Docker & Kubernetes - Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 3 Chart
Continued from Docker & Kubernetes - Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 2 Chart, in this post, we'll use Helm 3 instead of Helm 2.
Tiller is the server-side component of the Helm 2 architecture and is responsible to get all the information from Kube API-Server.
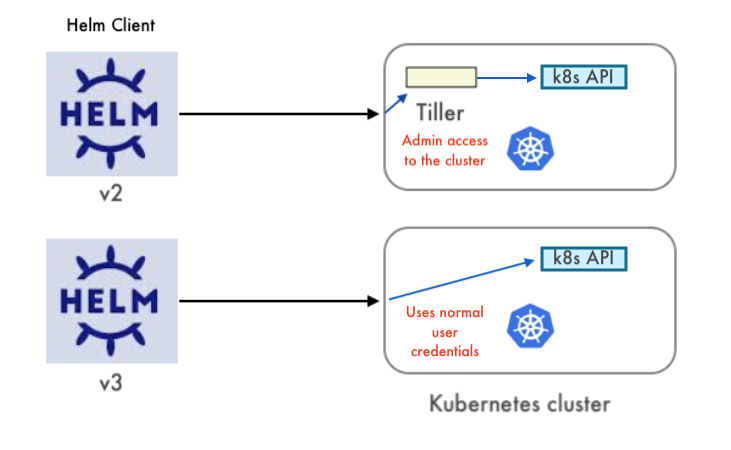
One of the biggest differences between Helm 2 and Helm 3 is its architecture - there is no more Tiller (the server-side component of Helm 2). Tiller was configured to have full access on all Kubernetes cluster. With this new architecture Helm 3 is more secure. Helm interacts directly with Kubernetes API server. The permissions are based on the Kubernetes config file.
In Helm3, its release information is stored into config maps by default and whenever we fire any command such helm ls,
tiller gets the config maps from api-server it returns the list of release and their metadata.
However, sometimes fails to respond to the API request. So, in this post, we'll do the same deploy as in the previous post except using Helm 3.
Before we proceed, let's check how the the two Helms are setup on my local laptop.
$ ls -la $(which helm) lrwxr-xr-x 1 kihyuckhong admin 30 Sep 7 19:59 /usr/local/bin/helm -> /usr/local/opt/helm@2/bin/helm $ ls -la $(which helm3) lrwxr-xr-x 1 kihyuckhong admin 28 Sep 7 19:59 /usr/local/bin/helm3 -> /usr/local/opt/helm/ bin/helm
As we can see, the default Helm is set to version 2, and on minikube, the helm3 does not have tiller!
$ helm init
$HELM_HOME has been configured at /Users/kihyuckhong/.helm.
Warning: Tiller is already installed in the cluster.
(Use --client-only to suppress this message, or --upgrade to upgrade Tiller to the current version.)
$ helm version
Client: &version.Version{SemVer:"v2.16.10", GitCommit:"bceca24a91639f045f22ab0f41e47589a932cf5e", GitTreeState:"clean"}
Server: &version.Version{SemVer:"v2.16.10", GitCommit:"bceca24a91639f045f22ab0f41e47589a932cf5e", GitTreeState:"clean"}
$ helm3 version
version.BuildInfo{Version:"v3.3.1", GitCommit:"249e5215cde0c3fa72e27eb7a30e8d55c9696144", GitTreeState:"dirty", GoVersion:"go1.15"}
Note that the helm3 has no init because it does not have tiller component in the cluster side.
In this post, we'll deploy the wordpress to Kubernetes cluster in AWS created using KOPS.
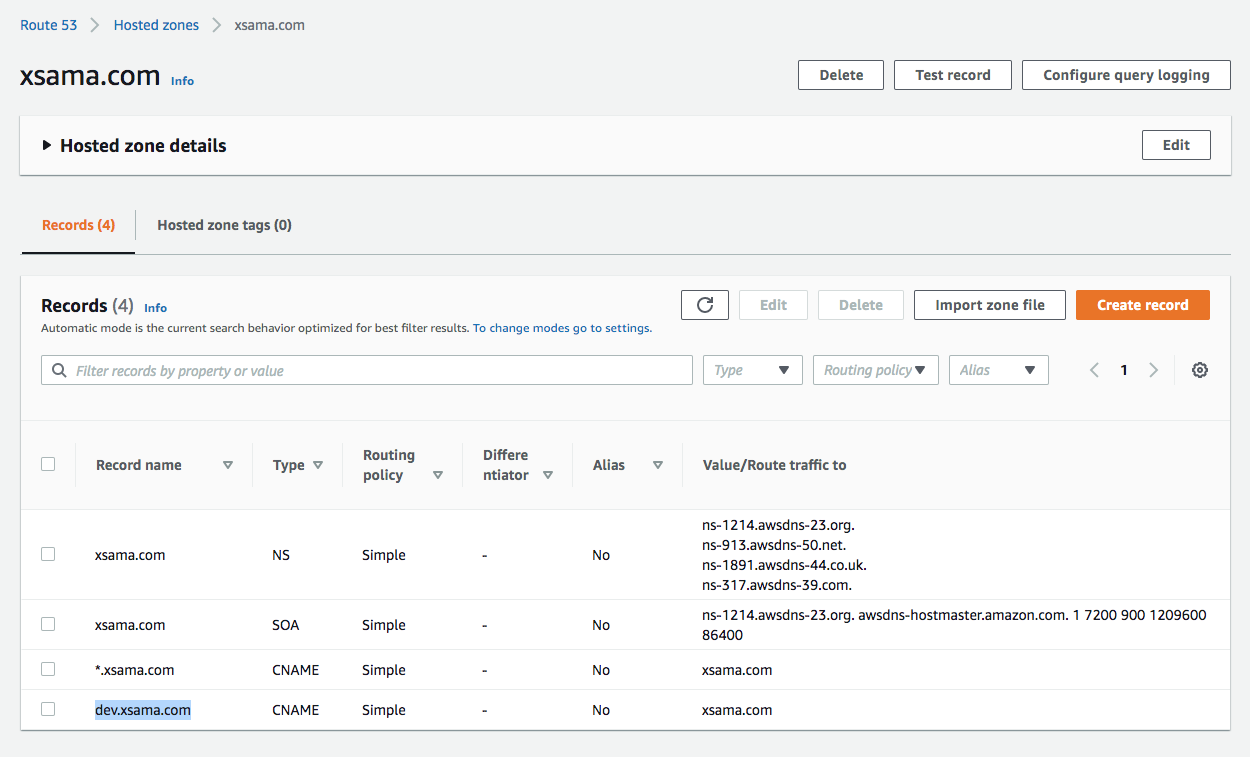
For the service discovery, we're going to use DNS, the subdomain of xsama.com:
- Create a S3 bucket to store our clusters state:
$ aws s3 mb s3://clusters.dev.xsama.com
- Export KOPS_STATE_STORE=s3://clusters.dev.xsama.com and then kops will use this location by default:
$ export KOPS_STATE_STORE=s3://clusters.dev.xsama.com
- Create a cluster configuration. While the following command does NOT actually create the cloud resources it gives us an opportunity to review the configuration or change it:
$ kops create cluster --zones=us-east-1a,us-east-1b,us-east-1c useast1.dev.xsama.com
The
kops create clustercommand creates the configuration for our cluster (default conf creates 1 master and 2 worker nodes). Note that it only creates the configuration, it does not actually create the cloud resources - we'll do that in the next step with akops update cluster.It prints commands we can use to explore further:
- List clusters with:
kops get cluster:
$ kops get cluster --state s3://clusters.dev.xsama.com NAME CLOUD ZONES useast1.dev.xsama.com aws us-east-1a,us-east-1b,us-east-1c
Or after setting export KOPS_STATE_STOR=s3://clusters.dev.xsama.com:
$ kops get cluster NAME CLOUD ZONES useast1.dev.xsama.com aws us-east-1a,us-east-1b,us-east-1c
- Edit the cluster with:
kops edit cluster useast1.dev.xsama.com:
# Please edit the object below. Lines beginning with a '#' will be ignored, # and an empty file will abort the edit. If an error occurs while saving this file will be # reopened with the relevant failures. # apiVersion: kops.k8s.io/v1alpha2 kind: Cluster metadata: creationTimestamp: "2020-10-20T17:55:08Z" name: useast1.dev.xsama.com spec: api: dns: {} authorization: rbac: {} channel: stable cloudProvider: aws configBase: s3://clusters.dev.xsama.com/useast1.dev.xsama.com containerRuntime: docker etcdClusters: - cpuRequest: 200m etcdMembers: - instanceGroup: master-us-east-1a name: a memoryRequest: 100Mi name: main - cpuRequest: 100m etcdMembers: - instanceGroup: master-us-east-1a name: a memoryRequest: 100Mi name: events iam: allowContainerRegistry: true legacy: false kubelet: anonymousAuth: false kubernetesApiAccess: - 0.0.0.0/0 kubernetesVersion: 1.18.8 masterInternalName: api.internal.useast1.dev.xsama.com masterPublicName: api.useast1.dev.xsama.com networkCIDR: 172.20.0.0/16 networking: kubenet: {} nonMasqueradeCIDR: 100.64.0.0/10 sshAccess: - 0.0.0.0/0 subnets: - cidr: 172.20.32.0/19 name: us-east-1a type: Public zone: us-east-1a - cidr: 172.20.64.0/19 name: us-east-1b type: Public zone: us-east-1b - cidr: 172.20.96.0/19 name: us-east-1c type: Public zone: us-east-1c topology: dns: type: Public masters: public nodes: public - Edit node instance group:
kops edit ig --name=useast1.dev.xsama.com nodes:
apiVersion: kops.k8s.io/v1alpha2 kind: InstanceGroup metadata: creationTimestamp: "2020-10-20T02:12:34Z" generation: 1 labels: kops.k8s.io/cluster: useast1.dev.xsama.com name: nodes spec: image: 099720109477/ubuntu/images/hvm-ssd/ubuntu-focal-20.04-amd64-server-20200907 machineType: t2.small maxSize: 1 minSize: 1 nodeLabels: kops.k8s.io/instancegroup: nodes role: Node subnets: - us-east-1a - us-east-1b - us-east-1c
- Edit master instance group:
kops edit ig --name=useast1.dev.xsama.com master-us-east-1a:
apiVersion: kops.k8s.io/v1alpha2 kind: InstanceGroup metadata: creationTimestamp: "2020-10-20T02:12:34Z" generation: 1 labels: kops.k8s.io/cluster: useast1.dev.xsama.com name: master-us-east-1a spec: image: 099720109477/ubuntu/images/hvm-ssd/ubuntu-focal-20.04-amd64-server-20200907 machineType: t3.micro maxSize: 1 minSize: 1 nodeLabels: kops.k8s.io/instancegroup: master-us-east-1a role: Master subnets: - us-east-1a
- Finally configure cluster with:
kops update cluster --name useast1.dev.xsama.com --yesSee next item. - Run
kops update clusterto preview what it is going to do our cluster in AWS:$ kops update cluster useast1.dev.xsama.com ...
Now we'll use the same command,
kops update clusterbut with --yes to actually create the cluster:$ kops update cluster useast1.dev.xsama.com --yes
- Optional:
In case when an instance type is not suitable for an app, we need to update the node instance type. Cluster changes such as instance types (t2.small => t2.medium for nodes) can be applied to the cloud with
kops update cluster useast1.dev.xsama.com --yesbut the changes may require instances to restart,kops rolling-update cluster:$ kubectl describe pod wordpress-mariadb-0 Name: wordpress-mariadb-0 Namespace: default Priority: 0 Node: <none> Labels: app=mariadb chart=mariadb-7.10.4 component=master controller-revision-hash=wordpress-mariadb-64ffbc9d4c heritage=Tiller release=wordpress statefulset.kubernetes.io/pod-name=wordpress-mariadb-0 Annotations: kubernetes.io/limit-ranger: LimitRanger plugin set: cpu request for container mariadb Status: Pending IP: IPs: <none> Controlled By: StatefulSet/wordpress-mariadb ... Events: Type Reason Age From Message ---- ------ ---- ---- ------- Warning FailedScheduling 16s (x11 over 9m12s) default-scheduler 0/2 nodes are available: 1 Insufficient cpu, 1 node(s) had taint {node-role.kubernetes.io/master: }, that the pod didn't tolerate. $ kops rolling-update cluster Using cluster from kubectl context: useast1.dev.xsama.com NAME STATUS NEEDUPDATE READY MIN TARGET MAX NODES master-us-east-1a Ready 0 1 1 1 1 1 nodes NeedsUpdate 1 0 1 1 1 1 Must specify --yes to rolling-update. $ kops rolling-update cluster --yes Using cluster from kubectl context: useast1.dev.xsama.com NAME STATUS NEEDUPDATE READY MIN TARGET MAX NODES master-us-east-1a Ready 0 1 1 1 1 1 nodes NeedsUpdate 1 0 1 1 1 1 I1020 16:52:23.806751 31047 instancegroups.go:383] Validating the cluster. I1020 16:52:25.084961 31047 instancegroups.go:416] Cluster validated. I1020 16:52:25.085015 31047 instancegroups.go:282] Tainting 1 node in "nodes" instancegroup. I1020 16:52:25.203052 31047 instancegroups.go:462] Detaching instance "i-01be4422d0ee4a0db", node "ip-172-20-93-80.ec2.internal", in group "nodes.useast1.dev.xsama.com". I1020 16:52:25.651067 31047 instancegroups.go:143] waiting for 15s after detaching instance I1020 16:52:40.655944 31047 instancegroups.go:383] Validating the cluster. I1020 16:52:41.970781 31047 instancegroups.go:440] Cluster did not pass validation, will retry in "30s": InstanceGroup "nodes" did not have enough nodes 0 vs 1. I1020 16:53:13.385367 31047 instancegroups.go:440] Cluster did not pass validation, will retry in "30s": machine "i-0630f195d1099285f" has not yet joined cluster. I1020 16:53:44.709361 31047 instancegroups.go:440] Cluster did not pass validation, will retry in "30s": machine "i-0630f195d1099285f" has not yet joined cluster. I1020 16:54:16.142520 31047 instancegroups.go:440] Cluster did not pass validation, will retry in "30s": machine "i-0630f195d1099285f" has not yet joined cluster. I1020 16:54:47.540192 31047 instancegroups.go:440] Cluster did not pass validation, will retry in "30s": machine "i-0630f195d1099285f" has not yet joined cluster. I1020 16:55:18.901202 31047 instancegroups.go:440] Cluster did not pass validation, will retry in "30s": machine "i-0630f195d1099285f" has not yet joined cluster. I1020 16:55:50.269109 31047 instancegroups.go:440] Cluster did not pass validation, will retry in "30s": machine "i-0630f195d1099285f" has not yet joined cluster. I1020 16:56:21.977314 31047 instancegroups.go:419] Cluster validated; revalidating in 10s to make sure it does not flap. I1020 16:56:33.350631 31047 instancegroups.go:416] Cluster validated. I1020 16:56:33.351908 31047 instancegroups.go:340] Draining the node: "ip-172-20-93-80.ec2.internal". evicting pod kube-system/kube-dns-64f86fb8dd-xncwl evicting pod default/wordpress-74cf55bf59-v22bd evicting pod kube-system/kube-dns-autoscaler-cd7778b7b-gbm9x evicting pod kube-system/tiller-deploy-6845b7d56c-rglwl evicting pod kube-system/kube-dns-64f86fb8dd-bmnp5 error when evicting pod "kube-dns-64f86fb8dd-bmnp5" (will retry after 5s): Cannot evict pod as it would violate the pod's disruption budget. evicting pod kube-system/kube-dns-64f86fb8dd-bmnp5 error when evicting pod "kube-dns-64f86fb8dd-bmnp5" (will retry after 5s): Cannot evict pod as it would violate the pod's disruption budget. evicting pod kube-system/kube-dns-64f86fb8dd-bmnp5 error when evicting pod "kube-dns-64f86fb8dd-bmnp5" (will retry after 5s): Cannot evict pod as it would violate the pod's disruption budget. evicting pod kube-system/kube-dns-64f86fb8dd-bmnp5 error when evicting pod "kube-dns-64f86fb8dd-bmnp5" (will retry after 5s): Cannot evict pod as it would violate the pod's disruption budget. evicting pod kube-system/kube-dns-64f86fb8dd-bmnp5 I1020 16:57:28.388767 31047 instancegroups.go:546] Waiting for 5s for pods to stabilize after draining. I1020 16:57:33.398918 31047 instancegroups.go:359] deleting node "ip-172-20-93-80.ec2.internal" from kubernetes I1020 16:57:43.226279 31047 instancegroups.go:486] Stopping instance "i-01be4422d0ee4a0db", node "ip-172-20-93-80.ec2.internal", in group "nodes.useast1.dev.xsama.com" (this may take a while). I1020 16:57:43.742995 31047 instancegroups.go:372] waiting for 15s after terminating instance I1020 16:57:58.751466 31047 instancegroups.go:383] Validating the cluster. I1020 16:58:00.124835 31047 instancegroups.go:419] Cluster validated; revalidating in 10s to make sure it does not flap. I1020 16:58:11.518297 31047 instancegroups.go:416] Cluster validated. I1020 16:58:11.518335 31047 rollingupdate.go:201] Rolling update completed for cluster "useast1.dev.xsama.com"!
-
Wait for about 10m, then the cluster will be ready. To check, we use
kops validate cluster:$ kops validate cluster Using cluster from kubectl context: useast1.dev.xsama.com Validating cluster useast1.dev.xsama.com INSTANCE GROUPS NAME ROLE MACHINETYPE MIN MAX SUBNETS master-us-east-1a Master t3.micro 1 1 us-east-1a nodes Node t2.medium 1 1 us-east-1a,us-east-1b,us-east-1c NODE STATUS NAME ROLE READY ip-172-20-40-142.ec2.internal master True ip-172-20-86-167.ec2.internal node True Your cluster useast1.dev.xsama.com is ready
- List nodes:
$ kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION ip-172-20-40-142.ec2.internal Ready master 58m v1.18.9 ip-172-20-86-167.ec2.internal Ready node 30m v1.18.9
Now, we want to deploy wordpress using helm3:
$ helm3 version
version.BuildInfo{Version:"v3.3.1", GitCommit:"249e5215cde0c3fa72e27eb7a30e8d55c9696144", GitTreeState:"dirty", GoVersion:"go1.15"}
The Bitnami repository can be added using helm repo add:
$ helm3 repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami $ helm3 repo list NAME URL bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
To deploy the WordPress chart, we can use either one of the following depending on the Helm version:
$ helm3 install my-release bitnami/<chart> # Helm 3 $ helm install --name my-release bitnami/<chart> # Helm 2
In this post, we'll use Helm 3.
If we want to use the parameters defined in ./values.yaml, the command should look like this:
$ helm3 install wordpress bitnami/wordpress -f ./values.yaml
NAME: wordpress
LAST DEPLOYED: Wed Oct 21 16:44:52 2020
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
NOTES:
** Please be patient while the chart is being deployed **
Your WordPress site can be accessed through the following DNS name from within your cluster:
wordpress.default.svc.cluster.local (port 80)
To access your WordPress site from outside the cluster follow the steps below:
1. Get the WordPress URL by running these commands:
NOTE: It may take a few minutes for the LoadBalancer IP to be available.
Watch the status with: 'kubectl get svc --namespace default -w wordpress'
export SERVICE_IP=$(kubectl get svc --namespace default wordpress --template "{{ range (index .status.loadBalancer.ingress 0) }}{{.}}{{ end }}")
echo "WordPress URL: http://$SERVICE_IP/"
echo "WordPress Admin URL: http://$SERVICE_IP/admin"
2. Open a browser and access WordPress using the obtained URL.
3. Login with the following credentials below to see your blog:
echo Username: wordpress
echo Password: $(kubectl get secret --namespace default wordpress -o jsonpath="{.data.wordpress-password}" | base64 --decode)
As we can see from the output, it appears that our chart has been deployed successfully.
$ kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE wordpress-84d7f785b-lwm9m 1/1 Running 0 12m wordpress-mariadb-0 1/1 Running 0 12m $ kubectl get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kubernetes ClusterIP 100.64.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 40m wordpress LoadBalancer 100.66.226.169 a9c6fdb474a25444aaec47e994c7d359-2116205925.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80:31338/TCP,443:30836/TCP 13m wordpress-mariadb ClusterIP 100.70.135.118 <none> 3306/TCP 51m $ kubectl get deployment NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE wordpress 1/1 1 1 14m $ kubectl get pv NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE pvc-5263ecbf-7802-4d25-8b79-238e802e4c0e 10Gi RWO Delete Bound default/wordpress kops-ssd-1-17 14m pvc-6ef94664-19af-4e7b-9669-83fafb7660a8 8Gi RWO Delete Bound default/data-wordpress-mariadb-0 kops-ssd-1-17 14m $ kubectl get pvc NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE data-wordpress-mariadb-0 Bound pvc-6ef94664-19af-4e7b-9669-83fafb7660a8 8Gi RWO kops-ssd-1-17 15m wordpress Bound pvc-5263ecbf-7802-4d25-8b79-238e802e4c0e 10Gi RWO kops-ssd-1-17 15m $ kubectl get configmap NAME DATA AGE wordpress-mariadb 1 15m $ kubectl get secrets NAME TYPE DATA AGE default-token-n4k92 kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 42m sh.helm.release.v1.wordpress.v1 helm.sh/release.v1 1 15m wordpress Opaque 1 15m wordpress-mariadb Opaque 2 15m $ kubectl get statefulsets NAME READY AGE wordpress-mariadb 1/1 16m $ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE default wordpress-84d7f785b-lwm9m 1/1 Running 0 16m default wordpress-mariadb-0 1/1 Running 0 16m kube-system dns-controller-f46fcf988-6pq9z 1/1 Running 0 43m kube-system etcd-manager-events-ip-172-20-61-195.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 0 42m kube-system etcd-manager-main-ip-172-20-61-195.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 0 42m kube-system kops-controller-fmfxj 1/1 Running 0 42m kube-system kube-apiserver-ip-172-20-61-195.ec2.internal 2/2 Running 2 42m kube-system kube-controller-manager-ip-172-20-61-195.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 0 42m kube-system kube-dns-64f86fb8dd-4f4s5 3/3 Running 0 43m kube-system kube-dns-64f86fb8dd-5qxkf 3/3 Running 0 41m kube-system kube-dns-autoscaler-cd7778b7b-f8tpm 1/1 Running 0 43m kube-system kube-proxy-ip-172-20-36-105.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 0 41m kube-system kube-proxy-ip-172-20-61-195.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 0 42m kube-system kube-scheduler-ip-172-20-61-195.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 0 42m $ kubectl exec -it wordpress-mariadb-0 -- dash $ ps aux USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND 1001 1 0.2 2.1 969780 86876 ? Ssl Oct21 0:02 /opt/bitnami/mariadb/sbin/mysqld --defaults-file=/opt/bitnami/mariadb/conf/my.cnf --basedir=/opt/bitnami/mariadb --datadir=/bitnami/mariadb 1001 1578 0.0 0.0 2384 764 pts/0 Ss 00:01 0:00 dash 1001 1665 0.0 0.0 7636 2596 pts/0 R+ 00:02 0:00 ps aux $ mysql -u wordpress -p Enter password: Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 3791 Server version: 10.3.24-MariaDB Source distribution Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [(none)]> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | test | | wordpress | +--------------------+ 3 rows in set (0.000 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> use wordpress; Reading table information for completion of table and column names You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A Database changed MariaDB [wordpress]> MariaDB [wordpress]> show tables; +-----------------------+ | Tables_in_wordpress | +-----------------------+ | wp_commentmeta | | wp_comments | | wp_links | | wp_options | | wp_postmeta | | wp_posts | | wp_term_relationships | | wp_term_taxonomy | | wp_termmeta | | wp_terms | | wp_usermeta | | wp_users | +-----------------------+ 12 rows in set (0.000 sec) MariaDB [wordpress]>
We deployed the wordpress with service type of LoadBalancer as we can see from the following output:
$ kubectl get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kubernetes ClusterIP 100.64.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 40m wordpress LoadBalancer 100.66.226.169 a9c6fdb474a25444aaec47e994c7d359-2116205925.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80:31338/TCP,443:30836/TCP 13m wordpress-mariadb ClusterIP 100.70.135.118 <none> 3306/TCP 51m
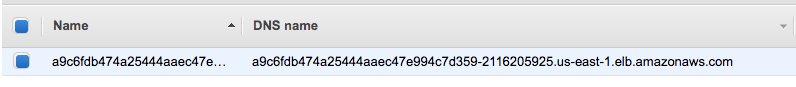
Put the LB DNS name into a browser:
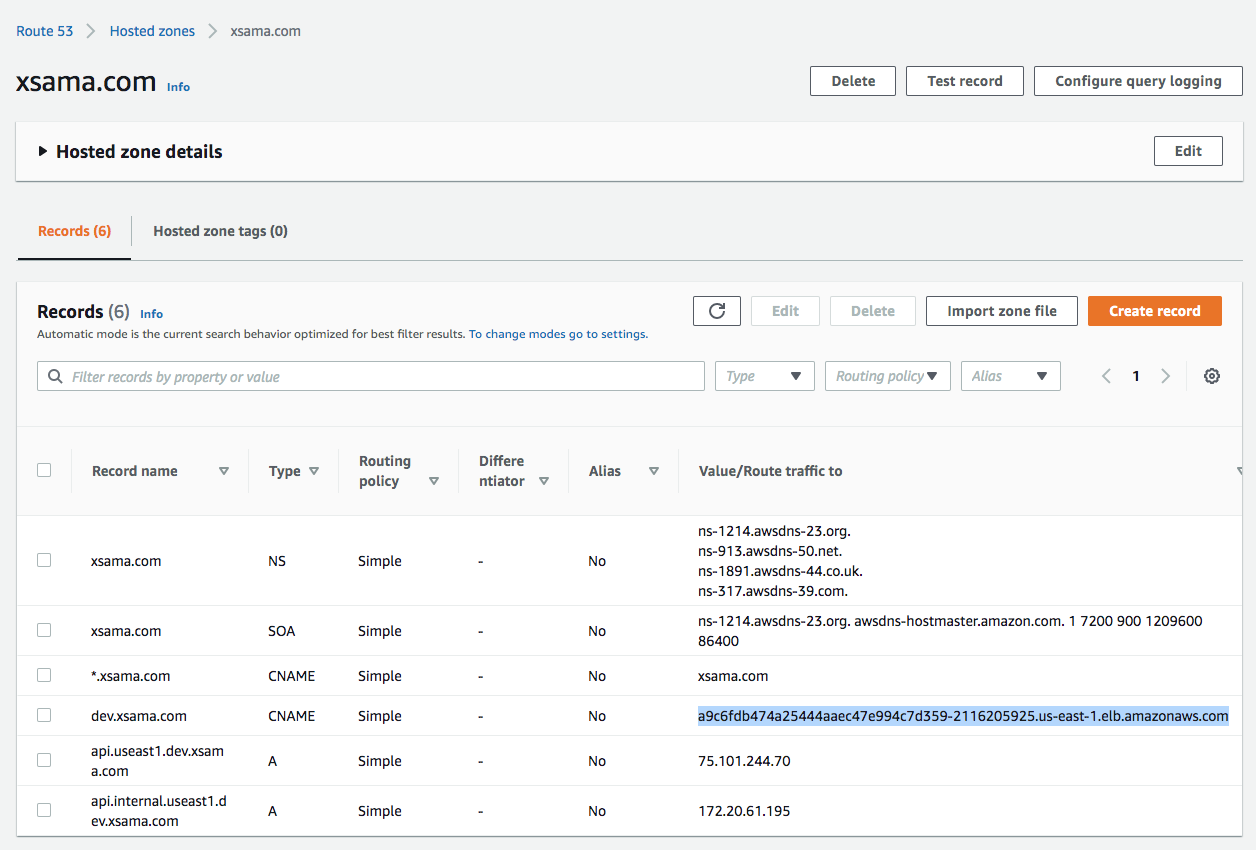
We can set the dev.xsama.com to point the LB:
Then, using the wordpress via the subdomain name (dev.xsama.com):
To uninstall/delete the my-release deployment, we can use helm3 uninstall my-release:
$ helm3 ls NAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION wordpress default 1 2020-10-21 16:44:52.224843 -0700 PDT deployed wordpress-9.8.0 5.5.1 $ helm3 uninstall wordpress release "wordpress" uninstalled $ helm3 ls NAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION
$ kops delete cluster useast1.dev.xsama.com --yes
Docker & K8s
- Docker install on Amazon Linux AMI
- Docker install on EC2 Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker container vs Virtual Machine
- Docker install on Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker Hello World Application
- Nginx image - share/copy files, Dockerfile
- Working with Docker images : brief introduction
- Docker image and container via docker commands (search, pull, run, ps, restart, attach, and rm)
- More on docker run command (docker run -it, docker run --rm, etc.)
- Docker Networks - Bridge Driver Network
- Docker Persistent Storage
- File sharing between host and container (docker run -d -p -v)
- Linking containers and volume for datastore
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically I - FROM, MAINTAINER, and build context
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically II - revisiting FROM, MAINTAINER, build context, and caching
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically III - RUN
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically IV - CMD
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically V - WORKDIR, ENV, ADD, and ENTRYPOINT
- Docker - Apache Tomcat
- Docker - NodeJS
- Docker - NodeJS with hostname
- Docker Compose - NodeJS with MongoDB
- Docker - Prometheus and Grafana with Docker-compose
- Docker - StatsD/Graphite/Grafana
- Docker - Deploying a Java EE JBoss/WildFly Application on AWS Elastic Beanstalk Using Docker Containers
- Docker : NodeJS with GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker : Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline with Jenkinsfile and Github
- Docker : Jenkins Master and Slave
- Docker - ELK : ElasticSearch, Logstash, and Kibana
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elasticsearch on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Filebeat on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Logstash on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Kibana on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elastic Stack with Docker Compose
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK) via Elasticsearch operator on minikube
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Stack via Helm on minikube
- Docker Compose - A gentle introduction with WordPress
- Docker Compose - MySQL
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services via docker-compose
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part A (install vault, unsealing, static secrets, and policies)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part B (EaaS, dynamic secrets, leases, and revocation)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part C (Consul)
- Docker Compose with two containers - Flask REST API service container and an Apache server container
- Docker compose : Nginx reverse proxy with multiple containers
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Getting started
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Front Proxy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ambassador - Envoy API Gateway on Kubernetes
- Docker Packer
- Docker Cheat Sheet
- Docker Q & A #1
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part I
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part II
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker II (snapshot app with nginx)
- Docker - NodeJS and MySQL app with React in a docker
- Docker - Step by Step NodeJS and MySQL app with React - I
- Installing LAMP via puppet on Docker
- Docker install via Puppet
- Nginx Docker install via Ansible
- Apache Hadoop CDH 5.8 Install with QuickStarts Docker
- Docker - Deploying Flask app to ECS
- Docker Compose - Deploying WordPress to AWS
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI EC2 type)
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI Fargate type)
- Docker - ECS Fargate
- Docker - AWS ECS service discovery with Flask and Redis
- Docker & Kubernetes : minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes 2 : minikube Django with Postgres - persistent volume
- Docker & Kubernetes 3 : minikube Django with Redis and Celery
- Docker & Kubernetes 4 : Django with RDS via AWS Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kops on AWS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ingress controller on AWS with Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul - Auto-unseal using Transit Secrets Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes & Persistent Volumes Claims - hostPath and annotations
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes - Dynamic volume provisioning
- Docker & Kubernetes : DaemonSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Secrets
- Docker & Kubernetes : kubectl command
- Docker & Kubernetes : Assign a Kubernetes Pod to a particular node in a Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : Configure a Pod to Use a ConfigMap
- AWS : EKS (Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Run a React app in a minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Minikube install on AWS EC2
- Docker & Kubernetes : Cassandra with a StatefulSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Terraform and AWS EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Pods and Service definitions
- Docker & Kubernetes : Service IP and the Service Type
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes DNS with Pods and Services
- Docker & Kubernetes : Headless service and discovering pods
- Docker & Kubernetes : Scaling and Updating application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Horizontal pod autoscaler on minikubes
- Docker & Kubernetes : From a monolithic app to micro services on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Rolling updates
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deployments to GKE (Rolling update, Canary and Blue-green deployments)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Slack Chat Bot with NodeJS on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery with Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline for Dev, Canary, and Production Environments on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : NodePort vs LoadBalancer vs Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB / MongoExpress on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Load Testing with Locust on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB with StatefulSets on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up Ingress with NGINX Controller on Minikube (Mac)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller for Dashboard service on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Ingress with AWS ALB Ingress Controller in EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up a private cluster on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Namespaces (default, kube-public, kube-system) and switching namespaces (kubens)
- Docker & Kubernetes : StatefulSets on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : RBAC
- Docker & Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, and IAM
- Docker & Kubernetes - Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, IAM with EKS ALB, Part 1
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : My first Helm deploy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Readiness and Liveness Probes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm chart repository with Github pages
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB with Ingress to Minikube using Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 2 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 3 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart for Node/Express and MySQL with Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using Helm and Prometheus Operator - Monitoring Kubernetes node resources out of the box
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using kube-prometheus-stack Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio (service mesh) sidecar proxy on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on Minikube with AWS EC2 for Bookinfo Application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part I)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part II - Prometheus, Grafana, pin a service, split traffic, and inject faults)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Package Manager with MySQL on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying Memcached on Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : EKS Control Plane (API server) Metrics with Prometheus
- Docker & Kubernetes : Spinnaker on EKS with Halyard
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery Pipelines with Spinnaker and Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-dind (docker-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-kind (k8s-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : nodeSelector, nodeAffinity, taints/tolerations, pod affinity and anti-affinity - Assigning Pods to Nodes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Jenkins-X on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD App of Apps with Heml on Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD on Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : GitOps with ArgoCD for Continuous Delivery to Kubernetes clusters (minikube) - guestbook
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization