DevOps / Sys Admin Q & A #13 : Is the Website down?
One of the first questions we want to answer when we can't reach a web server is whether the problem is on our end or on the remote end.
In this article, we assume that our problem is not on the network.
We can route to the machine, but we can't access the web server on port 80.
The next test is to see whether the port is even open. There are number of different ways to do this.
For one, we could try telnet:
$ telnet 54.153.94.154 80 Trying 54.153.94.154... telnet: Unable to connect to remote host: Connection timed out
If we see "Connection refused", then either the port is down (most likely Apache/Nginx isn't running on the remote host or isn't listening on that port) or the firewall is blocking our access.
If telnet can connect, then, well, we don't have a networking problem at all.
If the web service is up but just isn't working the way we expect it to, we need to investigate our Apache configuration on the web server.
We may want to use nmap (Network Mapper) to test ports because it can often detect firewalls.
The output from nmap is a list of scanned targets, with supplemental information on each depending on the options used.
Key among that information is the "interesting ports table". That table lists the port number and protocol, service name, and state. The state is either open, filtered, closed, or unfiltered:
- Open means that an application on the target machine is listening for connections/packets on that port.
- Filtered means that a firewall, filter, or other network obstacle is blocking the port so that Nmap cannot tell whether it is open or closed. In other words, a filtered Nmap cannot determine whether the port is open because packet filtering prevents its probes from reaching the port. The filtering could be from a dedicated firewall device, router rules, or host-based firewall software...
- Closed ports have no application listening on them, though they could open up at any time.
- Ports are classified as unfiltered when they are responsive to Nmap's probes, but Nmap cannot determine whether they are open or closed.
- The nmap reports the state combinations open|filtered and closed|filtered when it cannot determine which of the two states describe a port.
To test our server, we would type the following:
$ nmap -p 80 54.153.94.154 Starting Nmap 6.40 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2015-11-30 16:03 PST Note: Host seems down. If it is really up, but blocking our ping probes, try -Pn Nmap done: 1 IP address (0 hosts up) scanned in 3.27 seconds
If we open the port 80 on our Security group, we get the following output from nmap:
$ nmap -p 80 54.153.94.154 Starting Nmap 6.40 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2015-11-30 16:09 PST Nmap scan report for ec2-54-153-94-154.us-west-1.compute.amazonaws.com (54.153.94.154) Host is up (0.032s latency). PORT STATE SERVICE 80/tcp open http Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 1.52 seconds
If our web server is not running, we get:
$ nmap -p 80 54.153.94.154 Starting Nmap 6.40 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2015-11-30 16:12 PST Nmap scan report for ec2-54-153-94-154.us-west-1.compute.amazonaws.com (54.153.94.154) Host is up (0.033s latency). PORT STATE SERVICE 80/tcp closed http Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 1.51 seconds
nmap is smart enough that it can often tell the difference between a closed port that is truly closed and a closed port behind a firewall. Now normally when a port is actually down, nmap will report it as closed.
filtered: nmap cannot determine whether the port is open because packet filtering prevents its probes from reaching the port. The filtering could be from a dedicated firewall device, router rules, or host-based firewall software.
The 2nd case of following two examples shows the "filtered" situation, and nmap cannot determine whether the port is open.
k@laptop:~$ nmap -p 80 45.79.90.218 Starting Nmap 6.40 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2015-12-17 09:21 PST Nmap scan report for li1189-218.members.linode.com (45.79.90.218) Host is up (0.030s latency). PORT STATE SERVICE 80/tcp open http Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.21 seconds
This 2nd case is the case when we run the server for Django using:
(sfprojectenv)[sfvue@sf sfproject]$ ./manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8080
On local machine, we issue the nmap command, and get the following:
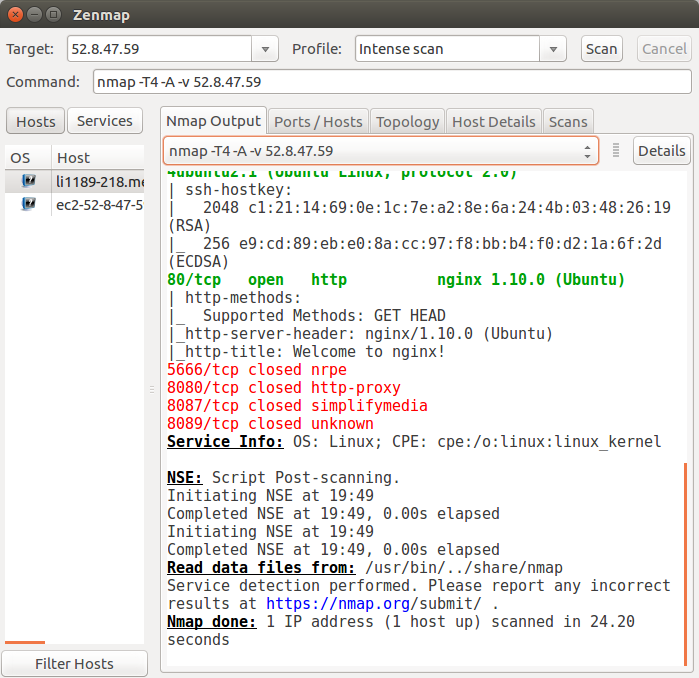
k@laptop:~$ nmap -p 8080 45.79.90.218 Starting Nmap 6.40 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2015-12-17 09:21 PST Nmap scan report for li1189-218.members.linode.com (45.79.90.218) Host is up (0.031s latency). PORT STATE SERVICE 8080/tcp filtered http-proxy Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.42 seconds
On the browser, we get "This webpage is not available"
Even when we do not run the server, we get the same output from the nmap.
So, it looks like firewall problem
Once I open the port with this command:
[sfvue@sf sfproject]$ sudo iptables -I INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 8080 -j ACCEPT [sfvue@sf sfproject]$ sudo service iptables save
we can see the port 8080 has been opened:
k@laptop:~$ nmap -p 8080 45.79.90.218 Starting Nmap 6.40 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2015-12-17 10:13 PST Nmap scan report for li1189-218.members.linode.com (45.79.90.218) Host is up (0.031s latency). PORT STATE SERVICE 8080/tcp open http-proxy Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.24 seconds
If we open up /etc/sysconfig/iptables, we can see the status of firewall settings. Actually, we could have edited the file directly to open up our port 8080:
... :INPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0] -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 8080 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -d 127.0.0.0/8 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable -A INPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 443 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -p tcp -m state --state NEW -m tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -p icmp -m icmp --icmp-type 8 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -m limit --limit 5/min -j LOG --log-prefix "iptables denied: " --log-level 7 ...
Regarding iptables setup, please consult: Securing Your Server.
We may want to install zenmap to use GUI feature of nmap:
$ sudp apt-get install zenmap
zenmap lets us create an interactive network map based on information gathered by nmap:
Let's log in to our web server and test whether port 80 is listening:
$ netstat -lnp | grep 80 tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
The first column tells us what protocol the port is using. The second and third columns are the receive and send queues (both set to 0 here).
The column we want to pay attention to is the fourth column, as it lists the local address on which the host is listening. Here the 0.0.0.0:80 tells us that the host is listening on all of its IPs for port 80 traffic.
Among command-line tools used to interface with web APIs curl has an advantage over raw telnet for web server troubleshooting in that it takes care of the HTTP protocol for us and makes things like testing authentication, posting data, using SSL, and other functions we take for granted in a GUI web browser much easier.
$ curl http://www.example.net <!doctype html> <html> <head> ...
When we're troubleshooting web server issues, the HTTP status code the web server returns for a request is invaluable source of information.
1xx: Informational Codes
| Message: | Description: |
|---|---|
| 100 Continue | The server has received the request headers, and the client should proceed to send the request body |
| 101 Switching Protocols | The requester has asked the server to switch protocols |
| 103 Checkpoint | Used in the resumable requests proposal to resume aborted PUT or POST requests |
2xx: Successful Codes
| Message: | Description: |
|---|---|
| 200 OK | The request is OK (this is the standard response for successful HTTP requests) |
| 201 Created | The request has been fulfilled, and a new resource is created |
| 202 Accepted | The request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been completed |
| 203 Non-Authoritative Information | The request has been successfully processed, but is returning information that may be from another source |
| 204 No Content | The request has been successfully processed, but is not returning any content |
| 205 Reset Content | The request has been successfully processed, but is not returning any content, and requires that the requester reset the document view |
| 206 Partial Content | The server is delivering only part of the resource due to a range header sent by the client |
3xx: Redirection Codes
| Message: | Description: |
|---|---|
| 300 Multiple Choices | A link list. The user can select a link and go to that location. Maximum five addresses |
| 301 Moved Permanently | The requested page has moved to a new URL |
| 302 Found | The requested page has moved temporarily to a new URL |
| 303 See Other | The requested page can be found under a different URL |
| 304 Not Modified | Indicates the requested page has not been modified since last requested |
| 306 Switch Proxy | No longer used |
| 307 Temporary Redirect | The requested page has moved temporarily to a new URL |
| 308 Resume Incomplete | Used in the resumable requests proposal to resume aborted PUT or POST requests |
4xx: Client Error Codes
| Message: | Description: |
|---|---|
| 400 Bad Request | The request cannot be fulfilled due to bad syntax |
| 401 Unauthorized | The request was a legal request, but the server is refusing to respond to it. For use when authentication is possible but has failed or not yet been provided |
| 402 Payment Required | Reserved for future use |
| 403 Forbidden | The request was a legal request, but the server is refusing to respond to it |
| 404 Not Found | The requested page could not be found but may be available again in the future |
| 405 Method Not Allowed | A request was made of a page using a request method not supported by that page |
| 406 Not Acceptable | The server can only generate a response that is not accepted by the client |
| 407 Proxy Authentication Required | The client must first authenticate itself with the proxy |
| 408 Request Timeout | The server timed out waiting for the request |
| 409 Conflict | The request could not be completed because of a conflict in the request |
| 410 Gone | The requested page is no longer available |
| 411 Length Required | The "Content-Length" is not defined. The server will not accept the request without it |
| 412 Precondition Failed | The precondition given in the request evaluated to false by the server |
| 413 Request Entity Too Large | The server will not accept the request, because the request entity is too large |
| 414 Request-URI Too Long | The server will not accept the request, because the URL is too long. Occurs when you convert a POST request to a GET request with a long query information |
| 415 Unsupported Media Type | The server will not accept the request, because the media type is not supported |
| 416 Requested Range Not Satisfiable | The client has asked for a portion of the file, but the server cannot supply that portion |
| 417 Expectation Failed | The server cannot meet the requirements of the Expect request-header field |
5xx: Server Error Codes
| Message: | Description: |
|---|---|
| 500 Internal Server Error | A generic error message, given when no more specific message is suitable |
| 501 Not Implemented | The server either does not recognize the request method, or it lacks the ability to fulfill the request |
| 502 Bad Gateway | The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and received an invalid response from the upstream server |
| 503 Service Unavailable | The server is currently unavailable (overloaded or down) |
| 504 Gateway Timeout | The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and did not receive a timely response from the upstream server |
| 505 HTTP Version Not Supported | The server does not support the HTTP protocol version used in the request |
| 511 Network Authentication Required | The client needs to authenticate to gain network access |
DevOps
DevOps / Sys Admin Q & A
Linux - system, cmds & shell
- Linux Tips - links, vmstats, rsync
- Linux Tips 2 - ctrl a, curl r, tail -f, umask
- Linux - bash I
- Linux - bash II
- Linux - Uncompressing 7z file
- Linux - sed I (substitution: sed 's///', sed -i)
- Linux - sed II (file spacing, numbering, text conversion and substitution)
- Linux - sed III (selective printing of certain lines, selective definition of certain lines)
- Linux - 7 File types : Regular, Directory, Block file, Character device file, Pipe file, Symbolic link file, and Socket file
- Linux shell programming - introduction
- Linux shell programming - variables and functions (readonly, unset, and functions)
- Linux shell programming - special shell variables
- Linux shell programming : arrays - three different ways of declaring arrays & looping with $*/$@
- Linux shell programming : operations on array
- Linux shell programming : variables & commands substitution
- Linux shell programming : metacharacters & quotes
- Linux shell programming : input/output redirection & here document
- Linux shell programming : loop control - for, while, break, and break n
- Linux shell programming : string
- Linux shell programming : for-loop
- Linux shell programming : if/elif/else/fi
- Linux shell programming : Test
- Managing User Account - useradd, usermod, and userdel
- Linux Secure Shell (SSH) I : key generation, private key and public key
- Linux Secure Shell (SSH) II : ssh-agent & scp
- Linux Secure Shell (SSH) III : SSH Tunnel as Proxy - Dynamic Port Forwarding (SOCKS Proxy)
- Linux Secure Shell (SSH) IV : Local port forwarding (outgoing ssh tunnel)
- Linux Secure Shell (SSH) V : Reverse SSH Tunnel (remote port forwarding / incoming ssh tunnel) /)
- Linux Processes and Signals
- Linux Drivers 1
- tcpdump
- Linux Debugging using gdb
- Embedded Systems Programming I - Introduction
- Embedded Systems Programming II - gcc ARM Toolchain and Simple Code on Ubuntu/Fedora
- LXC (Linux Container) Install and Run
- Linux IPTables
- Hadoop - 1. Setting up on Ubuntu for Single-Node Cluster
- Hadoop - 2. Runing on Ubuntu for Single-Node Cluster
- ownCloud 7 install
- Ubuntu 14.04 guest on Mac OSX host using VirtualBox I
- Ubuntu 14.04 guest on Mac OSX host using VirtualBox II
- Windows 8 guest on Mac OSX host using VirtualBox I
- Ubuntu Package Management System (apt-get vs dpkg)
- RPM Packaging
- How to Make a Self-Signed SSL Certificate
- Linux Q & A
- DevOps / Sys Admin questions
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization