon ECS does not try to start new tasks on our container instances while we are cleaning up.
Updating a Service and enter 0 in the Number of tasks field.
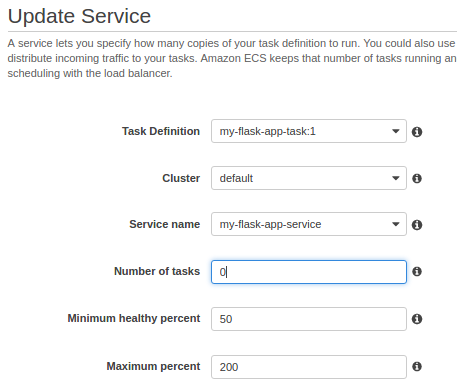
- Delete Services
Before we can delete a cluster, we must delete the services inside that cluster. After our service has scaled down to 0 tasks, we can delete it. For each service inside our cluster, follow the procedures in Deleting a Service to delete it.
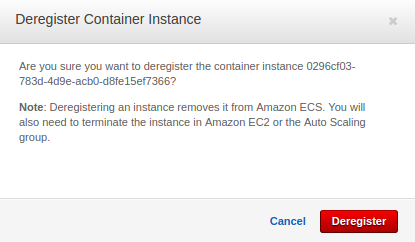
- Deregister Container Instances
Before we can delete a cluster, we must deregister the container instances inside that cluster. For each container instance inside our cluster, follow the procedures in Deregister a Container Instance to deregister it.
- Delete a Cluster
After we have removed the active resources from our Amazon ECS cluster, we can delete it.
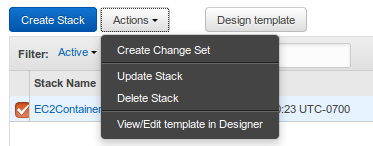
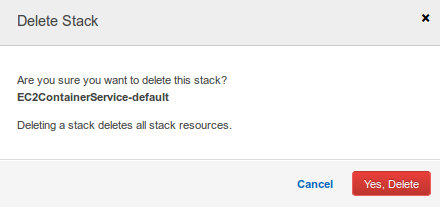
- Delete the AWS CloudFormation Stack
AWS (Amazon Web Services)
- AWS : EKS (Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes)
- AWS : Creating a snapshot (cloning an image)
- AWS : Attaching Amazon EBS volume to an instance
- AWS : Adding swap space to an attached volume via mkswap and swapon
- AWS : Creating an EC2 instance and attaching Amazon EBS volume to the instance using Python boto module with User data
- AWS : Creating an instance to a new region by copying an AMI
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 1
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 2 - Creating and Deleting a Bucket
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 3 - Bucket Versioning
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 4 - Uploading a large file
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 5 - Uploading folders/files recursively
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 6 - Bucket Policy for File/Folder View/Download
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 7 - How to Copy or Move Objects from one region to another
- AWS : S3 (Simple Storage Service) 8 - Archiving S3 Data to Glacier
- AWS : Creating a CloudFront distribution with an Amazon S3 origin
- AWS : Creating VPC with CloudFormation
- AWS : WAF (Web Application Firewall) with preconfigured CloudFormation template and Web ACL for CloudFront distribution
- AWS : CloudWatch & Logs with Lambda Function / S3
- AWS : Lambda Serverless Computing with EC2, CloudWatch Alarm, SNS
- AWS : Lambda and SNS - cross account
- AWS : CLI (Command Line Interface)
- AWS : CLI (ECS with ALB & autoscaling)
- AWS : ECS with cloudformation and json task definition
- AWS Application Load Balancer (ALB) and ECS with Flask app
- AWS : Load Balancing with HAProxy (High Availability Proxy)
- AWS : VirtualBox on EC2
- AWS : NTP setup on EC2
- AWS: jq with AWS
- AWS & OpenSSL : Creating / Installing a Server SSL Certificate
- AWS : OpenVPN Access Server 2 Install
- AWS : VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) 1 - netmask, subnets, default gateway, and CIDR
- AWS : VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) 2 - VPC Wizard
- AWS : VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) 3 - VPC Wizard with NAT
- DevOps / Sys Admin Q & A (VI) - AWS VPC setup (public/private subnets with NAT)
- AWS - OpenVPN Protocols : PPTP, L2TP/IPsec, and OpenVPN
- AWS : Autoscaling group (ASG)
- AWS : Setting up Autoscaling Alarms and Notifications via CLI and Cloudformation
- AWS : Adding a SSH User Account on Linux Instance
- AWS : Windows Servers - Remote Desktop Connections using RDP
- AWS : Scheduled stopping and starting an instance - python & cron
- AWS : Detecting stopped instance and sending an alert email using Mandrill smtp
- AWS : Elastic Beanstalk with NodeJS
- AWS : Elastic Beanstalk Inplace/Rolling Blue/Green Deploy
- AWS : Identity and Access Management (IAM) Roles for Amazon EC2
- AWS : Identity and Access Management (IAM) Policies, sts AssumeRole, and delegate access across AWS accounts
- AWS : Identity and Access Management (IAM) sts assume role via aws cli2
- AWS : Creating IAM Roles and associating them with EC2 Instances in CloudFormation
- AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) Roles, SSO(Single Sign On), SAML(Security Assertion Markup Language), IdP(identity provider), STS(Security Token Service), and ADFS(Active Directory Federation Services)
- AWS : Amazon Route 53
- AWS : Amazon Route 53 - DNS (Domain Name Server) setup
- AWS : Amazon Route 53 - subdomain setup and virtual host on Nginx
- AWS Amazon Route 53 : Private Hosted Zone
- AWS : SNS (Simple Notification Service) example with ELB and CloudWatch
- AWS : Lambda with AWS CloudTrail
- AWS : SQS (Simple Queue Service) with NodeJS and AWS SDK
- AWS : Redshift data warehouse
- AWS : CloudFormation
- AWS : CloudFormation Bootstrap UserData/Metadata
- AWS : CloudFormation - Creating an ASG with rolling update
- AWS : Cloudformation Cross-stack reference
- AWS : OpsWorks
- AWS : Network Load Balancer (NLB) with Autoscaling group (ASG)
- AWS CodeDeploy : Deploy an Application from GitHub
- AWS EC2 Container Service (ECS)
- AWS EC2 Container Service (ECS) II
- AWS Hello World Lambda Function
- AWS Lambda Function Q & A
- AWS Node.js Lambda Function & API Gateway
- AWS API Gateway endpoint invoking Lambda function
- AWS API Gateway invoking Lambda function with Terraform
- AWS API Gateway invoking Lambda function with Terraform - Lambda Container
- Amazon Kinesis Streams
- AWS: Kinesis Data Firehose with Lambda and ElasticSearch
- Amazon DynamoDB
- Amazon DynamoDB with Lambda and CloudWatch
- Loading DynamoDB stream to AWS Elasticsearch service with Lambda
- Amazon ML (Machine Learning)
- Simple Systems Manager (SSM)
- AWS : RDS Connecting to a DB Instance Running the SQL Server Database Engine
- AWS : RDS Importing and Exporting SQL Server Data
- AWS : RDS PostgreSQL & pgAdmin III
- AWS : RDS PostgreSQL 2 - Creating/Deleting a Table
- AWS : MySQL Replication : Master-slave
- AWS : MySQL backup & restore
- AWS RDS : Cross-Region Read Replicas for MySQL and Snapshots for PostgreSQL
- AWS : Restoring Postgres on EC2 instance from S3 backup
- AWS : Q & A
- AWS : Security
- AWS : Security groups vs. network ACLs
- AWS : Scaling-Up
- AWS : Networking
- AWS : Single Sign-on (SSO) with Okta
- AWS : JIT (Just-in-Time) with Okta
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization